Construction method of genetically engineered bacterium for producing astaxanthin
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and astaxanthin, applied in the field of microbial fermentation, can solve the problems of cumbersome operation and long cycle, and achieve the effects of avoiding cloning, shortening construction time, and high efficiency of homologous recombination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1 , experimental protocol and primer design
[0032] Experimental scheme design of the present invention is as follows:
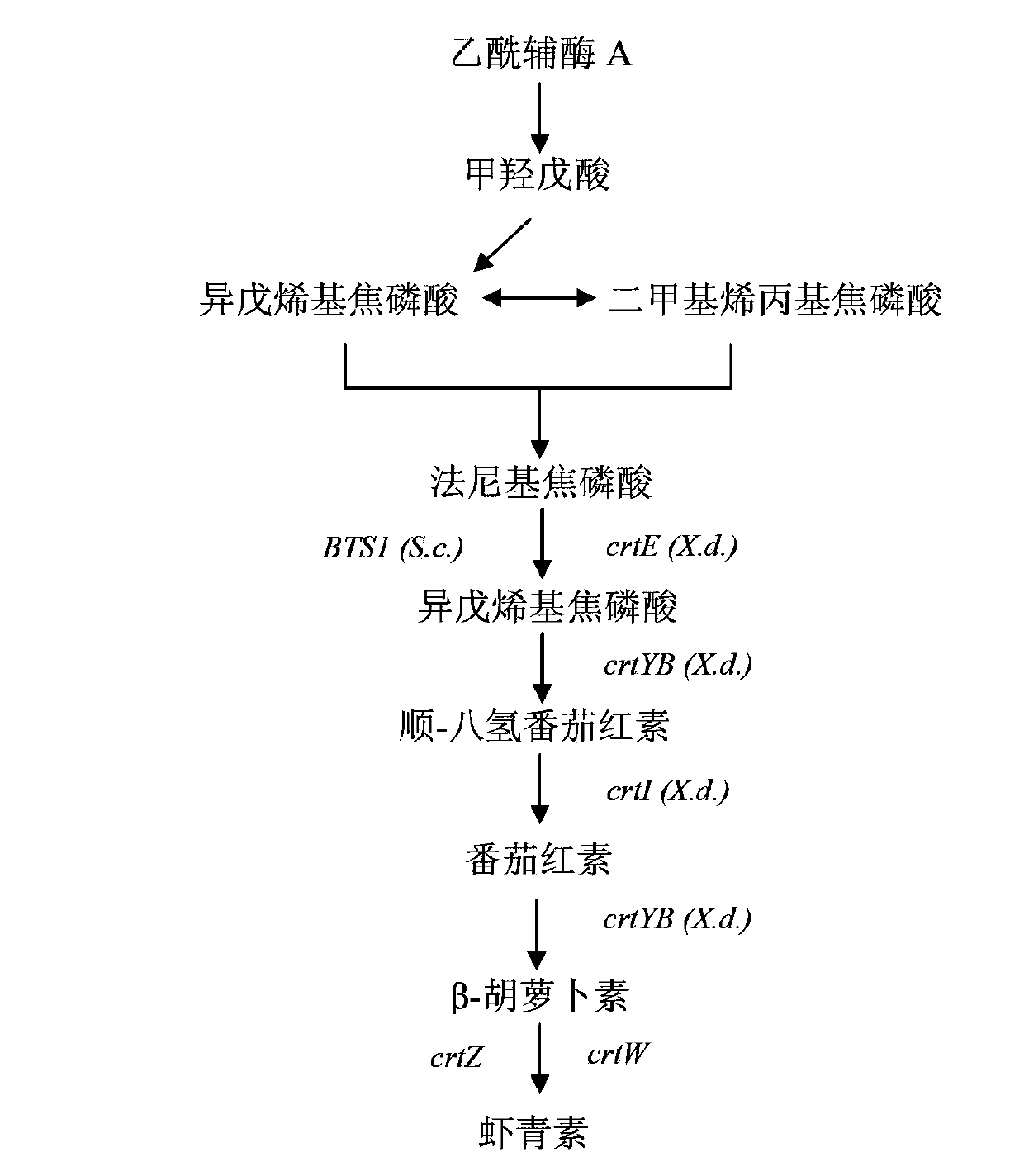
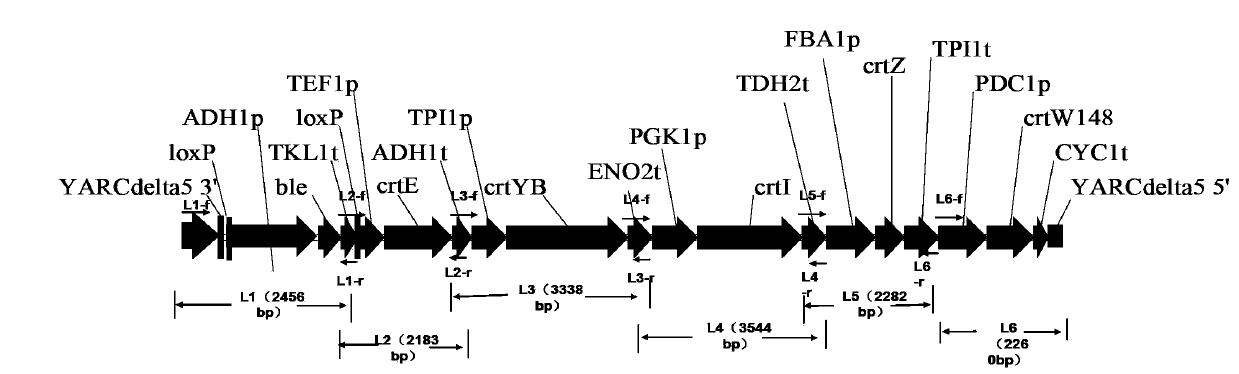
[0033] Five genes crtE (GenBank: DQ016502. 1, derived from Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous ATCC24202), crtYB (GenBank: AY177204.1, derived from Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous ATCC24202), crtI (GenBank: AY177424.1, derived from Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous ATCC24202), 3crt8:ABGenBrankevZ ( sp.SD212) and crtW (GenBank: CP001037.1, derived from Nostoc punctiforme PCC73102), and simultaneously expressed the ble gene (Zeocin resistance gene) as a screening marker, and selected the yeast chromosome δ site as the integration site, and each gene module was in The integrated assembly sequence on the chromosome is as follows figure 1 shown. The promoters and genes are numbered respectively, as shown in Table 1.
[0034] Table 1. Promoters and gene numbers
[0035] promoter number
promoter name
gene number
gene name
A ...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Example 2 , Construction of genetically engineered bacteria
[0046] 2.1 Construction of plasmids pYES2-CrtE, pYES2-CrtYB, pYES2-CrtI, pYES2-CrtZ and pSH62-CrtW
