Regenerated cellulose nano-particles and preparation method thereof
A technology of nanoparticles and cellulose, which is applied in the field of regenerated cellulose nanoparticles and its preparation, can solve problems such as poor compatibility, difficulty in uniform mixing, and weak interfacial interaction, and achieve low cost, green environmental protection, and heat protection The effect of decomposition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
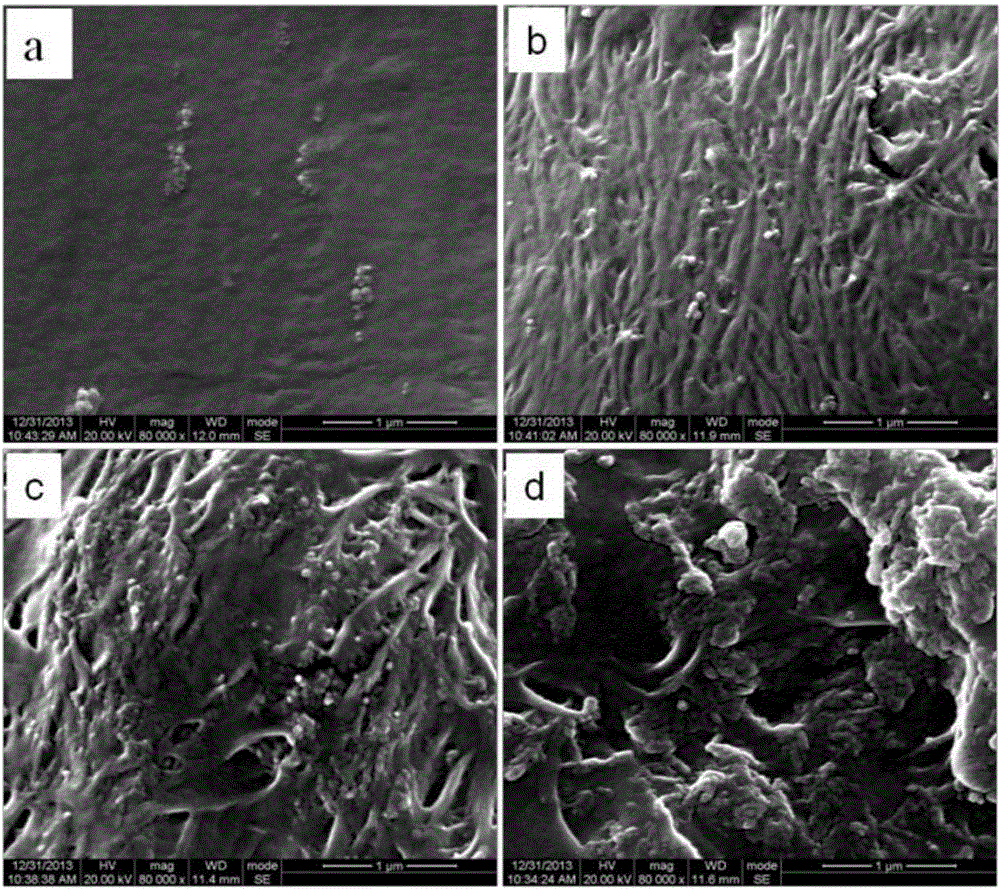
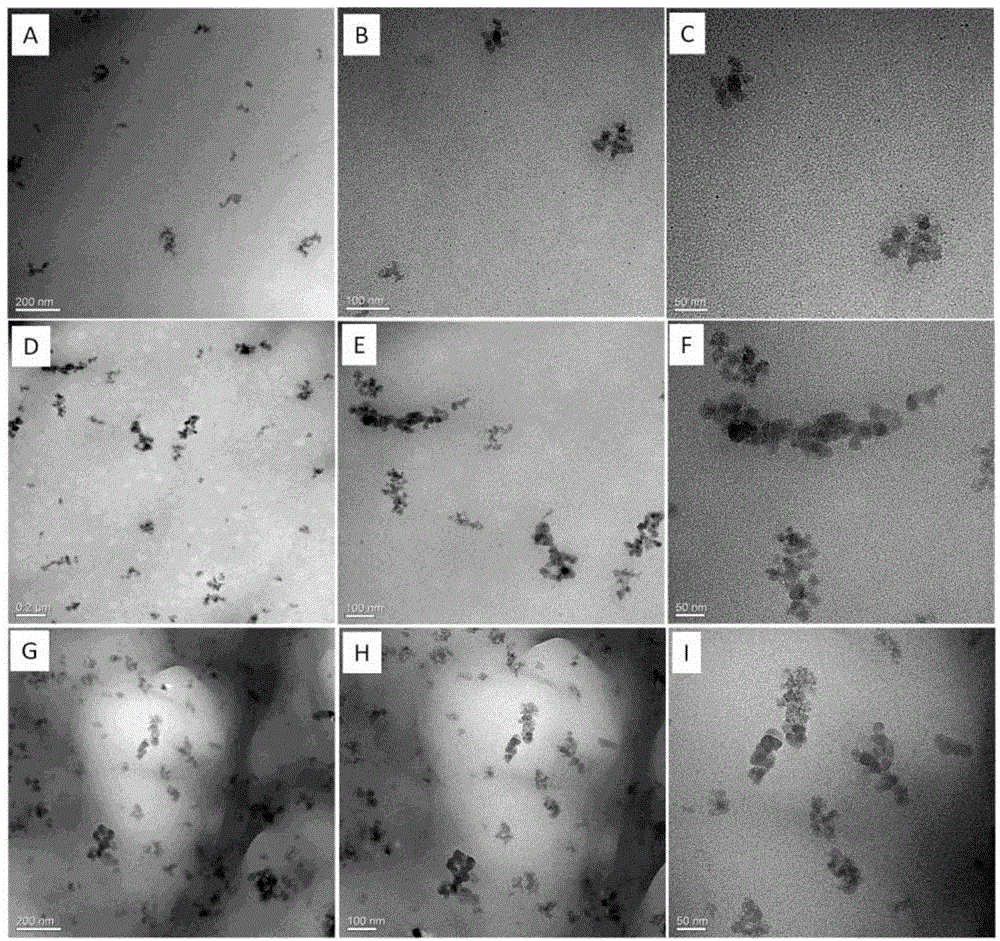
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~22
[0040] (1) Prepare cellulose solution: prepare 200g of sodium hydroxide / urea aqueous solution, wherein the mass fraction of sodium hydroxide and urea can be 5-10% and 7-15%, and place it in a low-temperature test chamber to pre-cool to 0-15%. -15°C, add an appropriate amount of cellulose, stir rapidly for 1 to 5 minutes, and prepare cellulose solutions with mass fractions of 1%, 2.5%, and 5%;
[0041] (2) Preparation of cellulose hydrogel: pour the obtained cellulose solution into a glass dish, and heat-treat in an oven at 60-80°C for 36-60 hours. After the cellulose solution is completely gelled, soak it in distilled water to remove sodium hydroxide and urea;
[0042] (3) Preparation of PEO aqueous solution: Weigh an appropriate amount of PEO and distilled water respectively, mix and stir to obtain a uniform and transparent PEO aqueous solution;
[0043] (4) Soak cellulose gel in PEO solution: Use a high-speed pulverizer and a 40-100-mesh copper screen to refine the cellulos...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com