Method for recovering palladium from waste palladium/alumina catalyst
A waste catalyst and alumina technology, which is applied in the field of palladium recovery, can solve problems such as complicated operation, and achieve the effects of simplifying the refining process, high recovery rate, and simplified process flow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
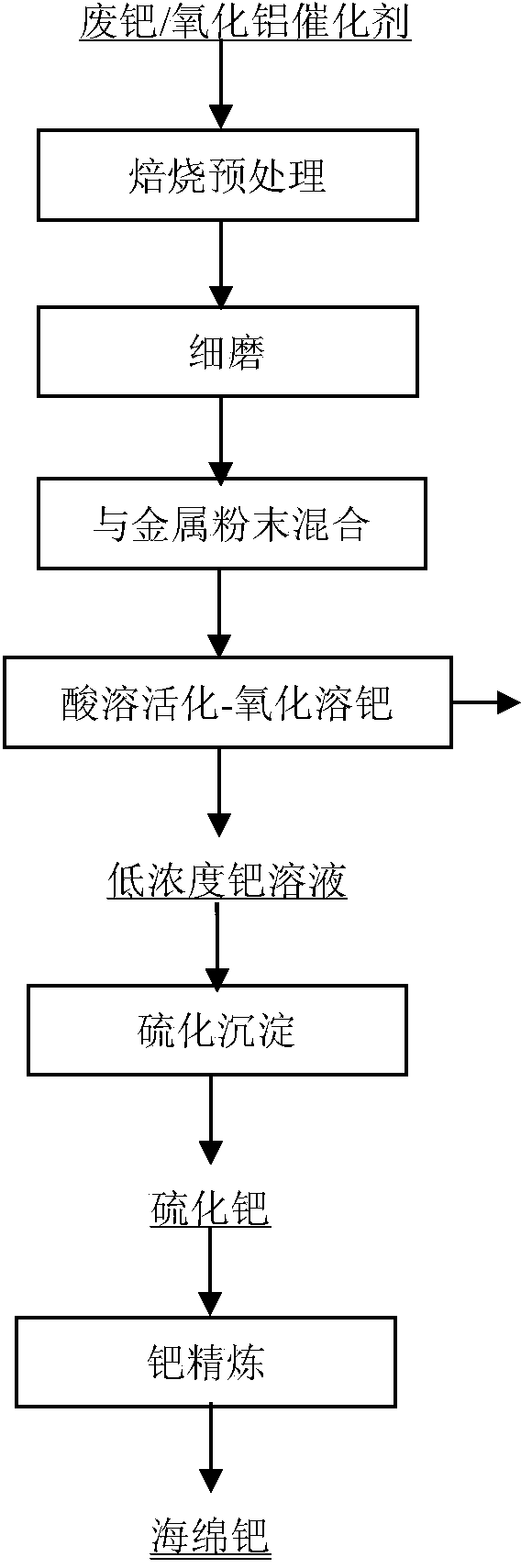
[0015] In Example 1, the spent palladium / alumina catalyst was roasted at 600°C for 1h, after cooling, it was finely ground to a particle size of -0.125mm, and 1000g of the finely ground material was weighed and mixed with 100g of iron powder, and added to the mass at a liquid-solid ratio of 5:1 In a sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of 30%, dissolve at a constant temperature of 80℃ for 2 hours; continue to slowly add sodium chlorate to the dissolution system to dissolve for 4 hours, after solid-liquid separation, a low-concentration palladium-containing solution is obtained; add to the low-concentration palladium-containing solution Sodium sulfide was stirred at a constant temperature of 80°C for 2 hours to completely precipitate palladium to obtain palladium sulfide. After solid-liquid separation, palladium sulfide was dissolved, separated, and refined to obtain sponge palladium with a purity of 99.95%. The recovery rate was 98.44%.
Embodiment 2
[0016] In Example 2, the spent palladium / alumina catalyst was roasted at 500°C for 2h. After cooling, it was finely ground to a particle size of -0.125mm. Weighed 1000g of finely ground material and mixed with 100g of aluminum powder, and added it to the mass at a liquid-solid ratio of 5:1 In a sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of 40%, stir and dissolve at a constant temperature of 80°C for 2h; continue to slowly pour chlorine into the dissolution system to dissolve for 2h, after solid-liquid separation, a low-concentration palladium-containing solution is obtained; add sulfur to the low-concentration palladium-containing solution Sodium was stirred at a constant temperature of 80°C for 2 hours to completely precipitate palladium to obtain palladium sulfide. After solid-liquid separation, palladium sulfide was purified by dissolving, separating, and refining to obtain sponge palladium with a purity of 99.95%, and the recovery rate was 98.56%.
Embodiment 3
[0017] Example 3, calcining the spent palladium / alumina catalyst at 500°C for 2h, after cooling, finely grind to a particle size of -0.125mm, weigh 1000g of finely ground material and mix with 100g of zinc powder, and add to the mass according to the liquid-solid ratio of 5:1 In a sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of 30%, stir and dissolve at 70°C for 3 hours; continue to slowly pass chlorine gas into the dissolution system to dissolve for 2 hours, after solid-liquid separation, a low-concentration palladium-containing solution is obtained; pass into the low-concentration palladium-containing solution Hydrogen sulfide gas was stirred at a constant temperature of 80°C for 2 hours to completely precipitate palladium to obtain palladium sulfide. After solid-liquid separation, palladium sulfide was dissolved, separated, and refined to obtain sponge palladium with a purity of 99.95%. The recovery rate was 98.32%. .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com