Method for extracting fungal oil
An oil extraction and fungus technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of time-consuming cell wall breaking, low wall breaking rate, affecting oil extraction efficiency, etc., and achieves large sample processing capacity, high environmental safety, energy saving and environmental protection boiling point. and the effect of latent heat of vaporization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] References (Li Yonghong et al. Screening of broad-spectrum carbon source oleaginous yeast. China Biotechnology Journal, 2005, 25 (12): 39-44), the cultivation method of oleaginous yeast, cultivating Rhodosporidium Rhodosporidium toruloides (China Ordinary Microorganism Culture Collection and Management Center, No. AS2.1389), centrifuge at 4000rpm / min for 15min, and collect the wet bacteria. The oil content of the dried bacteria is 52.6% as measured by the classic method.
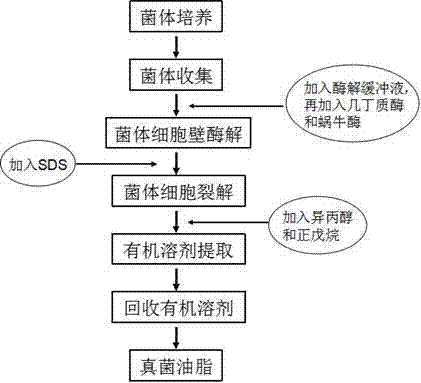
[0032] Refer to attached figure 1 A method for extracting fungal oil as shown, comprising the following steps: (1) cell culture: cultivating Rhodosporidium yeast (the same as the cultivation method of oleaginous yeast in the above reference); (2) cell collection: through a centrifuge Centrifuge the fungal culture solution, collect 20 g of wet fungal cells, and centrifuge at a centrifugation rate of 4000 rpm / min for 15 minutes; (3) enzymatic hydrolysis of the bacterial cell wall: dissolve the c...
Embodiment 2
[0035] References (He Rong et al., Agarita chrysogenum ( Umbelopsis isabellina ) Optimization of culture conditions for oil-producing fermentation of Hua 2-1. Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2012, 18 (1): 80-85) The cultivation method of filamentous oleaginous fungus, cultivating Mortierella chrysogenum Mortierella isabellina (China Ordinary Microorganism Culture Collection and Management Center, No. AS3.3410), centrifuge at 2000rpm / min for 40min, and collect the wet bacteria. The oil content of the dried bacteria is 45.4% as measured by the classic method.
[0036] The difference with embodiment 1 is:
[0037] Step (1) Bacteria culture: Cultivate Mortierella chrysogenum (same as the method for culturing filamentous oleaginous fungi in the above-mentioned references);
[0038] Step (2) Cell collection: collect 10 g of wet fungal cells, centrifuge at 2000 rpm / min for 40 min;
[0039] Step (3) Cell wall enzymatic hydrolysis: sorbic acid 0.5mmol / ...
Embodiment 3
[0045] References (Li Yonghong et al., Screening of broad-spectrum carbon source oleaginous yeast. China Biotechnology Journal, 2005, 25 (12): 39-44), the cultivation method of oleaginous yeast, cultivating Rhodotorula viscosus Rhodotorula glutinis (China Ordinary Microorganism Culture Collection and Management Center, No. AS2.703), centrifuge at 6500rpm / min for 5min, and collect the wet bacteria. The oil content of the dried bacteria is 50.8% as measured by the classic method.
[0046] The difference with embodiment 1 is:
[0047] Step (1) Bacterial culture: Cultivate Rhodotorula viscosus (same as the method for cultivating oleaginous yeast in the above-mentioned references);
[0048] Step (2) Bacteria collection: centrifugation speed 6500rpm / min, centrifugation 5min;
[0049] Step (3) Enzymolysis of bacterial cell wall: sorbic acid 2mmol / L, CaCl2 20mmol / L, EDTA 0.15mmol / L, take 40mL of enzymolysis buffer solution, pH5.8, add 0.125g chitinase (0.8 million U / ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com