Simple and convenient chemical industry method for extracting and recovering cobalt from waste neodymium-iron-boron magnetic material
An industrial method and NdFeB technology, applied in the field of comprehensive utilization of waste resources, can solve the problems of difficulty in reflecting economic benefits, combining together, and high recovery costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Take a batch of scraps from the machining process of NdFeB permanent magnet materials. After testing, the above-mentioned metal elements in each 100g of NdFeB scrap include: 32.10g of rare earth elements (the main component is Nd, including Pr, Dy, Gd), 61.22g of Fe element content, 3.56g of cobalt element content, Al The element content is 0.43g.
[0060] Take 1000Kg of the above-mentioned batch of NdFeB waste materials, grind and pulverize them through a ball mill until the average particle size is below 200 mesh, and oxidize and roast the pulverized materials in a rotary kiln (calcination temperature 700 ° C, roasting time 1.5 hours), and then The oxidized and roasted material is leached with 4N hydrochloric acid (leaching temperature is 85°C, and the pH value of the leaching end point is controlled to be 1.0). According to the process statistics, the consumption in Yancheng is about 1.38 cubic meters.
[0061] The Yourong leachate was detected, and its main compon...
Embodiment 2
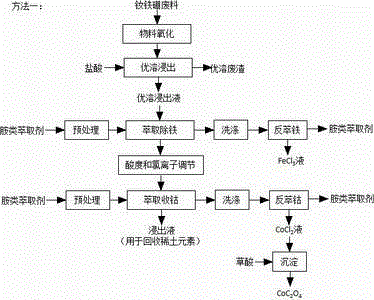
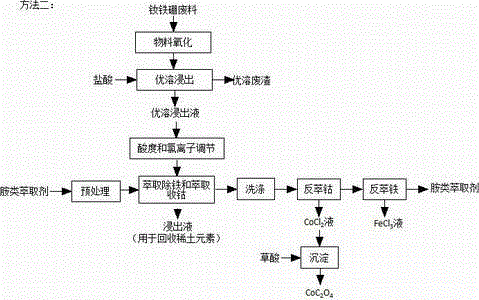
[0072] Take another part of the excellent solvent leaching solution in Example 1, and perform extraction to remove iron and extract cobalt according to method 2 (co-extraction).
[0073] Add sodium chlorate solution to the above-mentioned excellent solution leaching solution, so that the Fe in the leaching solution 2+ converted to Fe 3+ . According to the process statistics, the dosage of sodium chlorate is 3.58Kg (33.63mol); the calculation shows that the theoretical amount of sodium chlorate water required for the complete oxidation of divalent Fe elements in the above-mentioned excellent solution leachate to trivalent Fe elements is 31.73mol; The actual amount is 106% of the theoretical equivalent value.
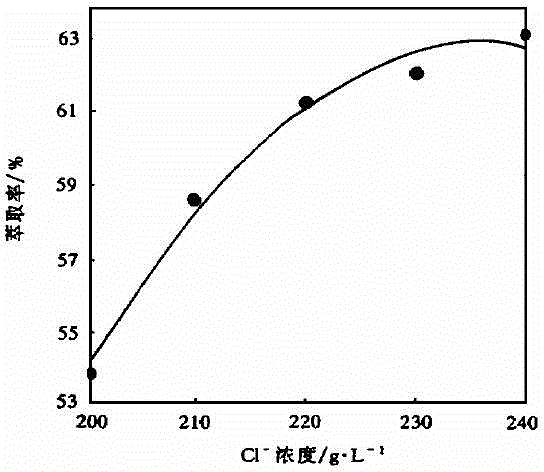
[0074] Add 30L of 4N hydrochloric acid and 130Kg of NaCl (solid) to the water phase of the leaching solution after extraction and iron removal, and after fully mixing, measure the [H + ]=0.25mol / L, [Cl - ]=236g / L.
[0075] Take the extracted solution as the water pha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com