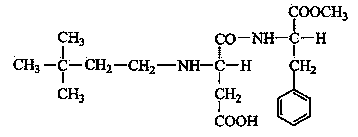Synthetic method of neotame
A synthetic method, neotame technology, applied in the field of food additives, achieves the effect of low cost, simple experimental steps, and beneficial to industrial production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] N-α-L-aspartame-L-phenylalanine 1-methyl ester 45 g, 3,3-dimethylbutyraldehyde 15 g, absolute ethanol 200 g, 5% Pd / C (based on Wet basis) 0.2 g was added to a 500 ml autoclave, sealed, tested for leaks with hydrogen gas, and replaced three times; hydrogen gas was passed to 0.7 Mpa, stirring and heating were started; during the hydrogenation process, the temperature was controlled at 35~40 °C, and the pressure was controlled at 0.4~ 0.7 MPa. The reaction consumes hydrogen faster in the early stage and slower in the later stage. After the reaction basically does not consume hydrogen, the reaction is carried out with heat preservation and pressure for 6 hours to ensure complete reaction.
[0032] The reaction solution was taken out, filtered with suction, and the catalyst was recovered; the reaction solution was concentrated by a rotary evaporator until it became viscous. Add 30 g of absolute ethanol to the above concentrate, stir in a water bath at 40°C until dissolved, ...
Embodiment 2
[0035] 43.5 g of N-α-L-aspartame-L-phenylalanine 1-methyl ester, 14.5 g of 3,3-dimethylbutyraldehyde, 190 g of absolute ethanol, 5% Pd / C (based on Wet basis) 0.2 g was added to a 500 ml autoclave, sealed, tested for leaks with hydrogen gas, and replaced three times; hydrogen gas was passed to 0.7 Mpa, stirring and heating were started; during the hydrogenation process, the temperature was controlled at 35~40 °C, and the pressure was controlled at 0.4~ 0.7 MPa. The reaction consumes hydrogen faster in the early stage and slower in the later stage. After the reaction basically does not consume hydrogen, the reaction is carried out with heat preservation and pressure for 6 hours to ensure complete reaction.
[0036] The reaction solution was taken out, filtered with suction, and the catalyst was recovered; the reaction solution was concentrated by a rotary evaporator until it became viscous. Add 27 g of absolute ethanol to the above concentrate, stir in a water bath at 40°C unti...
Embodiment 3
[0039] N-α-L-aspartame-L-phenylalanine 1-methyl ester 90 g, 3,3-dimethylbutyraldehyde 34 g, absolute ethanol 450 g, 5% Pd / C (based on Wet basis) 0.6 g was added to a 1 L autoclave, sealed, tested for leaks with hydrogen, and replaced three times; hydrogen was passed to 0.7 Mpa, stirring and heating were started; during the hydrogenation process, the temperature was controlled at 35~40°C, and the pressure was controlled at 0.4~ 0.7 MPa. The reaction consumes hydrogen faster in the early stage, and slower in the later stage. After the reaction basically does not consume hydrogen, the reaction is carried out under heat preservation and pressure for 6 hours to ensure complete reaction.
[0040] The reaction solution was taken out, filtered with suction, and the catalyst was recovered; the reaction solution was concentrated by a rotary evaporator until it became viscous. Add 65 g of absolute ethanol to the above concentrate, stir in a water bath at 40°C until dissolved, add 305 g ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com