Method for improving pre-oxidation speed of polyacrylonitrile fiber through physical blending
A technology of polyacrylonitrile fiber and physical blending, applied in the direction of fiber chemical characteristics, synthetic polymer artificial filament chemical post-treatment, melt spinning method, etc., to achieve the effect of eliminating environmental pollution, reducing production cost, and less micropores
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
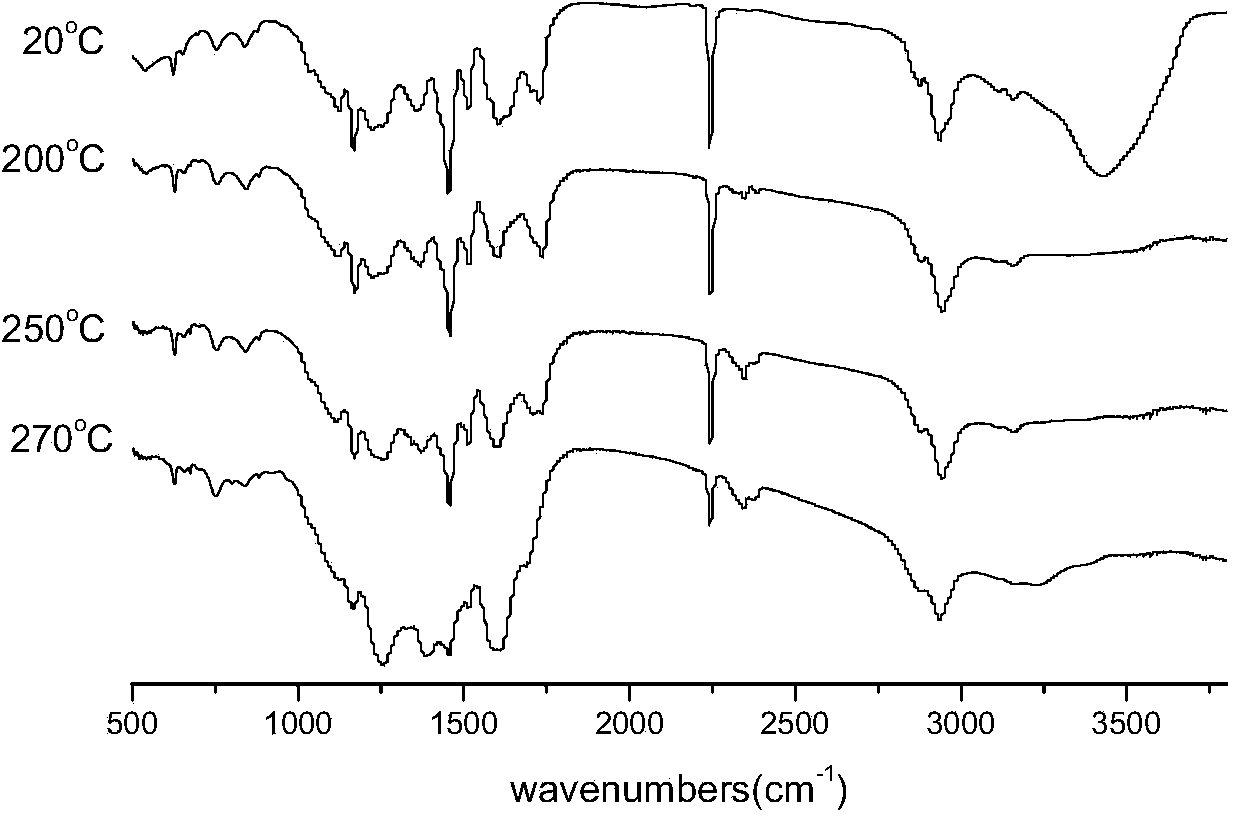
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Mix the lignin, polyacrylonitrile powder and plasticizer vacuum-dried at 60°C for 24 hours in a high-speed rotary mixer with a mass ratio of 0:40:60, and then add the mixture to the twin-screw spinning machine In a closed hopper, blend and melt at 140-220°C to obtain a homogeneously mixed blend melt; pass the thin flow of the blend melt flowing out of the spinneret through the spinning assembly through the hot air at 30°C Shaped, wound at a winding speed of 200m / min to obtain melt-spun fibers; the above-mentioned fibers were further drawn in a water bath, the temperature of the water bath was 60°C, and the total draw ratio was 3 times to obtain a melt-spun fiber with a strength of 4.63cN / dtex. spinning fibers. A new type of polyacrylonitrile precursor is pre-oxidized by passing air into a tube furnace, and the air flow rate is 5L min -1 , the pre-oxidation temperature is controlled in five temperature zones (170, 200, 220, 240, 260° C.), and the pre-oxidation 54min to ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Mix the lignin, polyacrylonitrile powder and plasticizer vacuum-dried at 60°C for 24 hours in a high-speed rotary mixer at a mass ratio of 10:30:60, and then add the mixture to the twin-screw spinning machine In a closed hopper, blend and melt at 140-220°C to obtain a homogeneously mixed blend melt; pass the thin flow of the blend melt flowing out of the spinneret through the spinning assembly through the hot air at 30°C Shaped, wound at a winding speed of 200m / min to obtain melt-spun fibers; the above-mentioned fibers were further drawn in a water bath, the temperature of the water bath was 60°C, and the total draw ratio was 3 times to obtain a melt-spun fiber with a strength of 4.43cN / dtex. spinning fibers. A new type of polyacrylonitrile precursor is pre-oxidized by passing air into a tube furnace, and the air flow rate is 5L min -1 , the pre-oxidation temperature is controlled in five temperature zones (170, 200, 220, 240, 260°C), and the pre-oxidized yarn with a r...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Mix the lignin, polyacrylonitrile powder and plasticizer vacuum-dried at 60°C for 24 hours in a high-speed rotary mixer at a mass ratio of 15:25:60, and then add the mixture to the twin-screw spinning machine In a closed hopper, blend and melt at 140-220°C to obtain a homogeneously mixed blend melt; pass the thin flow of the blend melt flowing out of the spinneret through the spinning assembly through the hot air at 30°C Shaped, wound at a winding speed of 200m / min to obtain melt-spun fibers; the above-mentioned fibers were further drawn in a water bath, the temperature of the water bath was 60°C, and the total draw ratio was 3 times to obtain a melt-spun fiber with a strength of 5.16cN / dtex. spinning fibers. A new type of polyacrylonitrile precursor is pre-oxidized by passing air into a tube furnace, and the air flow rate is 5L min -1 , the pre-oxidation temperature is controlled in five temperature zones (180, 200, 230, 250, 280°C), and the pre-oxidized yarn with a r...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com