OSBPL2 mutant gene as well as identification method and detection kit thereof
A detection kit and identification method technology, which is applied in the field of hereditary non-syndromic deafness-related genes, its identification method and detection kit, can solve the problems of time-consuming and laborious, and achieve the effect of convenient method and cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
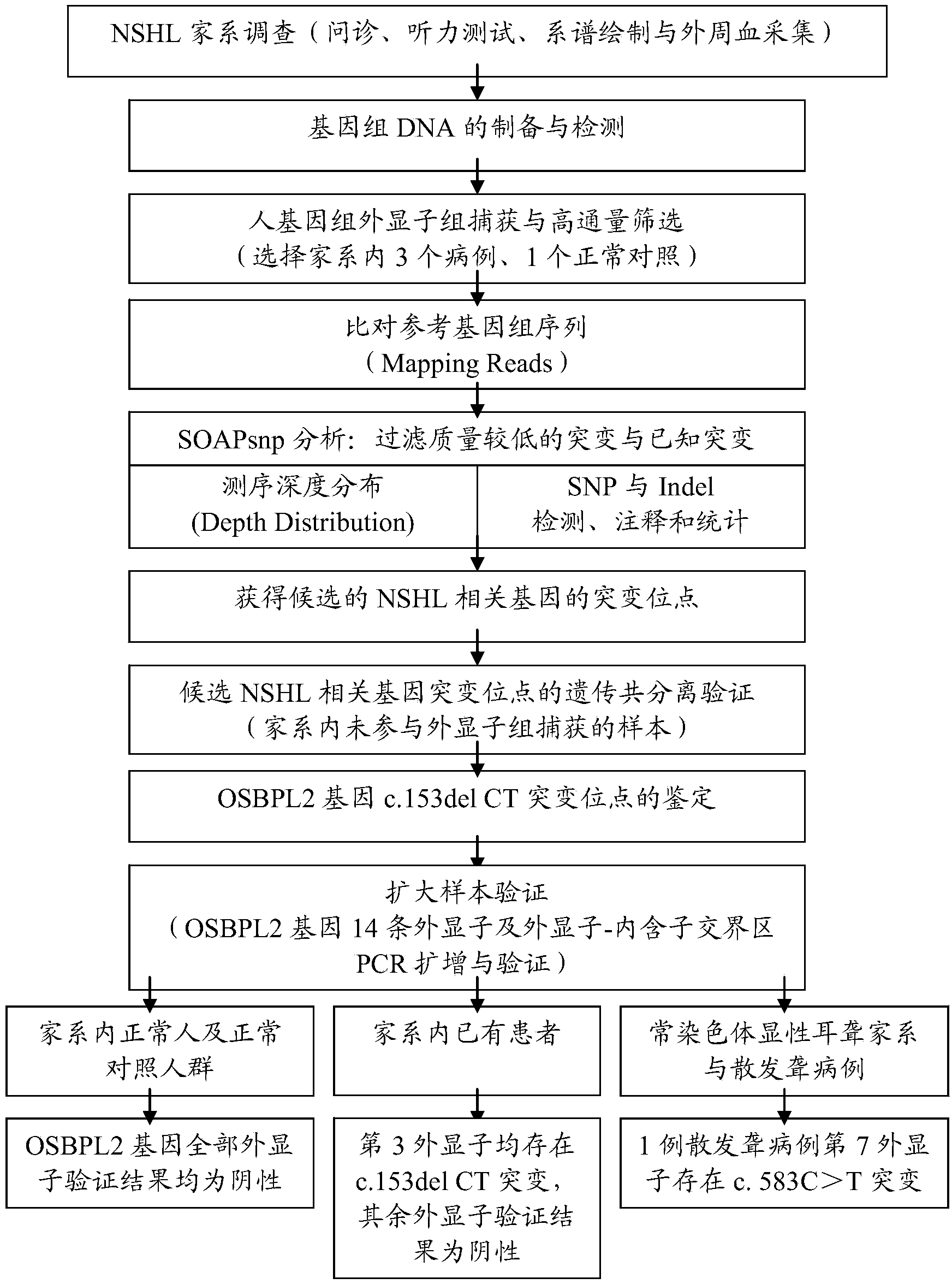
[0056] Taking NSHL as an example, the inventor detected a new deafness-related gene (flow chart as shown in figure 1 shown), which includes the following steps:
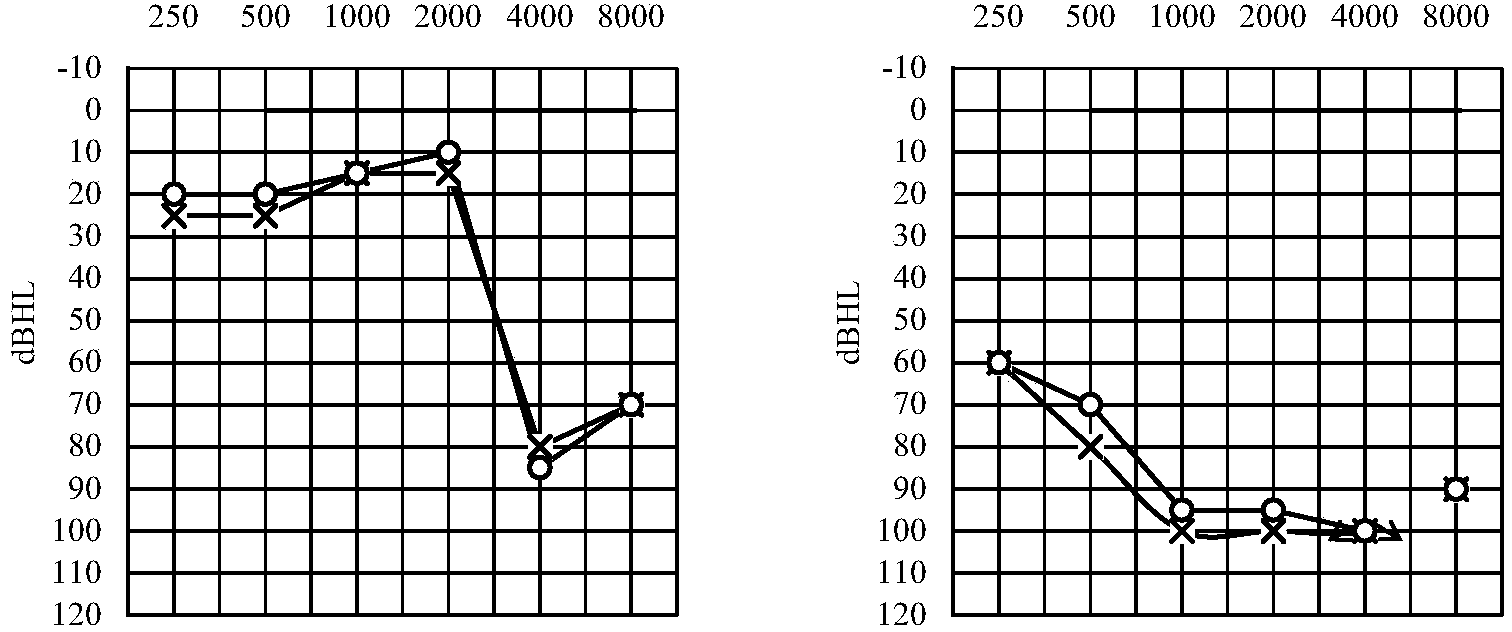
[0057] 1) The inventor collected a 7-generation autosomal dominant NSHL pedigree, and the results of consultation and hearing tests showed that all patients in the pedigree showed late-onset, progressive moderate and severe non-syndromic deafness. The peripheral blood of the family members was collected and genomic DNA was extracted.
[0058] 2) Using human genome exon capture technology to perform exon capture and analysis on the whole genome DNA of 3 patients and 1 normal control in the family described in 1), and obtain the mutation sites of candidate hereditary deafness-related genes.
[0059] 3) Combining conventional sequencing methods to identify the mutation sites of candidate genetic deafness-related genes: a. Perform genetic co-segregation verification on the rest of the samples in the family that did not ...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Example 2: Sequencing the causative genes of this NSHL family using human genome exome capture
[0062] Subsequently, the inventors used Agilent SureSelect Human All Exon Kit (38M) combined with Solexa high-throughput sequencing technology to sequence the exome sequences of 3 patients and 1 normal person in the NSHL family described in Example 1, and successfully A new NSHL-associated gene, a mutant of the OSBPL2 gene, was discovered. The specific operation steps are as follows:
[0063] 1) Randomly break the genomic DNA into fragments of about 150-200bp, and then connect adapters to both ends of the fragments to prepare a hybrid library (see the Illumina / Solexa standard library construction instructions provided by http: / / www.illumina.com / ; Accurate whole human genome sequencing using reversible terminator chemistry. Nature 2008, 456:53-59).
[0064] 2) After purification, the library was subjected to linear amplification of Ligation-mediated PCR (LM-PCR) and hybridi...
