Water treatment method for cyclic purification of shrimp breeding wastewater
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0012] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
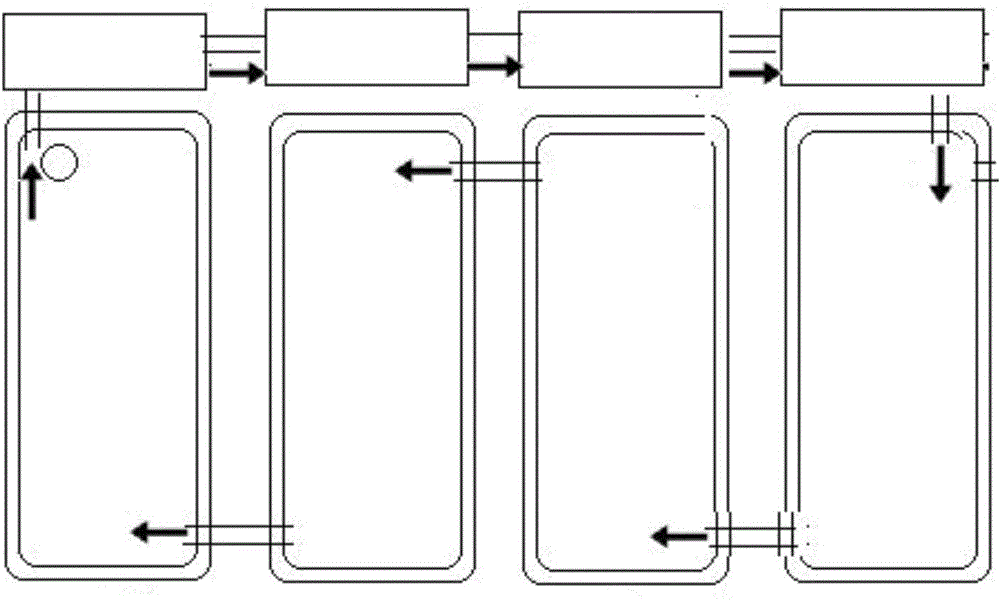
[0013] refer to figure 1 , a kind of prawn culture waste water circulation purification water treatment method, comprise the microbial pre-purification of prawn culture pond and the purification system connected successively by water pipe and prawn culture pond, described purification system comprises recoil type physical filter pond, settling pond, plant Filter tank, biological purification tank, water pump, water storage buffer tank, ozone / ultraviolet sterilizing, oxygenation, temperature-adjusted water quality optimization pool, the drain of the breeding tank is connected to the recoil physical filter tank, sedimentation tank, and reaction tank in turn through the flow channel. Flushing activated carbon filter tank, plant filter tank, recoil type biological purification tank, water storage buffer tank, ozone / ultraviolet sterilizing, aeration, temperature-a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com