A kind of genetically engineered bacteria co-producing geraniol and nerol and its construction method and application
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and nerol, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems affecting the quality of geraniol and downstream applications, environmental pollution by chemical methods, and many impurities in products, and achieve easy engineering operations, cheap raw materials, and high fermentation short cycle effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
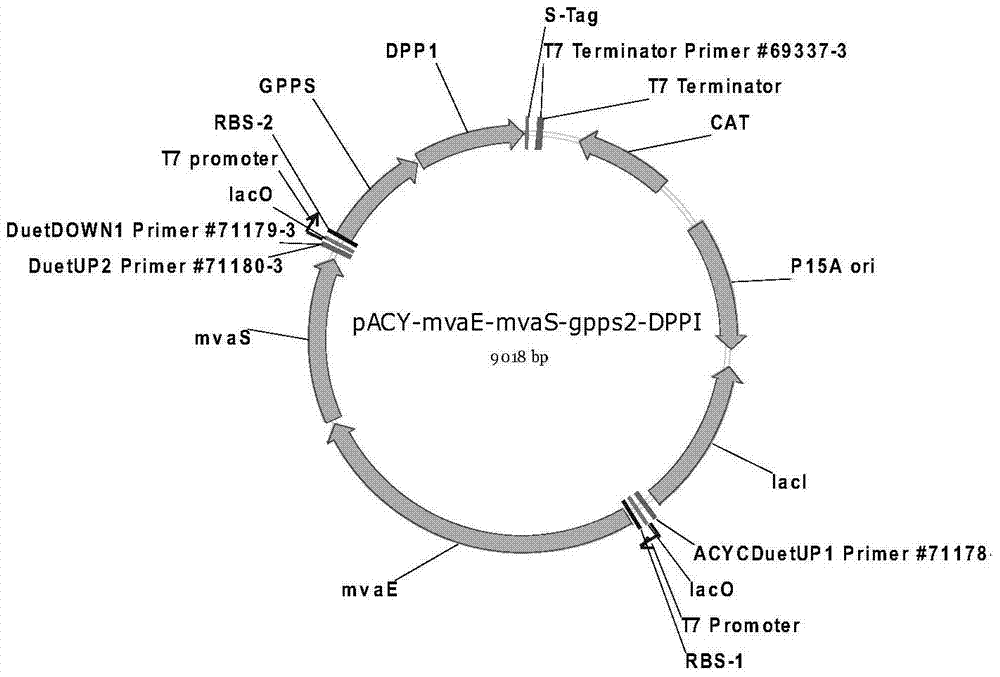
[0051] Example 1 Expression of phosphatidic acid phosphatase DPP1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae for biosynthesis of nerol and geraniol
[0052] By co-expressing the acetyl-CoA acyltransferase gene / hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase gene (mvaE) from Enterococcus faecalis in Escherichia coli, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthesis Enzyme gene (mvaS); mevalonate kinase gene (ERG12), mevalonate-5-phosphate kinase gene (ERG8), mevalonate-5-diphosphate decarboxylase gene (ERG19) from Saccharomyces cerevisiae , isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase gene (IDI1); geranyl diphosphate synthase gene (GPPS2) from North American fir and phosphatidic acid phosphatase DPP1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (NCBI Reference Sequence: NM_001180592.1) , the biosynthesis of geraniol from glucose.
[0053] (1) Cloning of DPP1 gene and construction of expression vector
[0054] Using Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288c genomic DNA as template, DPP1-rbs-F2 and DPP1-XhoR as primers for PCR amplification, PC...
Embodiment 2
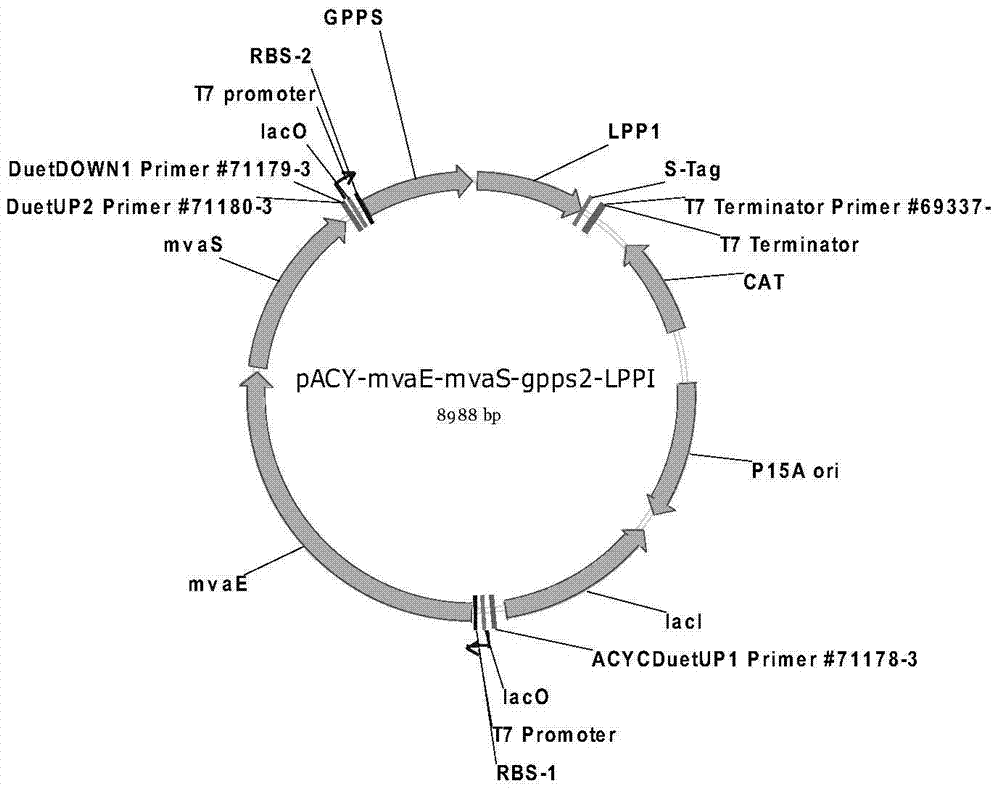
[0061] Example 2 Expression of phosphatidic acid phosphatase LPP1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae for biosynthesis of nerol and geraniol
[0062] By co-expressing the acetyl-CoA acyltransferase gene / hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase gene (mvaE) from Enterococcus faecalis in Escherichia coli, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthesis Enzyme gene (mvaS); mevalonate kinase gene (ERG12), mevalonate-5-phosphate kinase gene (ERG8), mevalonate-5-diphosphate decarboxylase gene (ERG19) from Saccharomyces cerevisiae , isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase gene (IDI1); geranyl diphosphate synthase gene (GPPS2) from North American fir and phosphatidic acid phosphatase LPP1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (NCBI Reference Sequence: NM_001180811.3) , the biosynthesis of geraniol from glucose.
