Fluoroplastic-based micro-nano composite wave-absorbing material and preparation method thereof
A composite wave absorbing material and fluoroplastic technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, other chemical processes, etc., can solve the problems of lack of shielding frequency band and wave absorbing performance characterization, and achieve excellent chemical corrosion resistance, good weather resistance, and preparation. The effect of method science
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] The concrete steps of preparation are:
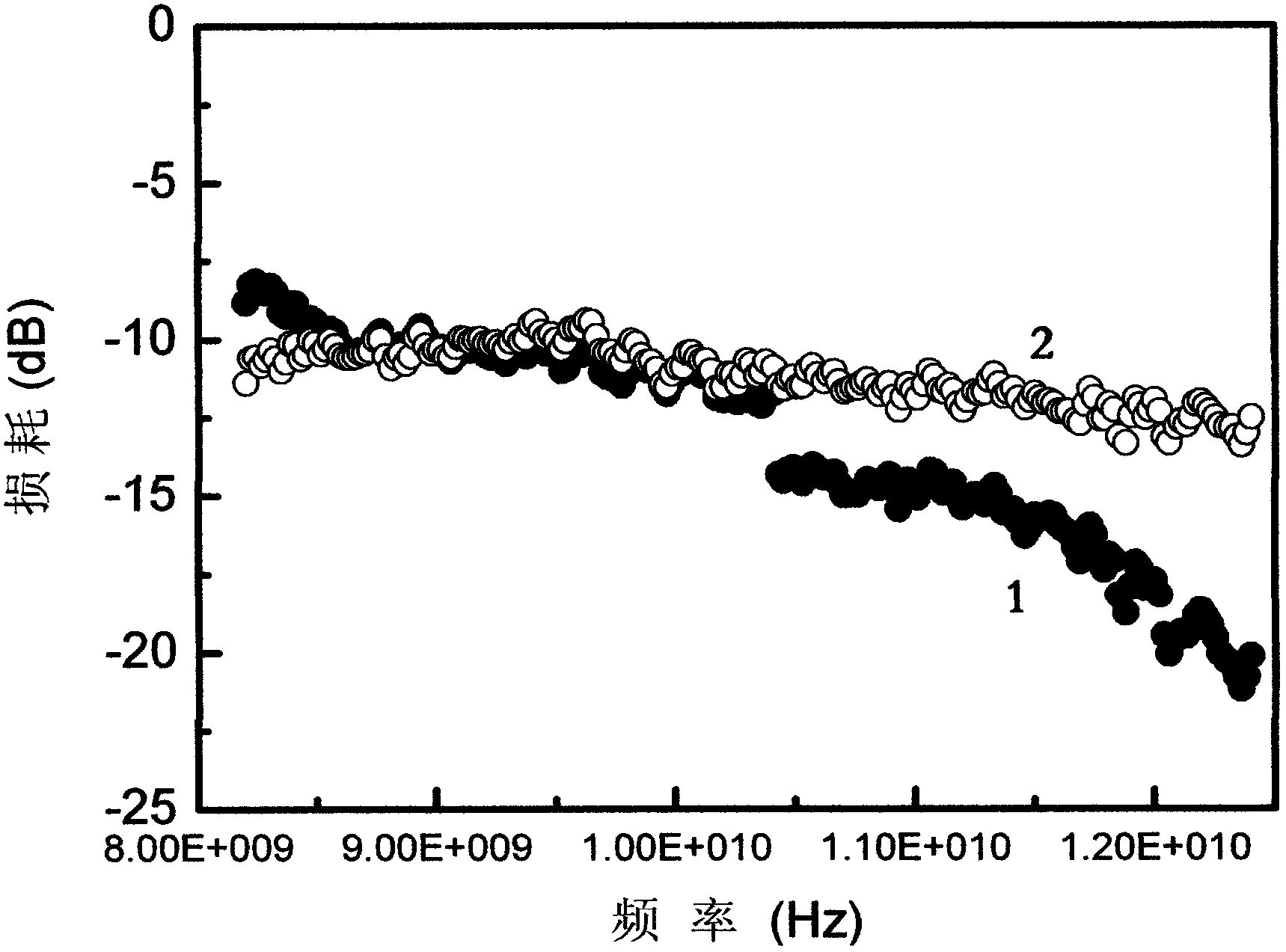
[0023] First, the fluoroplastic, carbon nanotube and basalt fiber are uniformly mixed according to the weight ratio of 100:0.5:20 to obtain a mixture; wherein, the fluoroplastic is polyvinylidene fluoride, and the carbon nanotube is single-wall carbon nanotube. The mixture was then placed in a torque rheometer and kneaded for 25 minutes at 200°C to obtain a mixture similar to figure 1 The fluoroplastic-based micro-nano composite absorbing material shown in curve 1.
Embodiment 2
[0025] The concrete steps of preparation are:
[0026] Firstly, the fluoroplastic, carbon nanotube and basalt fiber are uniformly mixed according to the weight ratio of 100:2:14 to obtain the mixture; wherein, the fluoroplastic is polyvinylidene fluoride, and the carbon nanotube is single-wall carbon nanotube. The mixture was then placed in a torque rheometer and kneaded at 240°C for 20 minutes to obtain figure 1 The fluoroplastic-based micro-nano composite absorbing material shown in curve 1.
Embodiment 3
[0028] The concrete steps of preparation are:
[0029] Firstly, the fluoroplastic, carbon nanotube and basalt fiber are uniformly mixed according to the weight ratio of 100:8:8 to obtain a mixture; wherein, the fluoroplastic is polyvinylidene fluoride, and the carbon nanotube is single-wall carbon nanotube. The mixture was then placed in a torque rheometer and kneaded for 15 minutes at 275°C to obtain a mixture similar to figure 1 The fluoroplastic-based micro-nano composite absorbing material shown in curve 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com