Preparation method of lightweight cordierite-based thermal insulation material
A technology of thermal insulation material and cordierite, which is applied in the field of thermal insulation materials, can solve the problems that organic thermal insulation materials are easy to burn, cannot have the same life span of buildings, and have hidden fire safety hazards, etc., and achieves environmental protection, good creep resistance and corrosion resistance. , the effect of low thermal expansion coefficient
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
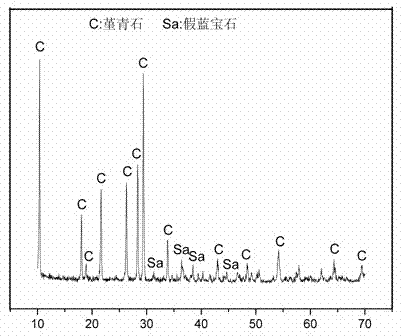
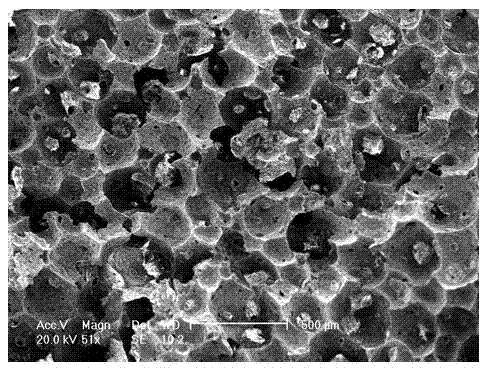
[0023] Add 58 parts of kaolin, 31 parts of attapulgite and 11 parts of magnesium oxide into the ball mill jar, add 0.8% gum arabic, and add an appropriate amount of water to prepare a slurry with a solid content of 30%, and ball mill for 24 h. Add 0.8% sodium lauryl sulfate to foam for 3 minutes, pour the foamed slurry directly into the gypsum abrasive, let it stand for 4 hours and then demould. After drying at room temperature for 24 h, the green body was dried in a drying oven at 100 °C for 24 h, and then sintered at 1200 °C. First, the temperature was raised to 500 °C at a rate of 2 °C / min and kept for 1 h; then the temperature was raised to 1200 °C at a rate of 5 °C / min and kept for 2 h; finally, the temperature was cooled to 500 °C at a rate of 5 °C / min; The furnace is cooled to room temperature to obtain a lightweight cordierite-based thermal insulation material. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern of the lightweight cordierite-based thermal insulation material is shown ...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Add 65 parts of kaolin, 14 parts of attapulgite and 21 parts of magnesium oxide into the ball mill jar, add 1.2% gum arabic, and add an appropriate amount of water to prepare a slurry with a solid content of 35%, and ball mill for 24 h. Add 0.8% sodium lauryl sulfate to foam for 3 minutes, pour the foamed slurry directly into the gypsum abrasive, let it stand for 4 hours and then demould. After drying at room temperature for 24 h, the green body was dried in a drying oven at 100 °C for 24 h, and then sintered at 1200 °C. First, the temperature was raised to 500 °C at a rate of 2 °C / min and kept for 1 h; then the temperature was raised to 1200 °C at a rate of 5 °C / min and kept for 2 h; finally, the temperature was cooled to 500 °C at a rate of 5 °C / min; The furnace was cooled to room temperature to obtain a lightweight cordierite-based insulation material.
[0027] The resulting lightweight cordierite-based insulation material has a porosity of 87% and a bulk density of...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Add 58 parts of kaolin, 13 parts of attapulgite and 29 parts of basic magnesium carbonate into the ball mill jar, add 0.8% gum arabic, add an appropriate amount of water, and prepare a slurry with a solid content of 30%, and ball mill for 24 h. Add 0.8% sodium lauryl sulfate to foam for 3 minutes, pour the foamed slurry directly into the gypsum abrasive, let it stand for 4 hours and then demould. After drying at room temperature for 24 h, the green body was dried in a drying oven at 100 °C for 24 h, and then sintered at 1200 °C. Firstly, the temperature was raised to 500 °C at a rate of 2 °C / min and kept for 1 h; then the temperature was raised to 1200 °C at a rate of 5 °C / min and kept for 2 h; finally, the temperature was cooled to 500 °C at a rate of 5 °C / min; The furnace was cooled to room temperature to obtain a lightweight cordierite-based insulation material.
[0030] The resulting lightweight cordierite-based insulation material has a porosity of 88% and a bulk...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com