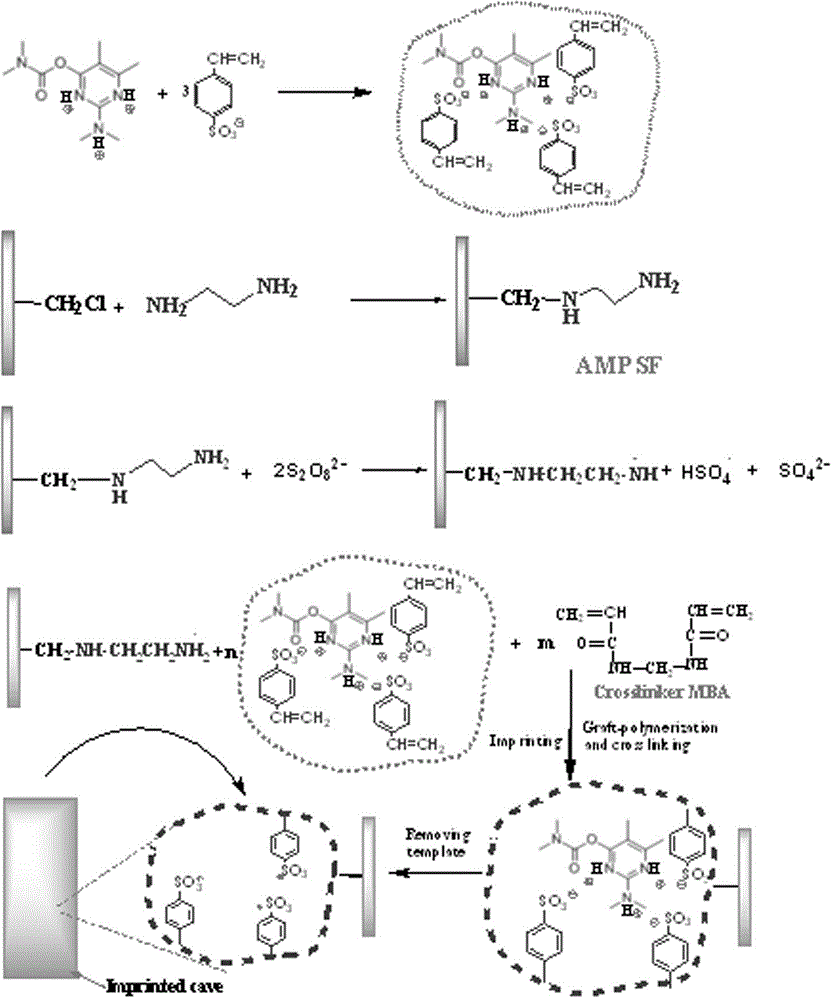
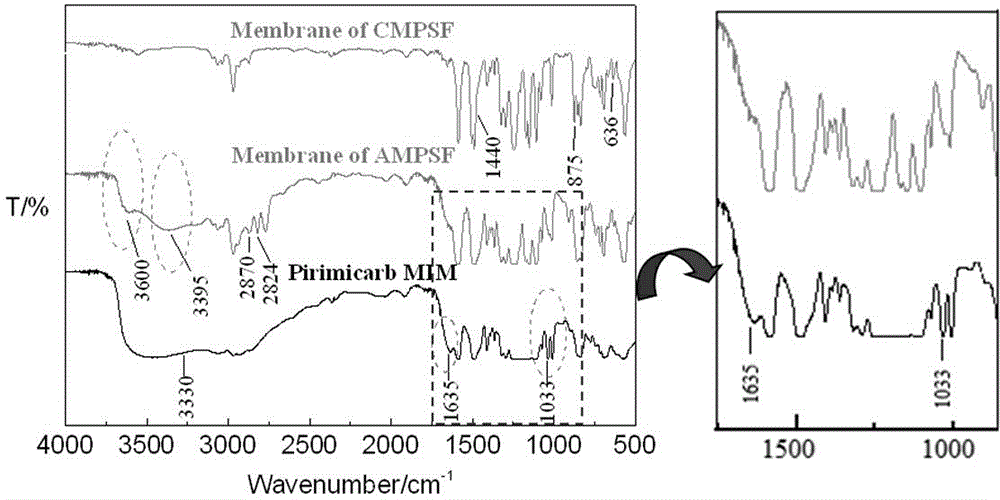
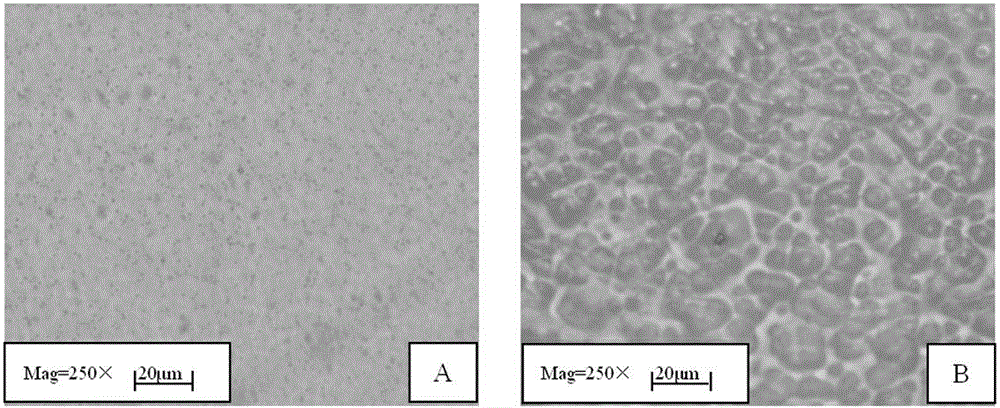
Synthetic method of potentiometric pesticide sensor
A synthesis method and sensor technology, applied in instruments, scientific instruments, material analysis through electromagnetic means, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] A method for synthesizing a pesticide potential type sensor identification material, comprising the following steps:
[0062] (1) Preparation and ammoniation of chloromethylated polysulfone-based membrane
[0063] Dissolve 0.8 g CMPSF in 50 mL dichloromethane, then add 0.04 g TDMAC, pour the casting solution into a glass Petri dish, cast it into a film, let it stand for defoaming, and after the solvent is completely volatilized, the obtained thickness is about 60 μm translucent CMPSF membrane, soak the membrane in ethylenediamine for surface amination treatment, and prepare an ammoniated polysulfone (AMPSF) membrane with amino groups on the surface, the amino group content on the surface of the AMPSF membrane is 18.16 μmmol / cm 2 ;
[0064] (2) Preparation of pirimicarb molecularly imprinted membrane
[0065] Add 50 mL of anhydrous methanol and 30 mL of distilled water dissolved with 8 g of sodium styrene sulfonate (SSS) into a four-neck flask, then add 2.5 g o...
Embodiment 2
[0070] A method for synthesizing a pesticide potential type sensor identification material, comprising the following steps:
[0071] (1) Preparation and ammoniation of chloromethylated polysulfone-based membrane
