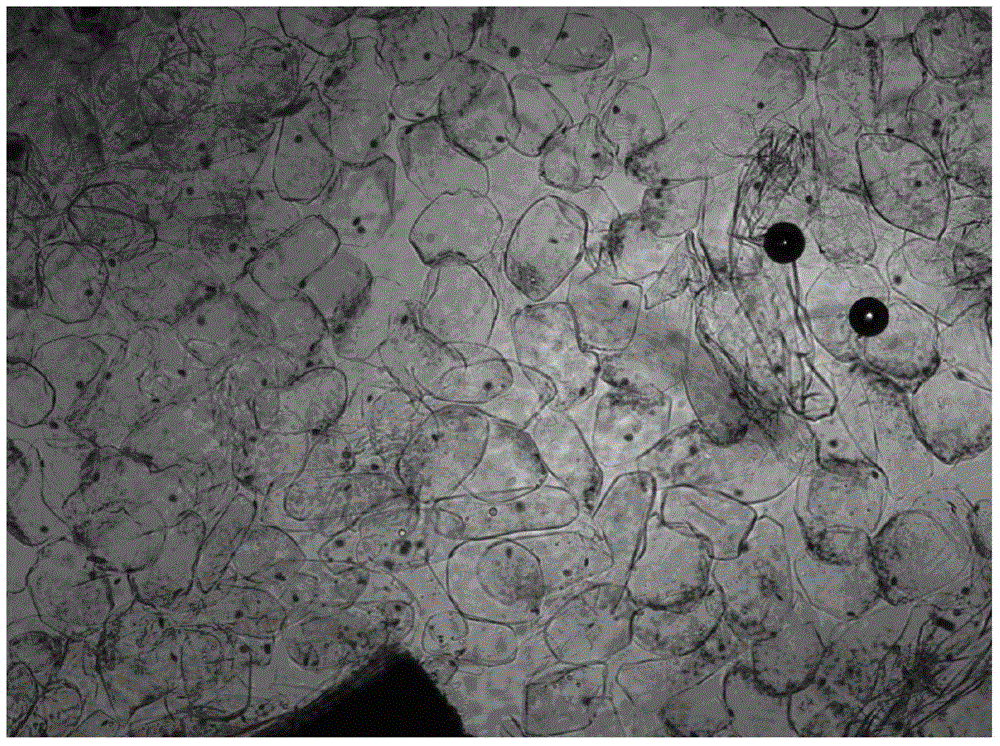
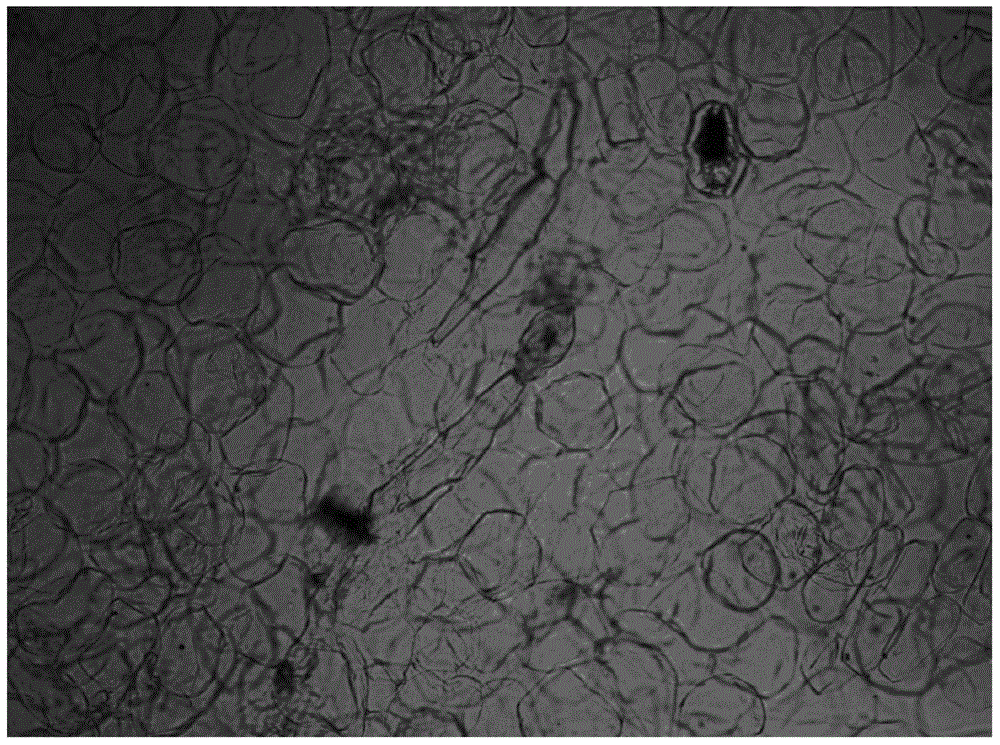
Rapid mycorrhization method of orchid aseptic seedlings
A sterile seedling and mycorrhizal technology, applied in the agricultural field, can solve the problems of death, slow growth of plants, entanglement of plants, etc., and achieve the effects of high infection rate, high quality of seedling growth and fast effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Example 1 Isolation and identification of orchid mycorrhizal fungi:
[0021] 1. Separation of root materials: Take the potted Chunlan from Shanghai Academy of Agricultural Sciences and move it to a shaded greenhouse for later use.
[0022] 2. Separation and identification medium:
[0023] Use malt extract medium (MEA), the formula is: malt extract 20g, tryptone 1g, glucose 20g, agar 20g, distilled water to 1000ml, then autoclave at 121°C for 20 minutes, cool to 60 When the temperature is below 0.03 g streptomycin is added.
[0024] 3. Separation and morphological identification methods:
[0025] Isolation of mycorrhizal fungal strains: take several sections of roots of fresh and healthy orchid plants, rinse them under tap water until there is no sludge on the surface of the roots. Cut the roots into several small sections about 10cm long, wash them three times with sterile water, soak the filter paper in 75% alcohol for 60s, then immerse in 2% sodium hypochlorite for...
Embodiment 2
[0040] 1. Orchid tissue culture seedling materials: collect tissue culture seedlings of orchid "Red Beauty", the selected tissue culture seedlings are basically the same, with a fresh weight of about 0.6g and a plant height of about 8cm.
[0041] 2. Cultivation substrate:
