A Strain of Staphylococcus Pasteur with Acetic Acid Degradation Ability and Its Application
A Staphylococcus, Pasteur's technology, applied in the direction of bacteria, microorganism-based methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of disguised phase transfer, no real removal of acetic acid, purification of acidic metabolites, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Example 1: Staphylococcus pasteuri Isolation, purification and identification of LWX.
[0020] 1. Staphylococcus pasteuri Isolation and purification of LWX.
[0021] After aerating the sludge of a certain urban sewage treatment plant with air for three days, take 50mL supernatant for centrifugation, place the activated sludge at the bottom in an inorganic salt medium containing only acetic acid for acclimatization and cultivation, and the concentration of acetic acid is from low to high ( 50~200mg / L), make acetic acid as the main carbon source for growth, and let it gradually adapt to the acidic environment. After domestication for about a month, measure the amount of acetate ions and total organic carbon in the water at regular intervals to determine whether the bacteria can degrade acetic acid. When the concentration of acetic acid drops obviously, take out 200mL of the mixed solution and spread it on the solid inorganic salt medium containing only acetic acid, a...
Embodiment 2
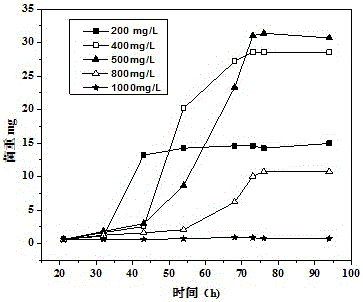
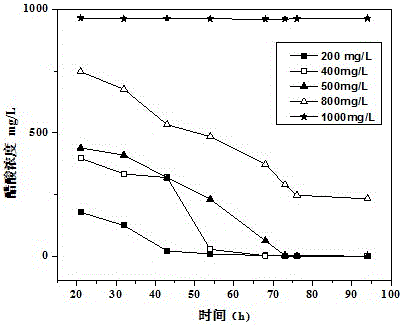
[0025] Example 2: Degradation curves of bacterial strain LWX to different concentrations of acetic acid.
[0026] The degradation of different concentrations of acetic acid by the bacterial strain LWX was investigated. The main steps were as follows: acetic acid with an initial concentration of 200, 400, 500, 800, and 1000 mg / L was added as the only carbon source in the sterilized inorganic salt medium, After the same amount of strain LWX was inoculated, the culture was sealed and shaken, and the temperature was set at 30°C. The concentration of acetic acid and the biomass of strains were detected at regular intervals.
[0027] The result is as figure 2 shown. Under the condition of 30℃, the degradation rates of strain LWX to the initial concentration of 200, 400, 500, 800 and 1000 mg / L acetic acid within 4 days were 100%, 100%, 100%, 45.94%, 0%, respectively. The strain LWX can basically degrade the low concentration of acetic acid (below 500mg / L), but the degradation eff...
Embodiment 3
[0028] Example 3: Carbon balance analysis and pH changes during degradation of acetic acid by strain LWX.
[0029] Strains analyzed Staphylococcus pasteuri Carbon balance of LWX to initial acetic acid concentration 200-1000 mg / L. The results showed that the strain LWX could convert acetic acid to CO 2 、H 2 O and cell biomass, when the concentration of acetic acid is <800mg / L, the average mineralization rate is about 70-80%, and the productivity coefficient is 0.210-0.279 mg cells / mg acetic acid. When the initial concentration of acetic acid is 200-500mg / L, the pH of the culture system tends to be neutral after the degradation is complete. The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0030] Add acetic acid as the sole carbon source to the sterilized inorganic salt medium, set the initial concentration to 200, 400, 500, 800, and 1000 mg / L, and inoculate the same amount of strains Staphylococcus pasteuri After LWX, seal and shake culture, and set the temperature at ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com