A samarium cobalt sintered permanent magnet material and its preparation method
A permanent magnet, samarium cobalt technology, applied in the direction of magnetic materials, magnetic objects, inorganic materials, etc., can solve the problem of increasing equipment, energy consumption and production costs, easily destroying magnetic powder anisotropy and particle size distribution, affecting columnar crystal growth, etc. problem, to achieve the same and uniform grain size, improve various properties, and reduce the effect of element segregation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
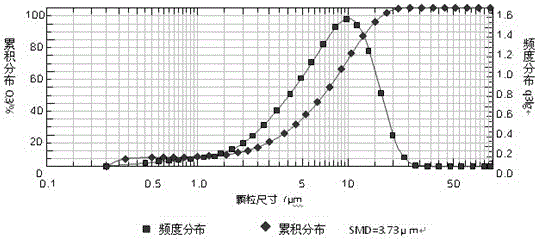
[0021] The raw materials were weighed according to the following weight fractions: samarium: 23.5%; cobalt: 51%; copper: 5%; zirconium: 3%; iron: 17.5%.
[0022] (1) Melting: Put the metal elements with the purity of Sm≥99.5%, Co≥99.6%, Cu≥99.7%, Zr≥99%, Fe≥99.8% in the crucible of the vacuum induction melting furnace, and evacuate to 5× 10 -2 Pa, filled with argon to 5×10 -2 Mpa, increase the power to gradually increase the melting temperature to 1500 ° C ~ 1600 ° C, refining under the protection of argon to obtain a uniform alloy melt;
[0023] (2) Ingot casting: After the smelting is complete, reduce the power of the smelting furnace, thereby reducing the temperature of the alloy solution to 1300-1400°C, and keep it for 2 minutes, then pour cooling water at 10°C-15°C into the cooling chamber of the ingot mold wall, Then the alloy melt is poured into an ingot cavity with a cavity thickness of 15 mm;
[0024] (3) Hydrogen absorption: 4.5 minutes after casting, at this time...
Embodiment 2
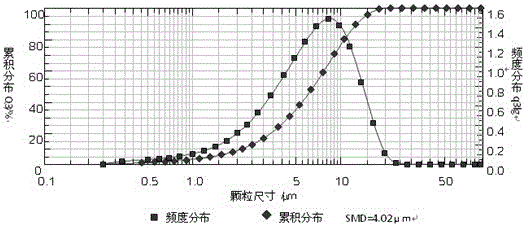
[0034] The raw materials were weighed according to the following weight fractions: samarium: 23.5%; cobalt: 51%; copper: 5.5%; zirconium: 3.2%; iron: 16.8%.
[0035] (1) Melting: Put the metal elements with the purity of Sm≥99.5%, Co≥99.6%, Cu≥99.7%, Zr≥99%, Fe≥99.8% in the crucible of the vacuum induction melting furnace, and evacuate to 5 ×10 -2 Pa, filled with argon to 5×10 -2 Mpa, increase the power to gradually increase the melting temperature to 1500 ° C ~ 1600 ° C, refining under the protection of argon to obtain a uniform alloy melt;
[0036] (2) Ingot casting: After the smelting is complete, reduce the temperature of the alloy solution in the melting furnace to 1300-1400°C and keep it for 2 minutes, then pour cooling water at 10°C-15°C into the cooling chamber of the ingot mold wall, and then put the alloy The melt is poured into an ingot cavity with a cavity thickness of 15 mm;
[0037] (3) Hydrogen absorption: 5 minutes after casting, at this time, the alloy temp...
Embodiment 3
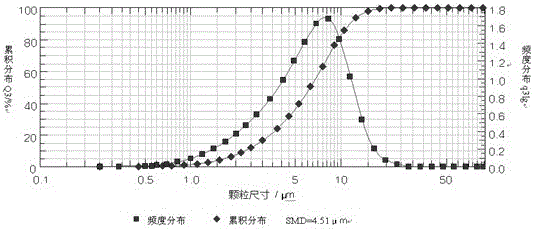
[0047] The raw materials were weighed according to the following weight fractions: samarium: 23.5%; cobalt: 51%; copper: 5%; zirconium: 3.5%; iron: 17%.
[0048] (1) Melting: Put the metal elements with the purity of Sm≥99.5%, Co≥99.6%, Cu≥99.7%, Zr≥99%, Fe≥99.8% in the crucible of the vacuum induction melting furnace, and evacuate to 5× 10 -2 When it is below Pa, fill it with argon to 5×10 -2 Mpa, increase the power to gradually increase the melting temperature to 1500 ° C ~ 1600 ° C, refining under the protection of argon to obtain a uniform alloy melt;
[0049] (2) Ingot casting: After the smelting is complete, reduce the power of the smelting furnace, thereby reducing the temperature of the alloy solution to 1300-1400°C, and keep it for 2 minutes, then pour cooling water at 10°C-15°C into the cooling chamber of the ingot mold wall, Then the alloy melt is poured into an ingot cavity with a cavity thickness of 15mm;
[0050] (3) Hydrogen absorption: 4.5 minutes after cast...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com