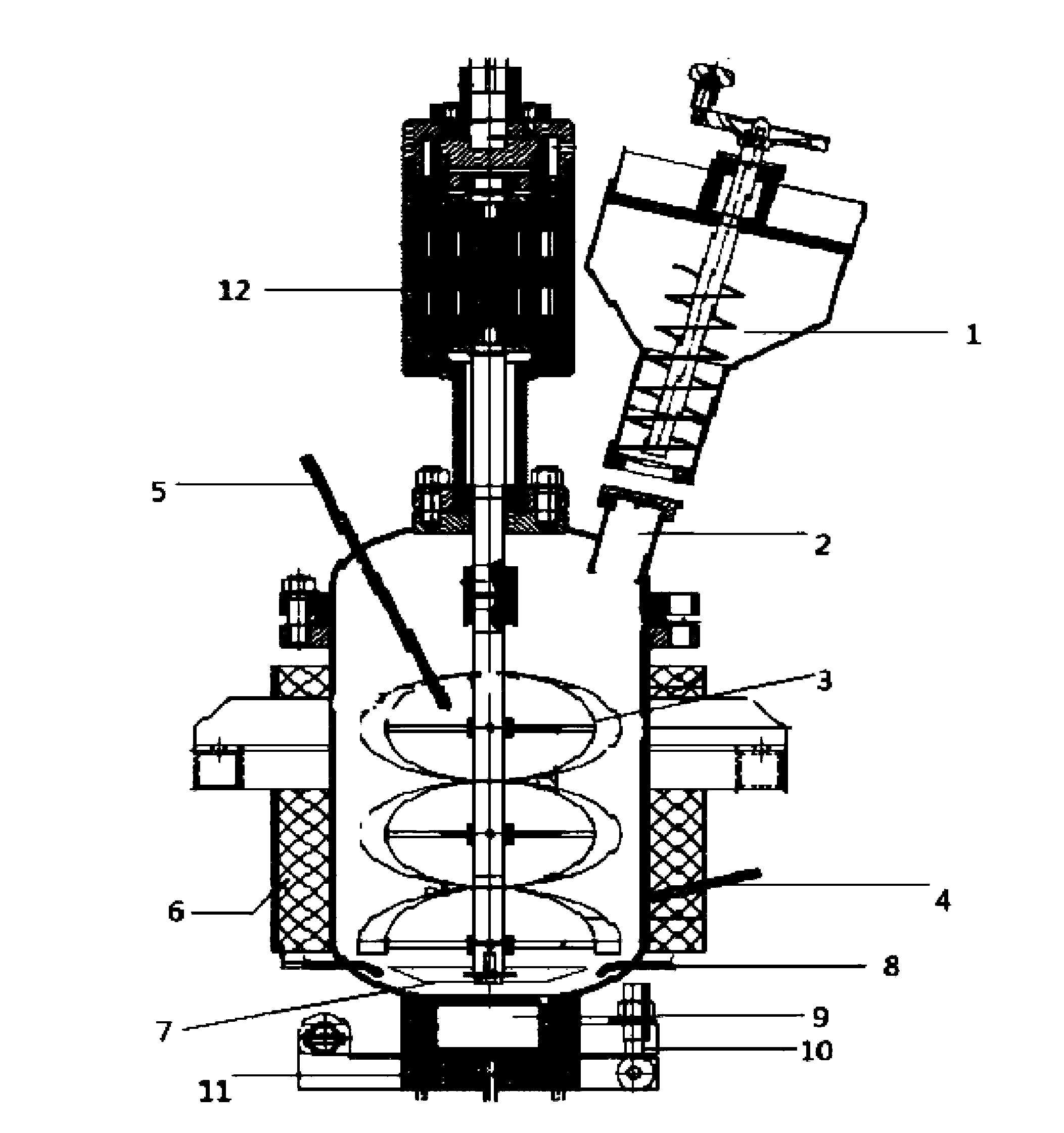
Post-treatment method for strengthening pretreatment effect of lignocellulose raw material through pulping
A lignocellulosic and pretreatment technology, applied in biofuel, waste fuel, fermentation, etc., can solve the problems of high energy consumption, limited promotion and application of pretreatment methods, high pretreatment intensity, etc., to increase specific surface area, shorten enzyme The effect of shortening the solution reaction time and improving the conversion rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] After dewatering the industrial residue of corncobs by pressing, directly add tap water to adjust its solid content to 5% (w / w), perform a refining treatment on a disk mill for 1 minute, and obtain a particle size distribution of 0.05-0.15mm of lignocellulose pulp. Put the refined slurry into an Erlenmeyer flask, add cellulase (Shanghai Youtel Biochemical Co., Ltd.), the enzyme amount is 15FPU / g dry material, and enzymatically hydrolyze at 50°C, pH 5.5, and 150rpm for 6h , the conversion rate of cellulose can reach 70.41%. The unrefined industrial residue of corncobs is enzymatically hydrolyzed under the same conditions, and the conversion rate of cellulose is only 53.93%.
Embodiment 2
[0028] Coarsely pulverize the air-dried corn stalks, remove sand, dust and other impurities, place them in a pretreatment reactor, and dry lignocellulose at 160°C, 0.5MPa, and dilute sulfuric acid concentration of 1% (w / w). Under the condition that the mass ratio of solid to dilute acid is 1:1, dilute sulfuric acid pretreatment is carried out for 15 minutes, and the equipment used for the treatment is a reactor. Add water to the pretreated straw raw material, adjust its solid content to 20% (w / w), and perform a refining treatment on a disc refiner for 5 minutes to obtain a lignocellulose slurry with a particle size of 0.01-0.08mm . Put the refined straw slurry into an Erlenmeyer flask, add tap water to adjust the solid content to 5% (w / w), and add cellulase (Shanghai Youtel Biochemical Co., Ltd.), the enzyme amount is 15 FPU / g dry The material is enzymatically hydrolyzed for 72 hours at 50°C, pH 4.8, and 150 rpm, and the conversion rate of cellulose can reach 82.79%. The con...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com