Method for processing multi-metal alloy
A processing method and multi-metal technology, applied in the field of metallurgy and chemical industry, to achieve the effects of low equipment investment, easy promotion and less equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
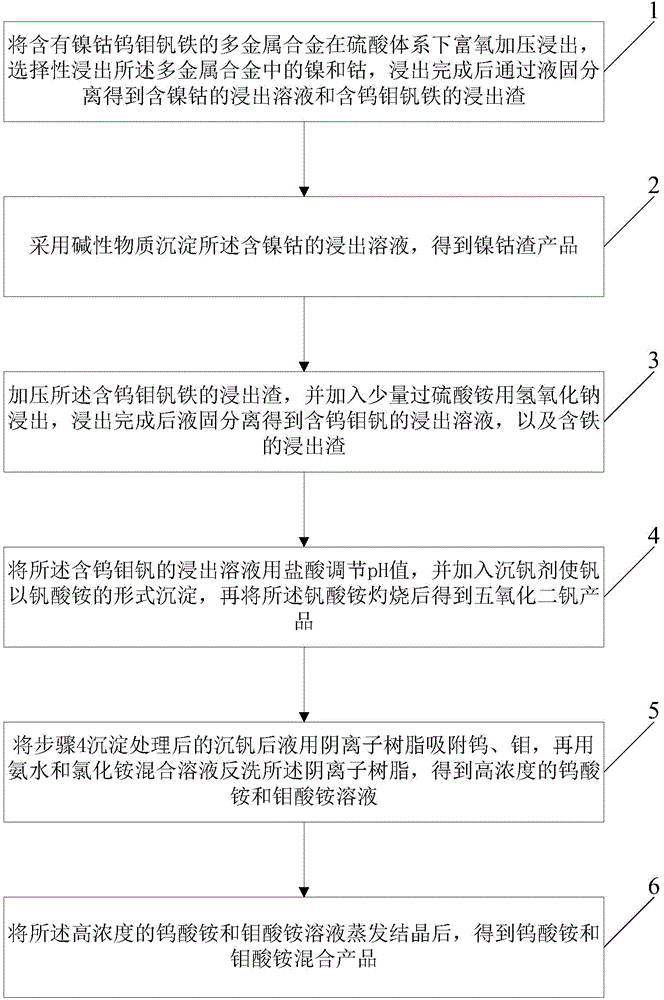
[0047] Pressure leaching: First, the multi-metal alloy containing nickel-cobalt-tungsten-molybdenum-iron-vanadium obtained by fire smelting is pressure-leached, the leaching time is 2.5 hours, the temperature is 150°C, the liquid-solid ratio is 5 / 1 (mL / g), and the total pressure is 0.8MPa , the pH of the leaching end point is 1.5, and the stirring speed is 500r / min; after the leaching is completed, the leaching solution containing nickel and cobalt and the leaching residue containing tungsten, molybdenum, vanadium and iron are obtained through liquid-solid separation. The leaching rates of nickel and cobalt in slag are 99.46% and 99.06% respectively, while tungsten, molybdenum and vanadium are not leached.
[0048] Pressure leaching residue, and alkaline leaching: leaching time 11 hours, temperature 99 ° C, liquid-solid ratio 5 / 1 (mL / g), stirring speed 500r / min. The leaching rates of tungsten, molybdenum and vanadium based on slag are 93.75%, 99.48% and 97.86%, respectively. ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Pressure leaching: firstly, the multi-metal alloy containing nickel-cobalt-tungsten-molybdenum-iron-vanadium obtained by fire smelting is subjected to pressure leaching, the leaching time is 3 hours, the temperature is 160°C, the liquid-solid ratio is 5 / 1 (mL / g), and the total pressure is 0.8 MPa, leaching end point PH1.5, stirring speed 6200r / min; after leaching, through liquid-solid separation to obtain leaching solution containing nickel and cobalt and leaching residue containing tungsten, molybdenum, vanadium and iron. The leaching rates of nickel and cobalt in slag are 97.0% and 97.66% respectively, while tungsten, molybdenum and vanadium are not leached.
[0053] Pressure leaching residue, and alkaline leaching: leaching time 12 hours, temperature 99 ° C, liquid-solid ratio 5 / 1 (mL / g), stirring speed 500r / min. The leaching rates of tungsten, molybdenum and vanadium based on slag were 95.12%, 99.58% and 98.29%, respectively.
[0054] Ammonium salt vanadium precipi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com