Application of aspirin in preparing anti-AIDs (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) drugs
An anti-AIDS and aspirin technology, applied in the new use of aspirin, the application in the preparation of anti-AIDS drugs, and the field of AIDS drug composition, can solve the problems of aspirin's anti-HIV effect and reports, and achieve good specificity and safety High, clear effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
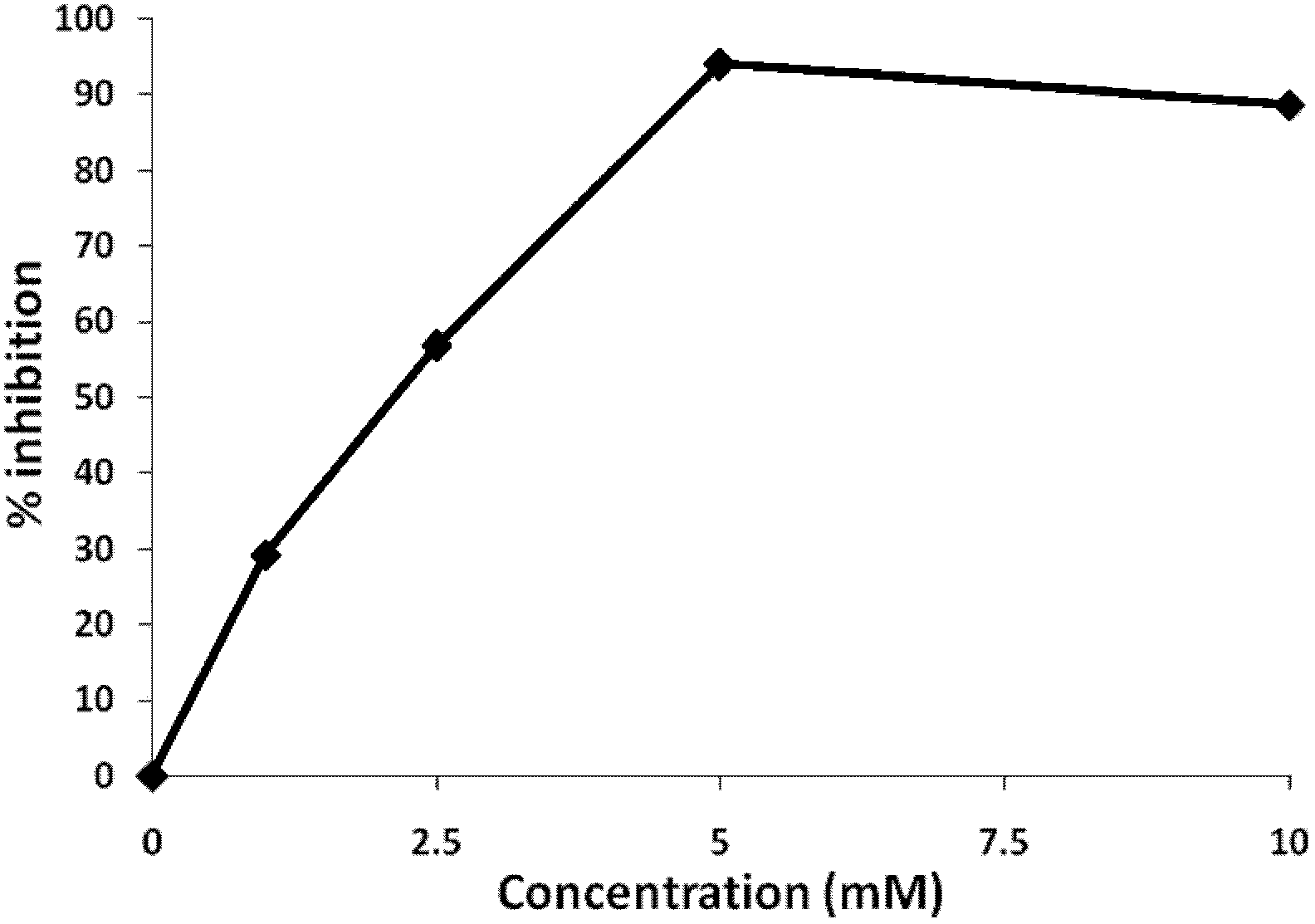
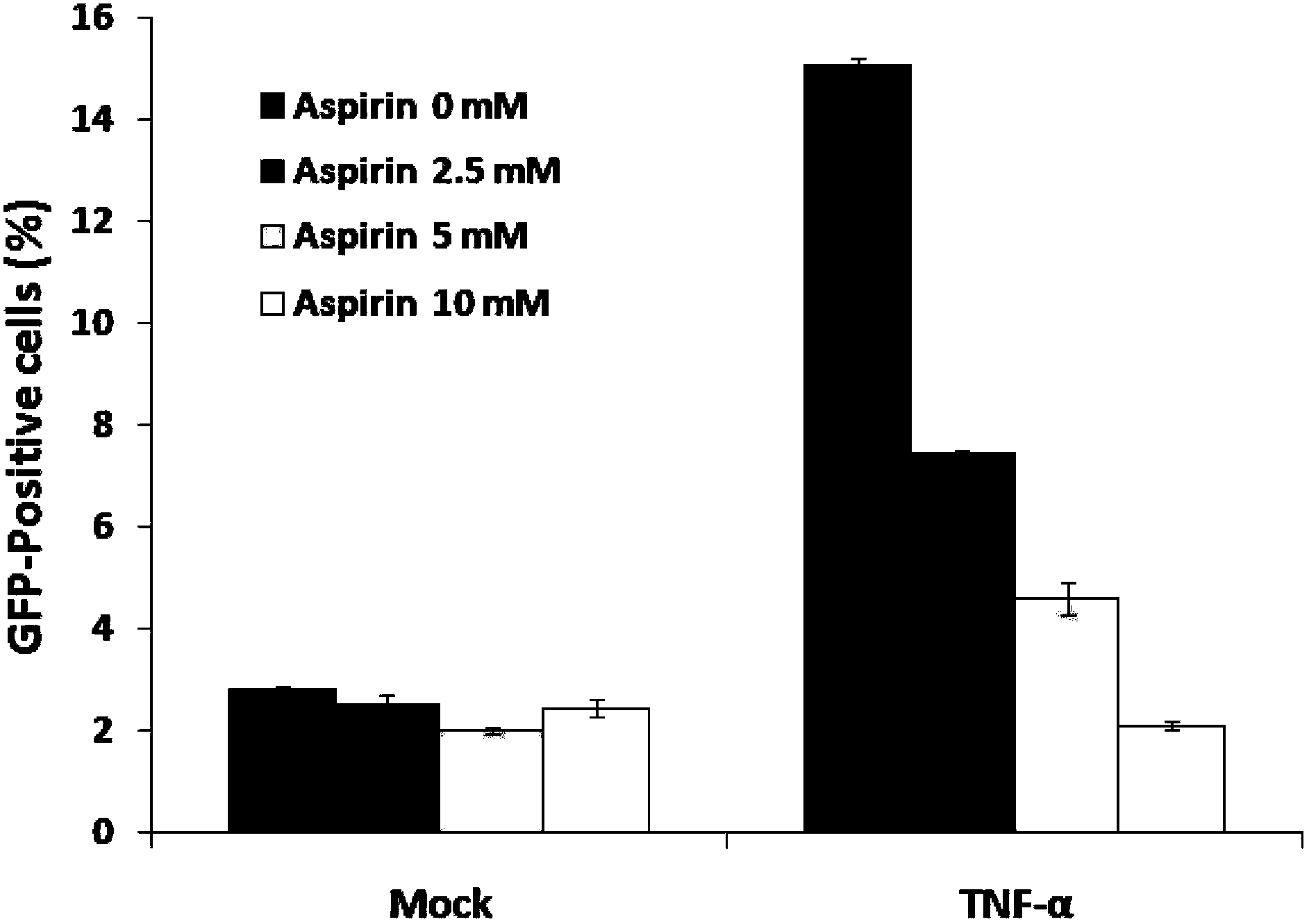
[0046] Example 1. The effect of the concentration of aspirin on HIV transcription inhibition
[0047] Prepare HIV pseudovirus carrying green fluorescent protein gene (pNL-4-3-EGFP) and infect Jurkat T cells, and screen stable strains of EGFP positive cells to establish a cell model of HIV pseudovirus infection. Cell culture conditions: RPMI 1640 medium plus 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% double antibodies (penicillin and streptomycin), 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cell culture incubator. Aspirin was added to the cell culture medium at different concentrations of 2.5mM, 5mM, and 10mM. The cells were kept at 37℃, 5% CO 2 Cultivate in a cell incubator, at different time points, observe the expression of green fluorescent protein in the cells with a fluorescence microscope and take pictures. At the same time, the cells at different time points were collected, centrifuged at 1000 rpm for 5 min, washed once with 500 μL PBS, and resuspended with 200 μL PBS, and the percentage of GFP-positive cell...
