Mutant nucleic acid, expression vector, yeast strain and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of expression vectors and yeast strains, which is applied in the fields of mutated nucleic acids, expression vectors, yeast strains and their preparation and application, can solve the problems of being unable to become dominant strains of lignocellulosic ethanol, inhibiting cell fermentation performance, and inhibiting component sensitivity, etc. Achieve the effects of strong practicability, high sugar utilization rate and stable genetic performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0027] According to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the expression vector is an expression vector obtained by inserting a mutated nucleic acid whose sequence is as described above between the BamHI restriction site and the XhoI restriction site of the plasmid pAUR123. When the expression vector in the preferred embodiment of the present invention is transformed into Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells, higher expression efficiency can be obtained, so that the purpose of the present invention can be better achieved.
[0028] In addition, the present invention also provides a method for preparing highly stress-resistant yeast strains, the method comprising: using the above-mentioned expression vector of the present invention to transform yeast cells to obtain transformed yeast cells.
[0029] In the present invention, various transformation methods commonly used in the art can be used to transform yeast cells with expression vectors, for example, electroporation or ch...
Embodiment 1
[0055] Entrust Shanghai Gemma (GenePharma) company to synthesize base sequence such as the mutated nucleic acid lsm1 shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, with reference to the method in the "Molecular Cloning Experiment Guide (Third Edition)" (Sambrook J, 2001), the lsm1 It was connected between the BamHI restriction site and the XhoI restriction site of Saccharomyces cerevisiae plasmid pAUR123 to constitute the recombinant expression vector pAUR-lsm1.
Embodiment 2
[0057] (1) Pick a single colony of Saccharomyces cerevisiae RIPP-0 into YEPD medium, culture at 30°C and 180r / min until mid-logarithmic late stage (about 16h), centrifuge at 4000r / min for 5min to collect the cells, and use 4°C sterile water and Wash twice with pH 7.5, 10mM Tris-HCl buffer, add 0.6M sorbitol solution to suspend the cells, and dilute to a concentration of about 10 5 -10 6 1 cell / mL, take 0.2ml bacterial liquid, transfer the recombinant expression vector pAUR-lsm1 obtained in Example 1 into S. -0 host bacteria, add 1 mL of YEPD medium to the bacterial solution, and incubate at 30 °C for 1 h.
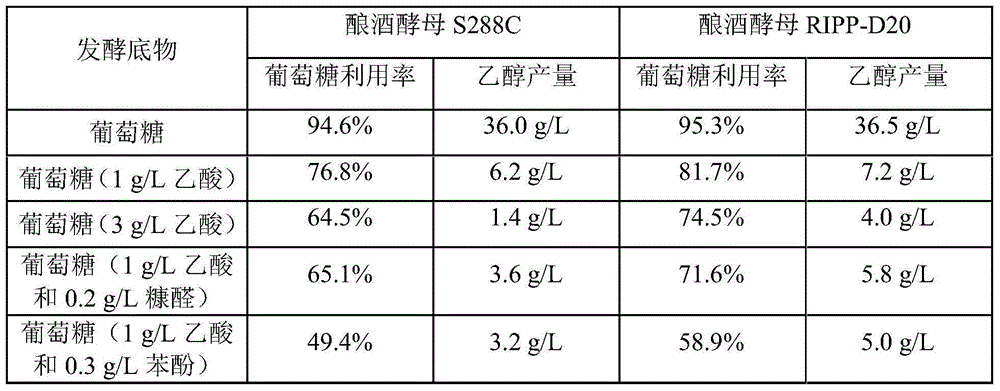
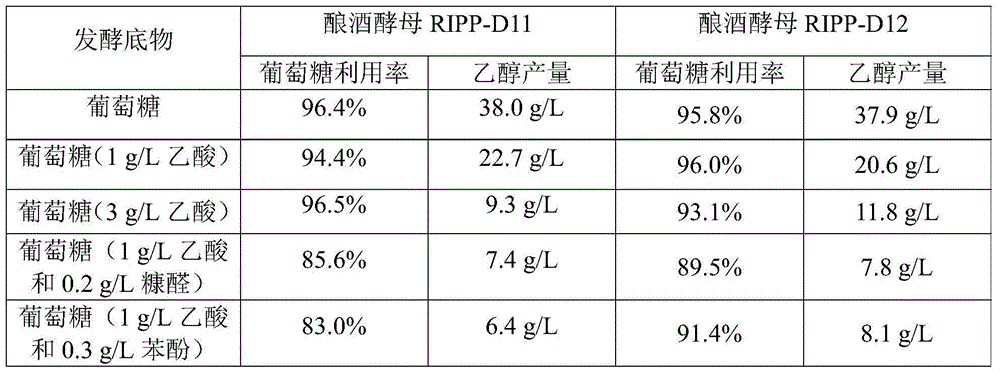
[0058] (2) Evenly spread the bacterial solution after step (1) incubation for 1 hour on the solution containing 3g / L acetic acid and 30g / L NH 4 Ac, and two composite screening plates of 3g / L acetic acid and 40g / L NaAc were cultured at 30°C for 60h to obtain 64 primary screened strains.
[0059] (3) Introduce the primary screened strains into the acidic seed medium, cultu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com