Method for recycling a plurality of metals from electronic wastes
A technology for electronic waste and metals, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems of serious environmental pollution, long leaching time, and low leaching rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
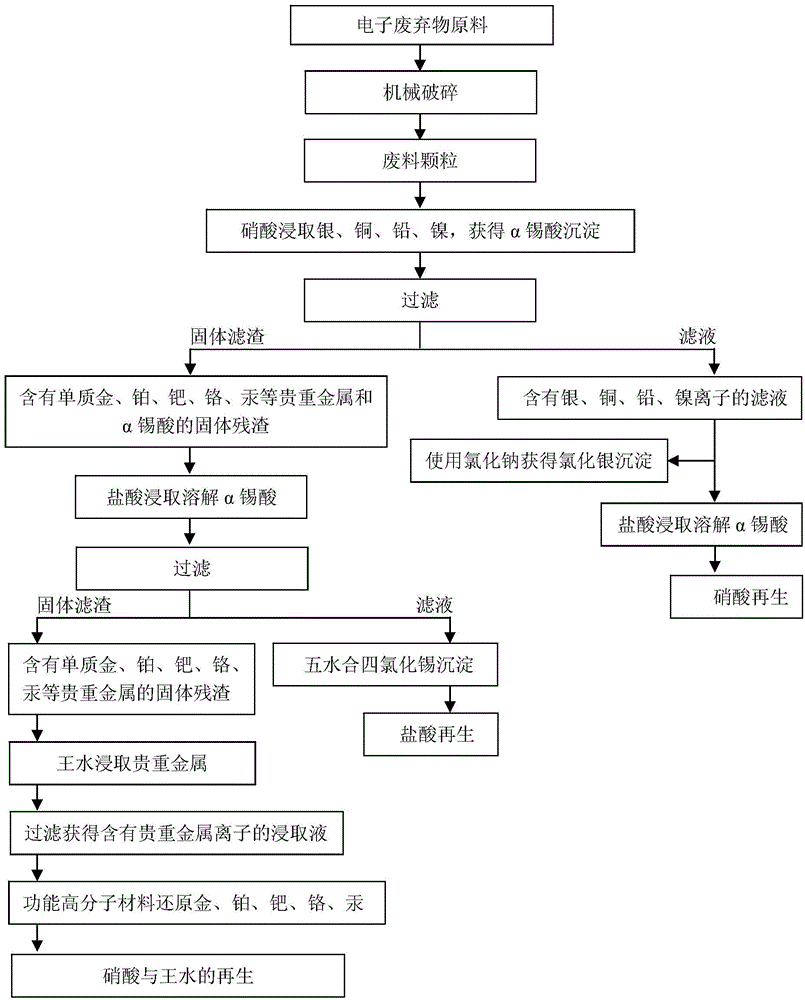
[0079] In this embodiment, the electronic waste is the circuit board of the Nokia 2100 mobile phone, and the method for recycling various metals from the electronic waste is as follows:
[0080] (1) A single discarded Nokia 2100 mobile phone circuit board, weighing 22 grams, is cut and crushed to obtain electronic waste particles with a particle size of 0.1 mm to 0.5 mm.
[0081] (2) After loading the electronic waste particles into the elution column, immerse them in an aqueous nitric acid solution with a concentration of 30% by mass at 70°C, with a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:3, so that the metal elements copper, nickel, and Lead and silver react and dissolve in nitric acid aqueous solution, and the metal tin contained therein reacts with nitric acid to form solid α-stannic acid, which is filtered and separated after leaching for 1 hour to obtain nitrate solution A and solid slag X rich in metal ions.
[0082] (3) Nitrate solution A is subjected to the following processing st...
Embodiment 2
[0104] In this embodiment, the electronic waste is a certain discarded bank IC card, and the method for recycling various metals from the electronic waste is as follows:
[0105] (1) A discarded bank IC card was sheared and crushed to obtain electronic waste particles with a particle size of 0.5 mm to 1 mm.
[0106] (2) After loading the electronic waste particles into the elution column, immerse them in an aqueous nitric acid solution with a concentration of 3% by mass at 70°C, with a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:1, so that the metal elements copper, nickel, and Lead and silver react and dissolve in nitric acid aqueous solution, and the metal tin contained therein reacts with nitric acid to form solid α-stannic acid, which is filtered and separated after leaching for 3 hours to obtain nitrate solution A and solid slag X rich in metal ions.
[0107] (3) Nitrate solution A is subjected to the following processing steps (3-1) and (3-2):
Embodiment 3
[0127] In this embodiment, the electronic waste is the scrap generated from the production of printed circuit boards, RFID cards and IC cards. The process of recycling various metals from the electronic waste is as follows:
[0128] (1) The scraps generated during the production of printed circuit boards, RFID cards, IC cards, etc. are cut and crushed to obtain electronic waste particles with a particle size of 1mm to 5mm.
[0129] (2) After loading the electronic waste particles into the elution column, immerse them in an aqueous solution of nitric acid with a concentration of 50% by mass at 50°C, with a solid-liquid ratio of 1:10, so that the metal elements copper, nickel, and Lead and silver react and dissolve in nitric acid aqueous solution, and the metal tin contained therein reacts with nitric acid to form solid α-stannic acid, which is filtered and separated after leaching for 1 hour to obtain nitrate solution A and solid slag X rich in metal ions.
[0130] (3) Nitrate ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com