[0063] (1) Cloning of LPP1 gene and construction of expression vector
[0064] Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288c genomic DNA was used as a template, and LPP1-rbs-F2 and LPP1-XhoR were used as primers for PC...
Embodiment 3
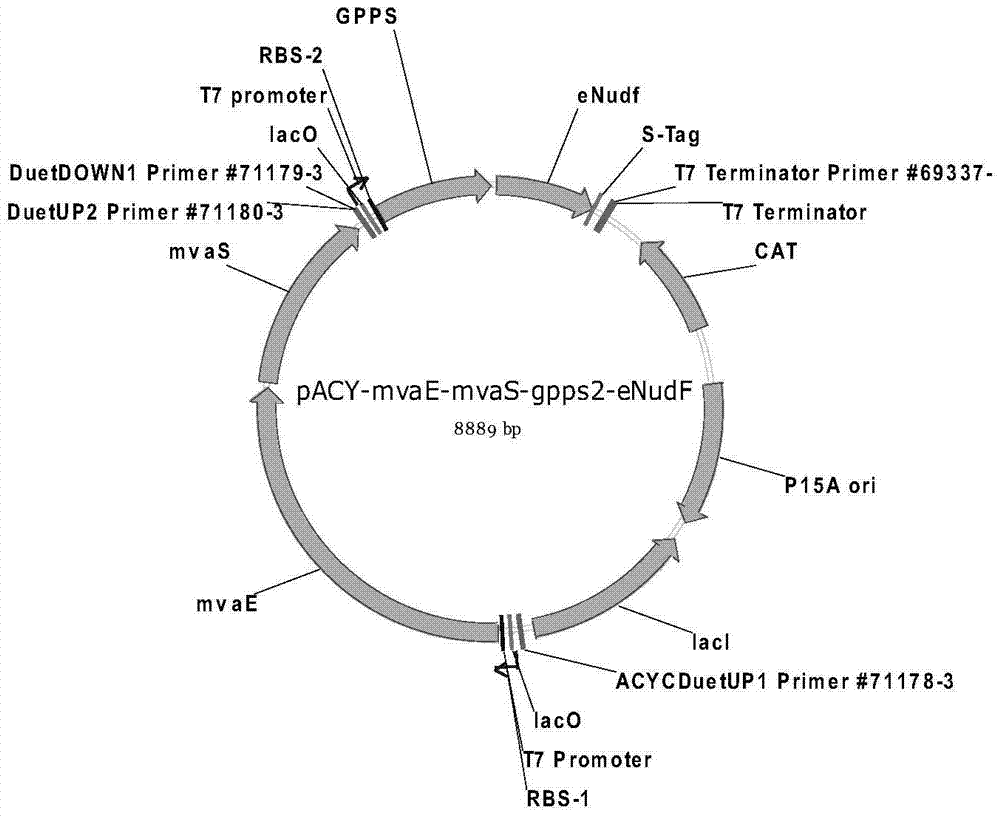
[0072] Example 3 Expression of ADP-ribose pyrophosphatase gene EcNudF derived from Escherichia coli for biosynthesis of nerol and geraniol
[0073] By co-expressing the acetyl-CoA acyltransferase gene / hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase gene (mvaE) from Enterococcus faecalis in Escherichia coli, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthesis Enzyme gene (mvaS); mevalonate kinase gene (ERG12), mevalonate-5-phosphate kinase gene (ERG8), mevalonate-5-diphosphate decarboxylase gene (ERG19) from Saccharomyces cerevisiae , isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase gene (IDI1); geranyl diphosphate synthase gene (GPPS2) from North American fir and ADP-ribose pyrophosphatase gene EcNudF from Escherichia coli (GenBank: U22009.1 ), using glucose to biosynthesize geraniol.
[0074] (1) Cloning of EcNudF gene and construction of expression vector
[0075] Using Escherichia coli K12 genomic DNA as a template, eNudF-rbs-BglF and eNudF-XhoR as primers for PCR amplification, PCR amplification conditions...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com