Embodiment 2
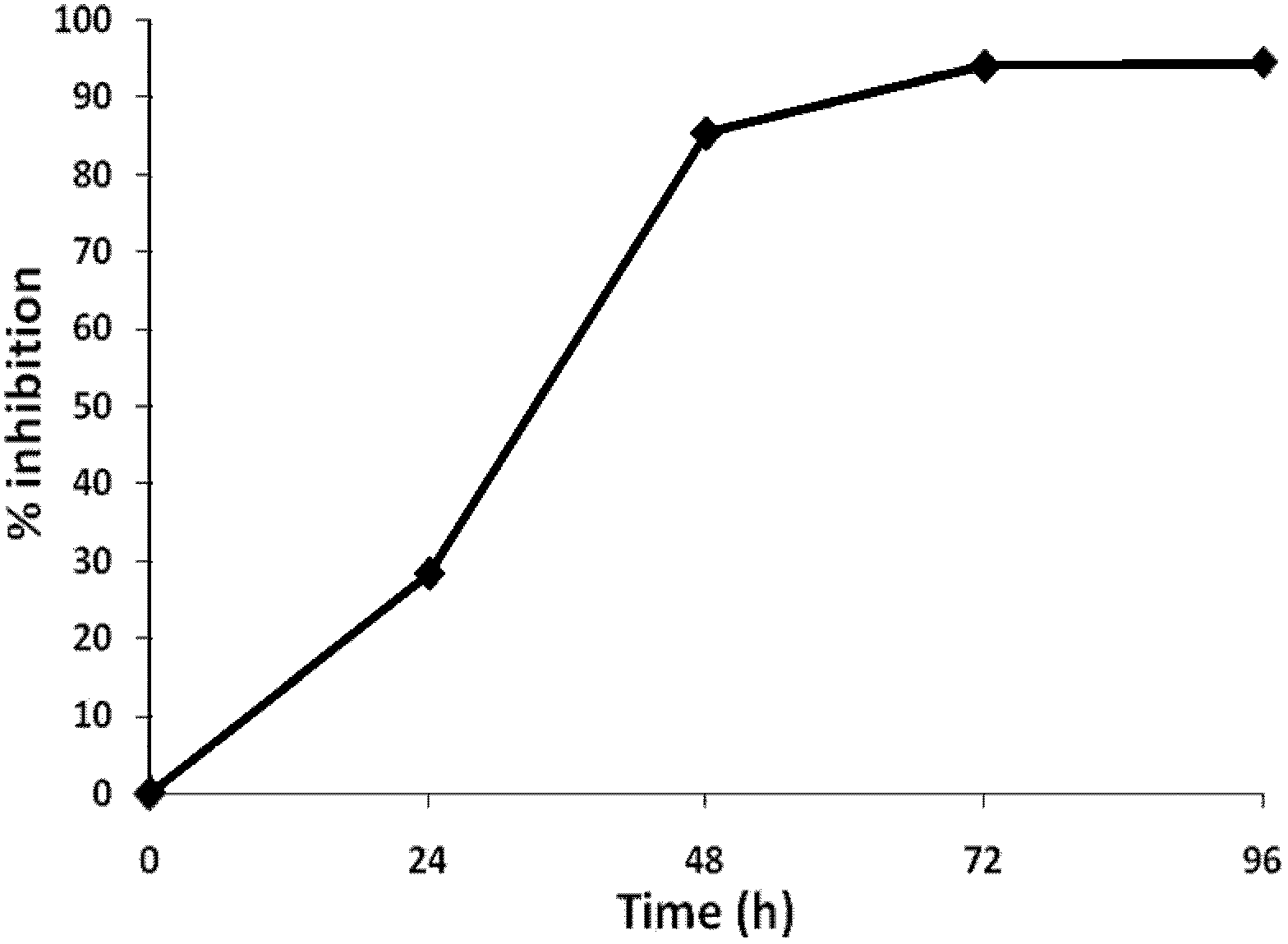
[0049] Example 2. The effect of the duration of action of aspirin compounds on HIV transcription inhibition
[0050] To obtain a better activation concentration of the drug to treat the HIV-infected cell model, 1 day, 2 days, 3 days, 4 days after the drug treatment of HIV pseudovirus-infected cells, through the fluorescence microscope of the reporter gene green fluorescent protein Observe and detect by flow cytometry, analyze the inhibitory efficiency of HIV-infected cells, and obtain the time-effect relationship of drug action.
[0051] The results showed that over time, the number of green fluorescence-positive cells gradually decreased. After 96 hours of treatment with aspirin in the HIV-infected cell model, the proportion of green fluorescence-positive cells dropped to 12%, while the green fluorescence-positive cells in the HIV-infected cell model group were not treated with the drug. The proportion of cells is 98.7%. The results suggest that aspirin has a time-effect relation...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3. Inhibition experiment of aspirin on HIV-1 replication in chronically infected H9 / HIV-1ⅢB cells.
[0053] Chronic infection H9 / HIV-1ⅢB cells originated from the NIH AIDS Research and Reference Reagent Program (Cat. No. 87). The drug antiviral experiment was carried out according to the method described in the literature (Wang RR, Gu Q, Yang LM, et a1. Anti-H1V-1 activities of extracts from the medicinal plant Rhus Chinensis. J Ethnopharmaco1.2006.105:269-73). The test drug is diluted in a 96-well micro-culture plate with complete medium, and each dilution is set to 3 wells, and each well is 100 μl. At the same time, a control well without drug and a positive control drug for zidovudine (AZT, purchased from Sigma) are set. Add 4×10 drops to each hole 8 / L 100μl of chronically infected cells HIV-1ⅢB / H9 cells. After culturing for 4 days, the supernatant was collected by centrifugation and inactivated by Triton X-100. The ELISA method measures the level of HIV-1 p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com