[0047] References (Ken Ukibe, Keisuke Hashida, Nobuyuki Yoshida, and Hiroshi Takagi. Metabolic Engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for Astaxanthin Production and Oxidative Stress Tolerance. APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, 2009: 7205-7211; Venjnanger, JM, R .High-level production of Beta-carotene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by successful transformation with carotenogenic genes from Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2007, 73:4342-4350) method, obtain crtE, crtYB and crtI genes, and insert them into pYES2 respectively .0 (purchased from Invitrogen) to obtain plasmids pYES2-CrtE, pYES2-CrtYB and pYES2-CrtI, transform them into E.coli strain DH5α, and save the plasmids.
[0048] A synthetic company (Nanjing GenScript Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) was commissioned to construct plasmids...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Example 3 , Fermentation of genetically engineered bacteria and detection of astaxanthin
[0077] 3.1. Fermentation
[0078] The seed cultivation method is as follows:
[0079] Pick a single colony of the positive clone obtained from the screening in Example 2 from the culture plate, insert it into 25ml of YPD medium (250ml shake flask), culture at 30°C, 220rpm / min, for 48h.
[0080] The fermentation culture method is as follows:
[0081]The seed solution was added to 25ml YPD medium (250ml shake flask) according to the inoculation ratio of 4%, cultured at 30°C and 220rpm / min for 72h.
[0082] 3.2. Extraction of Astaxanthin
[0083] The extraction method of astaxanthin is as follows:
[0084] Transfer the fermentation broth to a weighed centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 4°C, 4000r / min, for 5min, discard the supernatant, wash once with sterile water, discard the supernatant, and weigh. For each gram of wet bacteria, add 17.5ml of DMSO preheated to 55°C, mix well, and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com