Embodiment 3
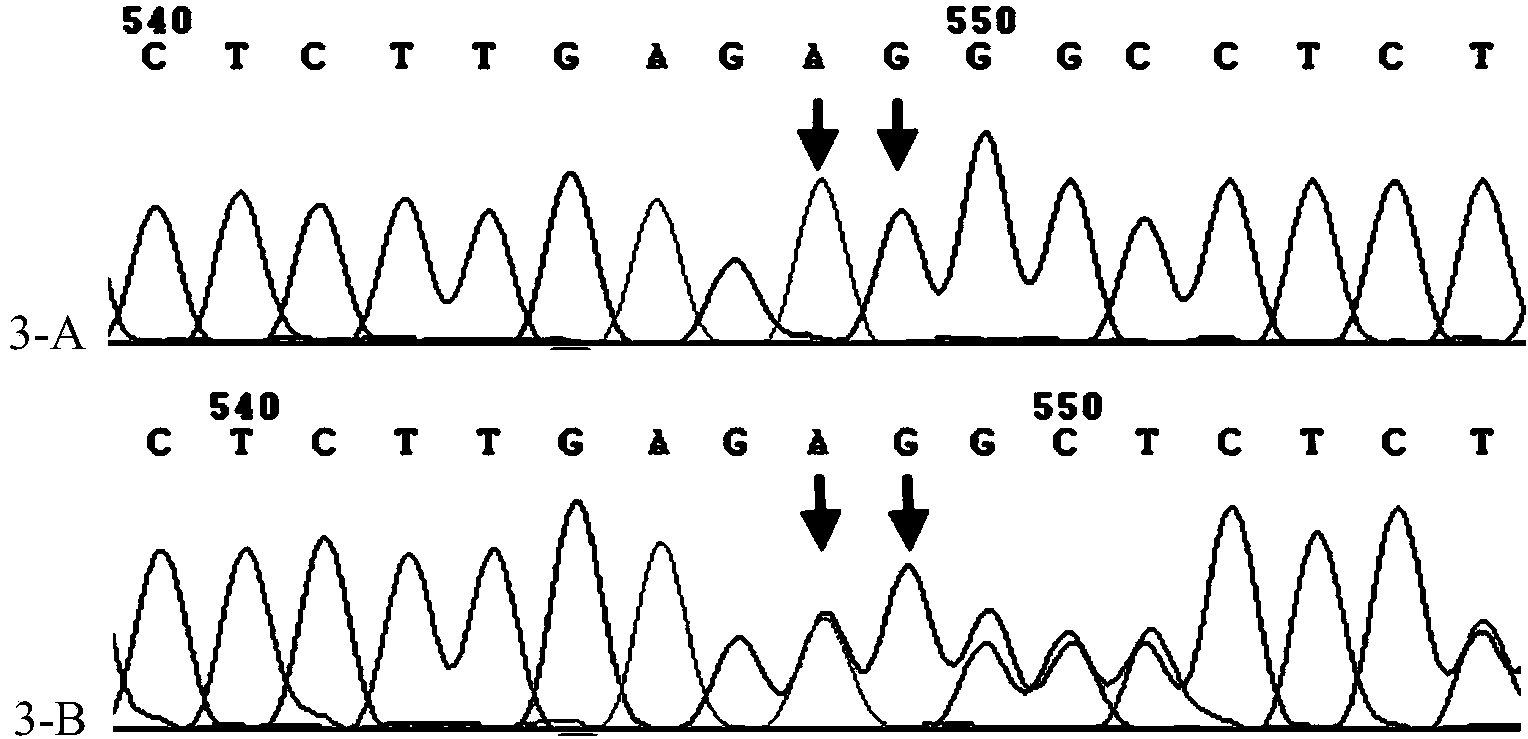
[0094] Example 3: Further verification of the c.153del CT mutation site of the OSBPL2 gene
[0095] The inventor verified the c.153del CT mutation site of the OSBPL2 gene by combining conventional sequencing methods: ① Verify the genetic co-segregation of all samples in the family described in Example 1; ② Verify the exon and exon of the ① verified gene PCR amplification and detection of the sequence of the sub-intron junction region; ③ Expand the sample size (normal controls outside the family, small autosomal dominant families, sporadic deaf cases) verification.
[0096] 1) Amplify the mutation by PCR
[0097] Genomic DNA was prepared from the peripheral blood samples of all patients in the family according to the method in Example 1. After the concentration was adjusted to 25ng / μl, PCR reaction was carried out.
[0098] PCR primers were designed by Primer v5.0, and the sequences are as follows:
[0099] Upstream primer: CTGGATCTCACTCACATTCT (SEQ ID NO: 21)
[0100] Down...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com