Method for repairing metabolic defects of ketogulonigenium sp. cofactors and improving 2-KGA (2-keto-L- gulonic acid) producing capacity
A technology for cofactor and production capacity of uric acid bacteria, which is applied in the field of microbial fermentation to achieve the effects of improving electron transfer efficiency, increasing yield and improving bacterial growth.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
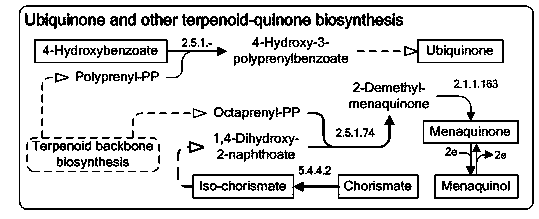
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
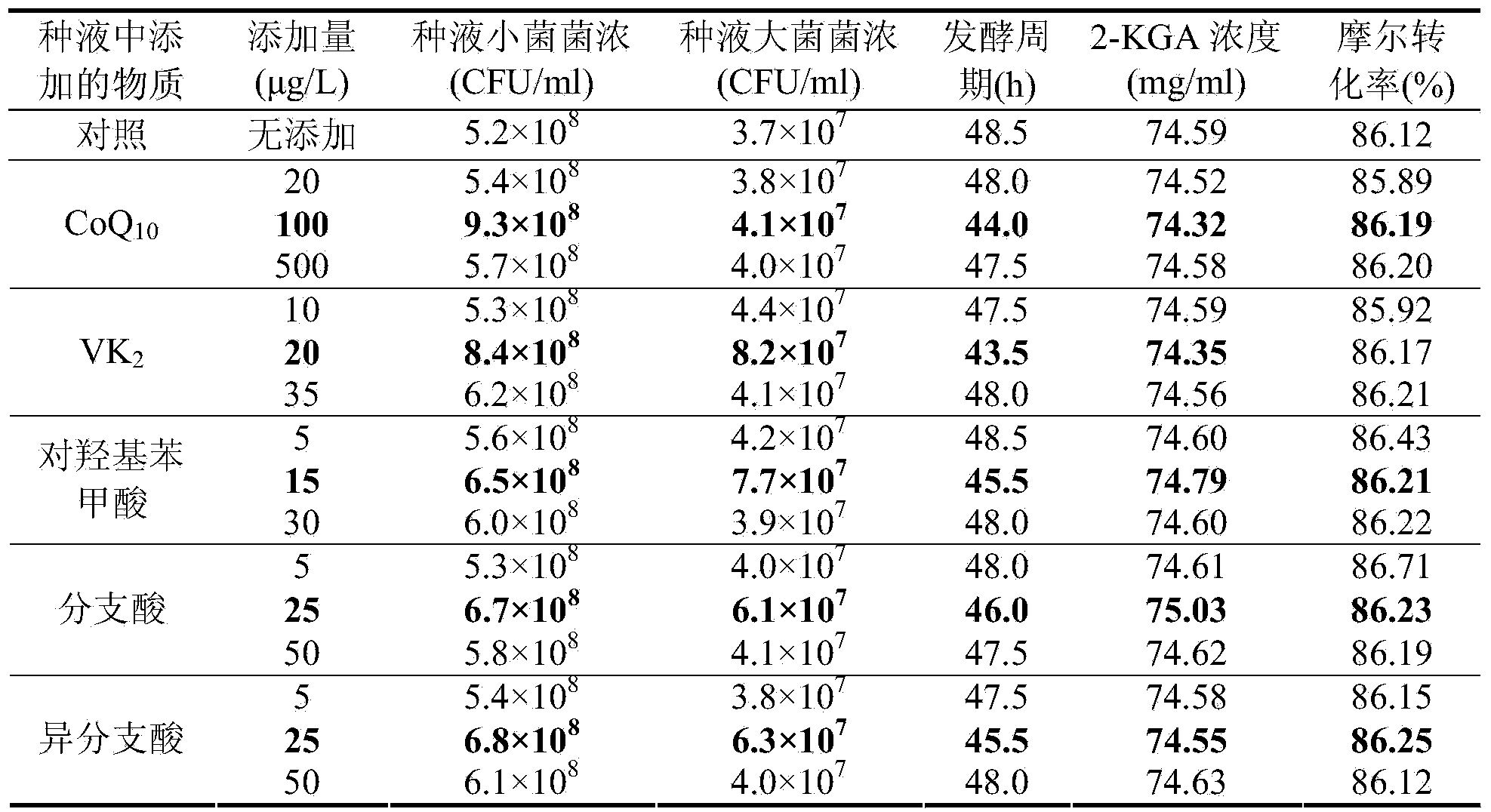
[0040] Implementation Example 1: Investigating the Effect of Adding Small Bacterial Metabolism Deficient Substances on the Production Capacity of 2-KGA in the Seed Solution under Single Factor Conditions
[0041] Conventional seed medium is: 2% L-sorbose, 0.5% corn steep liquor, 0.2% glucose, 0.1% urea, 0.2% calcium carbonate, pH6.7-7.0.
[0042] The conventional fermentation medium is: 8% L-sorbose, 1.5% corn steep liquor, 0.1% potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.1% urea, 0.01% magnesium sulfate, 0.5% calcium carbonate, pH6.7-7.0.
[0043] Culture conditions: the slant of the mixed bacteria culture is inoculated in the conventional seed liquid medium, 30°C, 220 rpm, shake flask culture for 20 hours to make the seed liquid, 10% is inoculated into the conventional fermentation culture with different metabolic defective substances of small bacteria added medium, 30°C, 220 rpm, shake flask culture until the substrate L-sorbose is less than 1mg / L and the fermentation ends.
