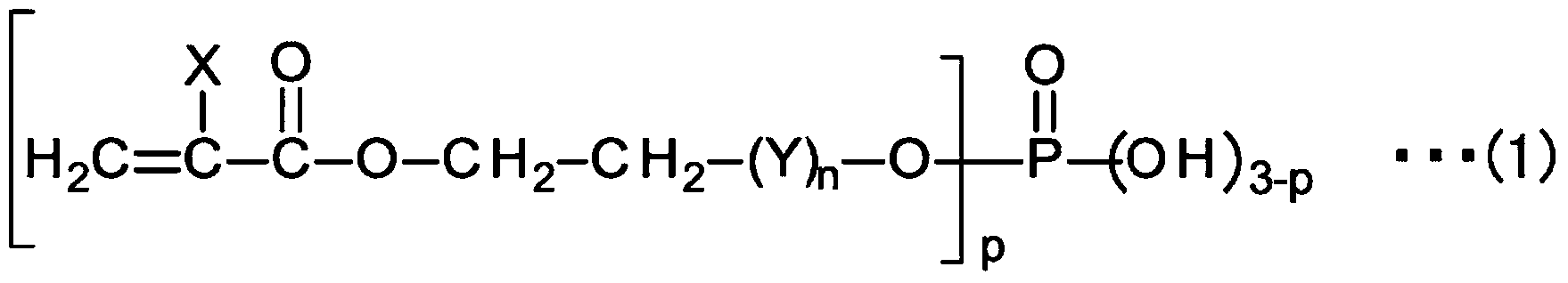Method for producing infrared radiation reflecting film
A manufacturing method, infrared technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, sputtering plating, ion implantation plating, etc., can solve the problems of reduced productivity, complicated equipment, increased film production times, etc., to improve the film production rate, Effects of improving productivity and improving adhesion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0133] Formation of hard coat at substrate
[0134] On one side of a polyethylene terephthalate film (manufactured by TORAY INDUSTRIES, INC., trade name "Lumirror U48", visible light transmittance: 93%) with a thickness of 50 μm, an acrylic ultraviolet curing type is formed with a thickness of 2 μm Hard coating (manufactured by Nippon Soda, NH2000G). Specifically, a hard coat solution was applied by a gravure coater, dried at 80°C, and then irradiated with a cumulative light intensity of 300mJ / cm by an ultra-high pressure mercury lamp. 2 UV light for curing.
[0135] Formation of infrared reflective layer
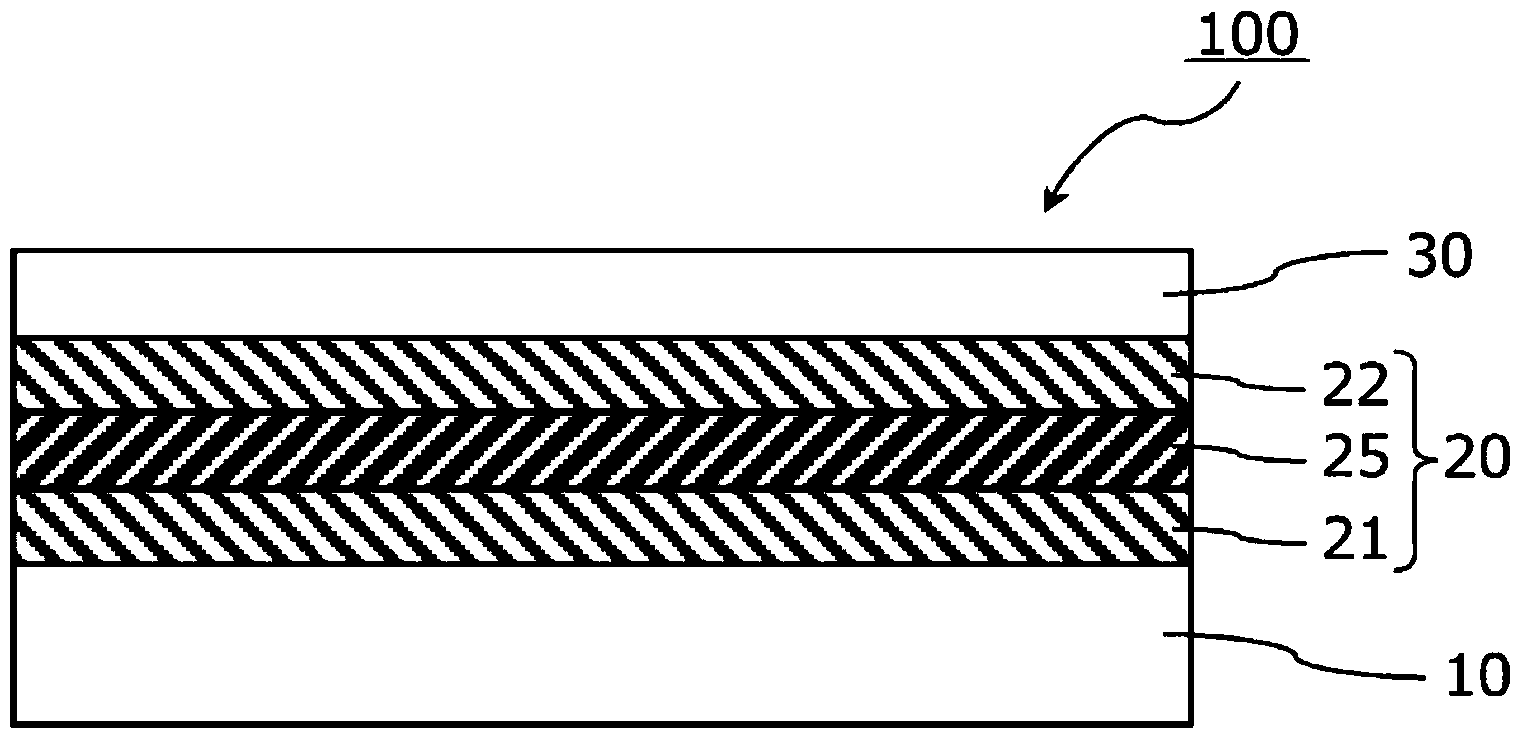
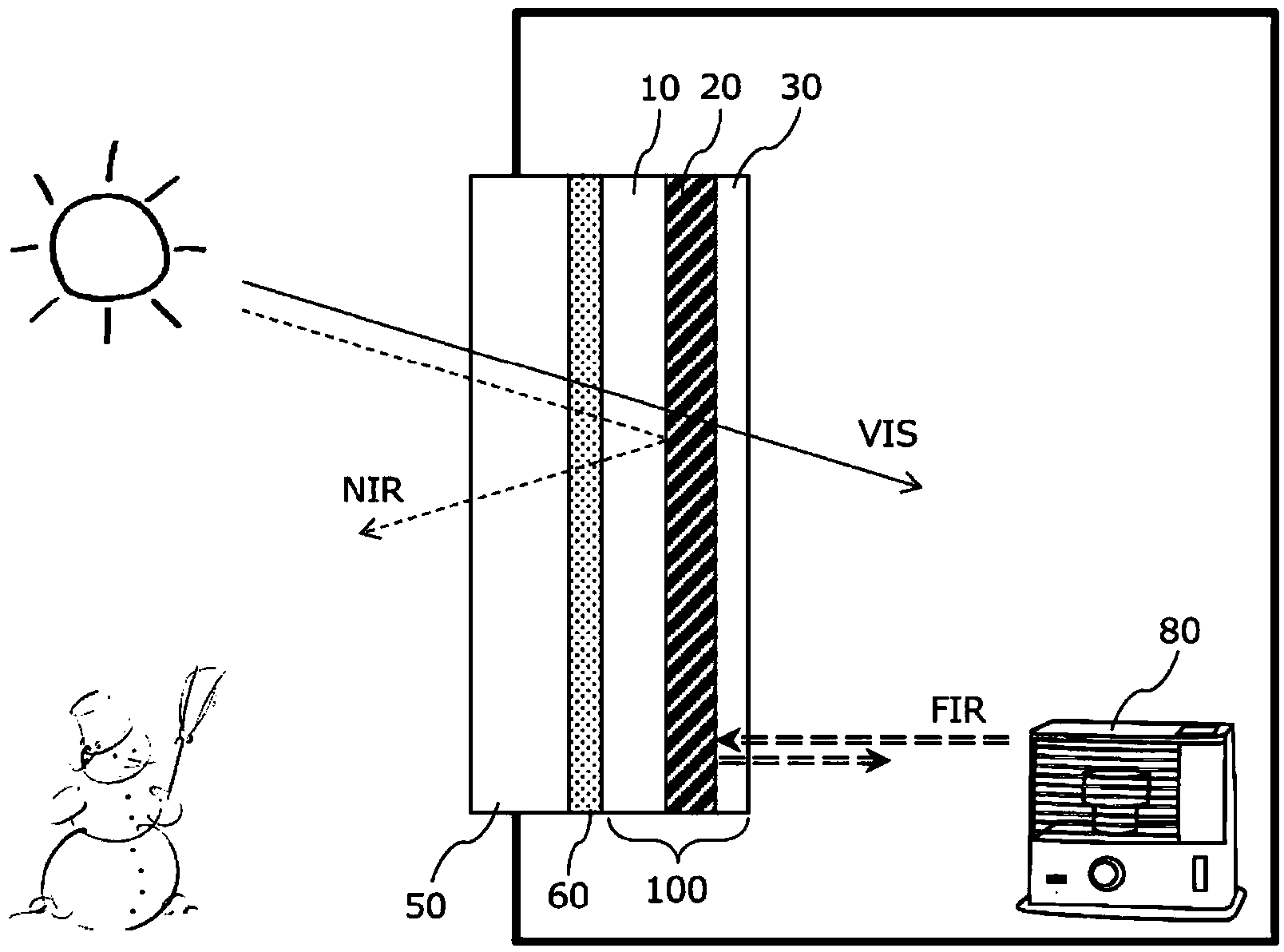
[0136] On the hard coat layer of the polyethylene terephthalate film substrate, an infrared reflective layer was formed using a roll-to-roll sputtering device. Specifically, a 30-nm-thick substrate-side metal oxide layer made of zinc-tin composite oxide (ZTO) and a 15-nm-thick metal oxide layer made of an Ag-Pd alloy were sequentially formed by DC magnetron sputterin...
Embodiment 2A and 2B
[0140] The amount of gas introduced into the sputtering film deposition chamber during the film formation of the metal oxide layer on the substrate side was changed to Ar:O by volume ratio. 2 =90:10 (Example 2A) and Ar:O 2 =95:5 (Example 2B). Among them, the Ar gas / O 2 The amount of gas introduced is Ar:O in the same manner as in Example 1 2 =98:2. An infrared reflective film was produced in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the amount of gas introduced during film formation of the substrate-side metal oxide layer was changed as described above.
Embodiment 3
[0142] As a sputtering target for forming the metal oxide layer on the base material side and the surface side, a target obtained by sintering zinc oxide:tin oxide:metal zinc powder at a weight ratio of 19:73:8 was used. Except for this, it carried out similarly to Example 1, and produced the infrared reflection film.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electrical resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com