[0072] Dissolve 0.8 g of CMPSF in 50 mL of dichloromethane, then add 0.04 g of TDMAC, pour this casting solution into a glass petri dish, cast it into a film, let it stand for defoaming, and after the solvent is completely volatilized, a thickness of 65 μm is obtained. A translucent CMPSF membrane was soaked in ethylenediamine for surface amination treatment to obtain an aminated polysulfone (AMPSF) membrane with amino groups on the surface. The amino group content on the surface of the AMPSF membrane was 18.16 μmmol / cm 2 ;
[0073] (2) Preparation of pirimicarb molecularly imprinted membrane
[0074] Add 50 mL of anhydrous methanol and 35 mL of distilled water dissolved with 8 g of sodium styrene sulfonate (SSS) into a four-neck flask, then add 2.5 g of pi...
Embodiment 3
[0079] A method for synthesizing a pesticide potential type sensor identification material, comprising the following steps:
[0080] (1) Preparation and ammoniation of chloromethylated polysulfone-based membrane
[0081] Dissolve 0.8 g of CMPSF in 50 mL of dichloromethane, and then add 0.04 g of TDMAC. The casting solution is poured into a glass petri dish, cast into a film, and left to defoam. After the solvent is completely evaporated, a thickness of 55 μm is obtained. A translucent CMPSF membrane was soaked in ethylenediamine for surface amination treatment to obtain an aminated polysulfone (AMPSF) membrane with amino groups on the surface. The amino group content on the surface of the AMPSF membrane was 18.16 μmmol / cm 2 ;
[0082] (2) Preparation of pirimicarb molecularly imprinted membrane
[0083] Add 50 mL of anhydrous methanol and 35 mL of distilled water dissolved with 8 g of sodium styrene sulfonate (SSS) into a four-neck flask, then add 2.5 g of pirimicarb...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com