Amidase, coding gene and applications thereof
An amidase and gene technology, which is applied to amidase and its encoding gene and application fields, can solve the problems of low amidase yield, reduced product purity, inability of amidase to effectively hydrolyze macromolecular aromatic amide compounds, etc. The effect of stereoselectivity and high catalytic activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
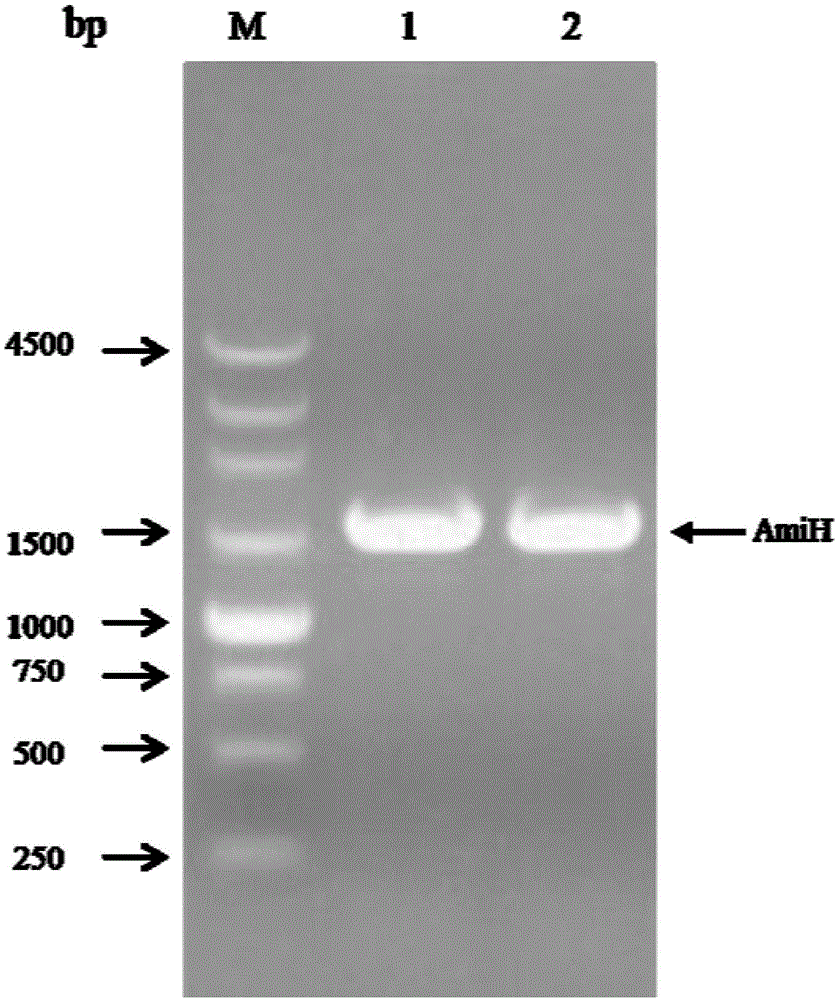
[0038] 1. Cloning the AmiH gene from the genome of Klebsiella oxytoca KCTC 1686 (Klebsiella oxytoca KCTC 1686).
[0039] Primers AmiH-F and AmiH-R were designed according to the genomic DNA sequence of Klebsiella oxytoca KCTC 1686 (GenBank accession number: CP003218.1).
[0040] AmiH-F sequence: 5'-CCG GAATTCATGGCTATTCAACGTCCCACTG-3'
[0041] AmiH-R sequence: 5'-TTCCC AAGCTT GTTAAAACGTCCGCCAGTCAC-3'
[0042] Restriction sites EcoRI and HindIII (underlined) were added to the upstream and downstream primers, respectively. Klebsiella oxytoca KCTC 1686 genomic DNA was used as a template, and AmiH-F and AmiH-R were used as primers for PCR amplification. The PCR reaction system and reaction conditions were as follows:
[0043] PCR amplification system:
[0044]
[0045] PCR amplification conditions:
[0046] 1) Pre-denaturation: 95°C for 5 minutes;
[0047] 2) Denaturation: 98°C for 10s; Annealing: 55°C for 15s; Extension: 72°C for 60s; a total of 30 cycles;
[0048] 3)...
Embodiment 2
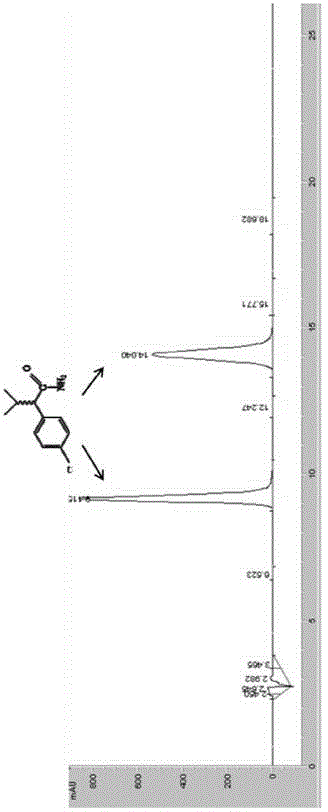
[0058] Embodiment 2 amidase hydrolysis butanamide
[0059] Get 50mL of the engineering bacteria E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET-30a(+)-AmiH fermentation broth in Example 1, centrifuge at 10000 rpm to collect the thalline, then resuspend with 50mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) buffer Bacteria cells, that is, the resting cell suspension of engineering bacteria E.coliBL21(DE3) / pET-30a(+)-AmiH. The control cell load was 3g stem cells / L. Butanamide was added to the resuspension to a final concentration of 20 mM, and the catalytic reaction was carried out at 35° C. for 2 hours. Then detect the content of butanamide and butyric acid in the reaction system by gas chromatography. As a result, it was found that there was no butanamide in the reaction system, and all of them were converted into butyric acid.
Embodiment 3
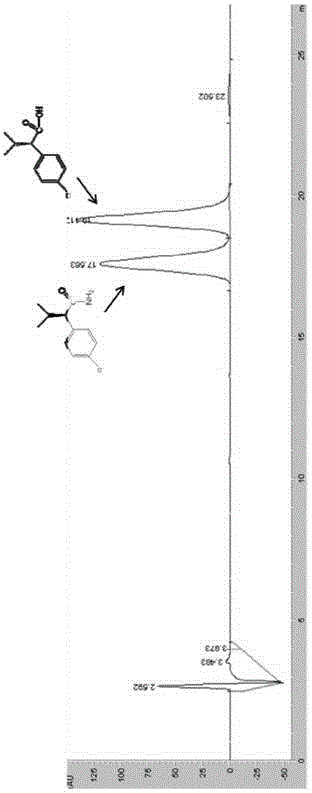
[0060] Embodiment 3 amidase hydrolysis caproamide
[0061] Get 50mL of the engineering bacteria E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET-30a(+)-AmiH fermentation broth in Example 1, centrifuge at 10000rpm to collect the thalline, then resuspend the bacteria with a buffer of 50mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) Somatic cells, that is, the resting cell suspension of engineering bacteria E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET-30a(+)-AmiH. The control cell load was 3g stem cells / L. Hexanamide was added to the resuspension to a final concentration of 30 mM, and the catalytic reaction was carried out at 30° C. for 2 hours. Then gas chromatography was used to detect the contents of caproamide and caproic acid in the reaction system. As a result, it was found that there was no caproamide remaining in the reaction system, and all of them were converted into caproic acid.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-denatured | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Extend | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com