Method for rapidly detecting pathogenic bacteria
A technology for pathogenic bacteria and food-borne pathogenic bacteria, applied in the field of microbial detection, can solve the problem of high dosage of nanoparticles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
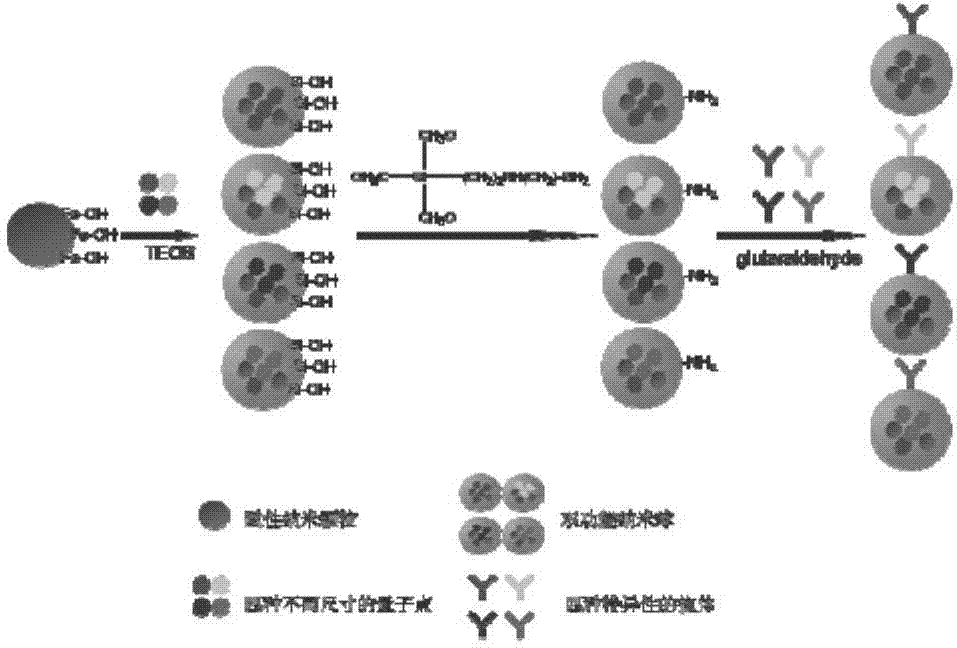
[0033] Example 1: Preparation of four bifunctional silicon-based nanospheres with different optical properties
[0034] In the present invention, the bifunctional nanosphere is improved by obtained by the method. Specifically, it is obtained by hydrolyzing ethyl orthosilicate in ethanol solution under the catalysis of a certain concentration of ammonia water. By adjusting the relative concentrations of ammonia water, tetraethyl orthosilicate, ethanol, water, magnetic nanoparticles and quantum dots, the bifunctional nanospheres meeting the detection requirements are obtained. Add quantum dots with different optical properties (such as emission wavelengths of 481nm, 518nm, 565nm and 610nm), thereby changing the optical properties of the bifunctional composite nanospheres, and obtaining four bifunctional nanospheres with different optical properties (marked as nanospheres 481 , nanosphere 518 , nanosphere 565 , nanosphere 610 ). A typical synthesis process is as follows: ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2: Four kinds of immune bifunctional nanospheres capturing enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli (E.coli O157:H), Salmonellae, Listeria and Campylobacter respectively Probe construction
[0037] Firstly, the surface of the above four kinds of bifunctional composite nanospheres was modified. Specifically, 0.5 g of nanospheres were dissolved in 50 mL of pyridine, 0.2 g of succinic anhydride and 0.02 g of 4-dimethylaminopyridine were added, stirred at room temperature overnight, magnetically separated, and methanol Wash twice with water.
[0038] Then, enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli antibody, Salmonella antibody, Listeria monocytogenes antibody and Campylobacter antibody were covalently linked to the above four bifunctional nanospheres to obtain four kinds of immune bifunctional nanosphere probes (labeled for nanospheres 481 -E, nanospheres 518 -S, nanospheres 565 -L, nanosphere 610 -C). The operation steps are as follows:
[0039] Take 500μg of nanosphere...
Embodiment 3
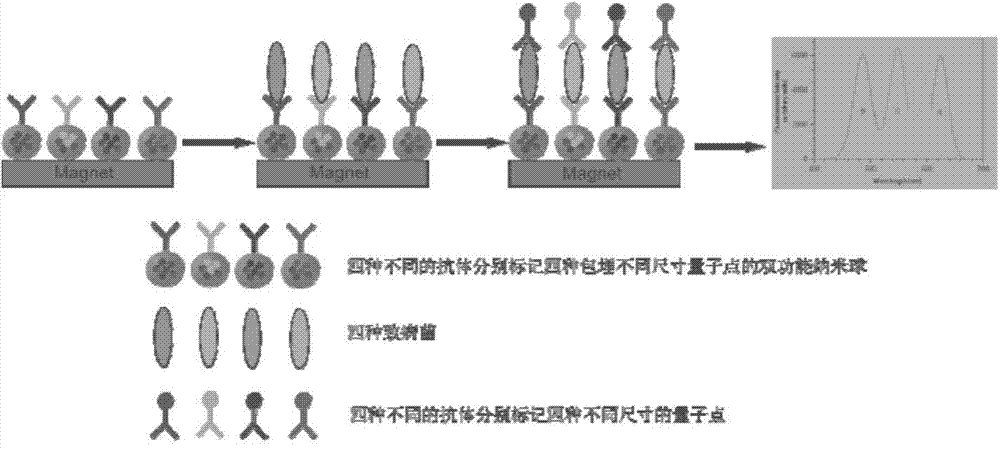
[0040] Example 3: Four immune quantum dot probes for respectively labeling E.coli O157:H, Salmonellae, Listeria and Campylobacter build
[0041] The monoclonal antibodies that specifically recognize the target foodborne pathogenic bacteria enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli antibody, Salmonella antibody, Listeria monocytogenes antibody and Campylobacter antibody were connected with the corresponding quantum dots to form four kinds of immune quantum Point probes (labeled as quantum dots 481 -E, quantum dots 518 -S, quantum dots 565 -L, quantum dots 610 -C). The size of the antibody and quantum dots labeled by this probe corresponds to the size of the labeled antibody and quantum dots embedded in the immune complex nanospheres, which can be similar to the formation of immune complex nanosphere probes, and the formation of target food-borne pathogenic bacteria Similar to a sandwich structure. The operation steps are as follows:
[0042] Take 500 μL of quantum dots in a 1.5...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com