[0044]...
Embodiment 2
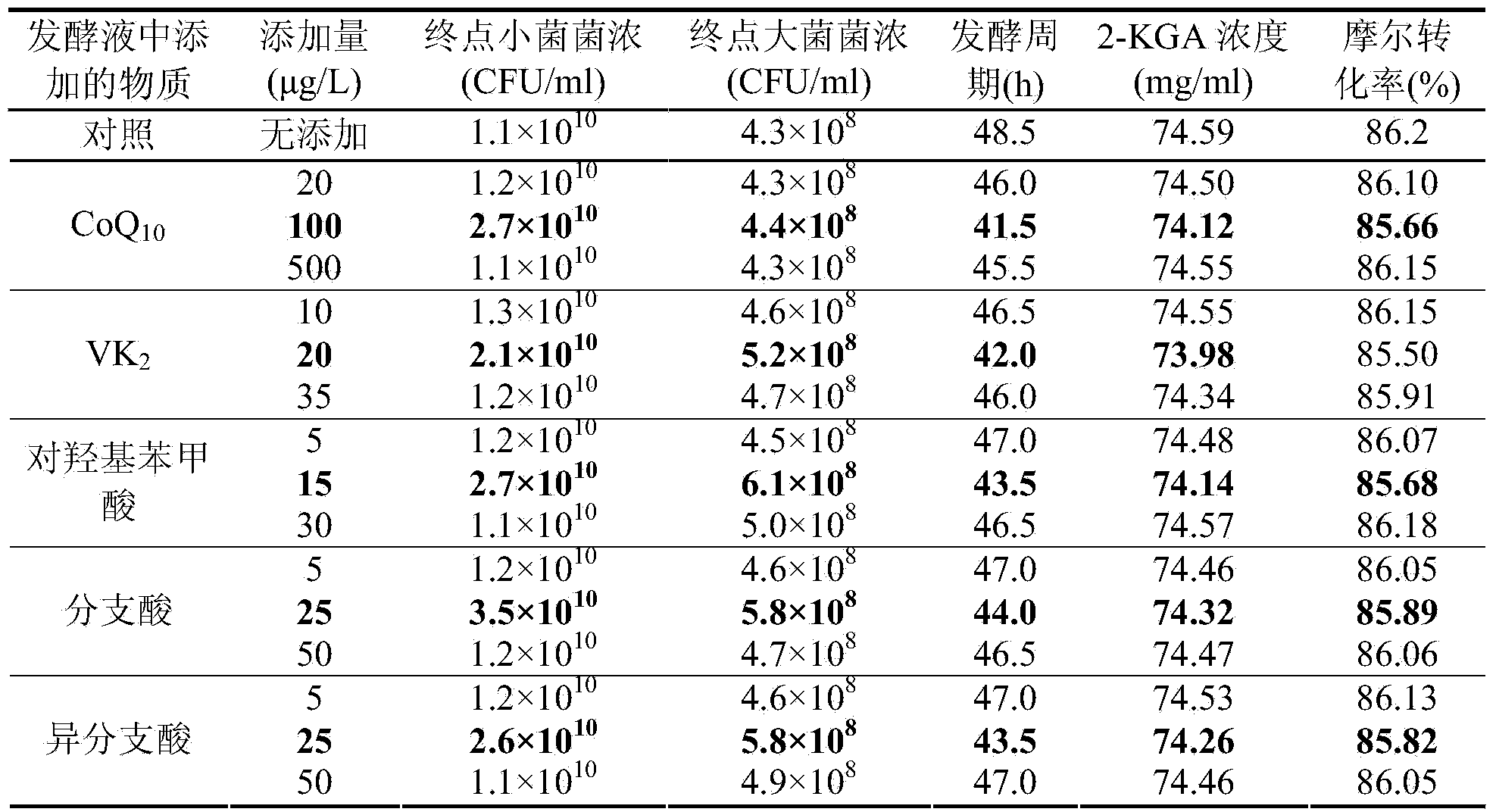
[0049] Implementation Example 2: Investigating the Effect of Adding Small Bacterial Metabolism Deficient Substances on the Production Capacity of 2-KGA in Conventional Fermentation Liquid under Single Factor Conditions
[0050] The concentrations of the microbacterial metabolic defect substances added respectively in the conventional fermentation medium are shown in Table 2.
[0051] Conventional seed medium: see Example 1.
[0052] Conventional fermentation medium is: referring to example 1.
[0053] Culture conditions: see Example 1. The experimental results are shown in Table 2.
[0054] Table 2. The effect of adding microbacterial metabolic defect substances in the fermentation broth on fermentation under single factor conditions.
[0055]
[0056] [Note] The bold font is the effect of the optimum concentration of active substances on fermentation.
[0057] It can be seen from Table 2 that the above-mentioned 5 bacterial metabolic defect substances all promoted the g...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Implementation Example 3: The effect of adding the optimized small bacterial metabolic defect substance combination to the seed liquid or fermentation liquid on the ability to produce 2-KGA
[0059] Conventional seed medium: see Example 1.
[0060] Conventional fermentation medium is: referring to example 1.
[0061] Culture conditions: see Example 1.
[0062] The orthogonal analysis method was used to add different combinations of metabolic defect substances to the seed solution, and the fermentation period of the fermentation broth was used as the result to investigate the effect of adding different combinations of active substances in the seed solution on the final fermentation cycle. The experimental results are shown in Table 3.
[0063] Table 3.L 16 The results of (4^5)4-level 5-factor orthogonal analysis.
[0064]
[0065] [Note] The bold font is the effect of the optimum concentration of active substances on fermentation.
[0066] As can be seen from Tabl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com