[0042] Select fully sterilized and dried peat: yellow sand mixed in a certain proportion as the cultivation substrate, the specific formula is peat: yellow sand 1:2, pour MMN liquid medium, 500mL / 1500g cultivation substrate, mix evenly and pack to 640mL cultivation flat, after autoclaving, cool to room temperature. Under aseptic conditions, 3 orchid seedlings were transplanted in each bottle, and 6 bottles of orchid seedlings were inoculated in each treatment as a repetition, and placed in the tissue culture room for sterile culture. After one week of growth, check for contamination, and inoculate the strains to be tested in non-polluted tissue culture bottles, that is, place a 0.5 cm diameter bacterial ca...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Materials for orchid tissue culture seedlings: The tissue culture seedlings of the orchid "Red Beauty" were collected, and the selected tissue culture seedlings were basically the same, with a fresh weight of about 0.9g and a plant height of about 10cm. The test is provided with 2 kinds of inoculation conditions, one adopts the method of the present invention, that is, the cultivation substrate and the inoculation treatment method are the same as the implementation case 3; the other uses DE medium (prescription: 10 grams of glucose, 5 grams of tryptone, dihydrogen phosphate Potassium 1 g, magnesium sulfate 0.5 g, Bengal red 0.033 g, agar 20 g, distilled water to 1000 ml, adjust the pH value to 5.0, then autoclave at 121°C for 20 minutes, cool down to below 60°C and pour the plates for use ), the inoculation method is similar to the method of the present invention. In this case, the strain LH53 was inoculated, and the seedling growth and infection were counted after 80 d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com