A kind of preparation method of loaded nanometer zero valent iron composite material
A nano-zero-valent iron and composite material technology, applied in nanotechnology, chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, etc., can solve the problems of limited physical adsorption and precipitation in pollutant removal, limited effect of stubborn organics and metal ions, etc. Achieve the effect of cost reduction, green mass production, and uniform appearance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
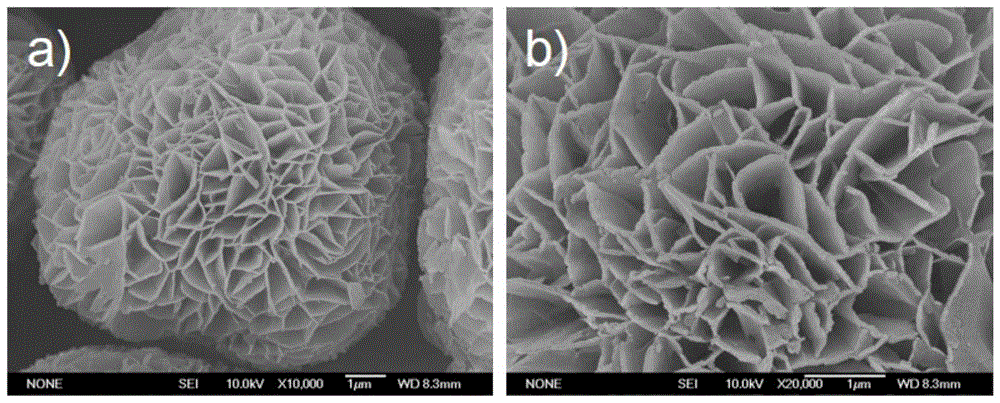
[0027] Step 1. At room temperature, slowly add 1mol / L NaOH aqueous solution to the same volume of 0.5mol / LMgSO 4 solution (v C 3 h 8 o 3 :v H 2 (0=15:85), keep stirring vigorously during the dropwise addition, continue to stir for 6 hours after the dropwise addition is completed, then age for 24 hours, centrifuge, wash with deionized water and absolute ethanol three times successively, and dry at 50°C to obtain micro / Nanocomposite flower-like self-supporting Mg(OH) 2 Microspheres;
[0028] Step 2, 0.416g Mg(OH) 2 Disperse in 75mL absolute ethanol (ultrasonic dispersion 5min), 2.085g FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O was dissolved in 75mL deionized water, and the two were transferred into a 500ml three-neck flask (concentration was 0.05mol / L (v absolute ethanol:v deionized water=1:1) FeSO 4 solution);
[0029] Step 3. Keep mechanical stirring at 300r / min, feed N 2 Isolate and protect, then add dropwise an equal volume (150mL) of 0.25mol / L NaBH to the three-necked flask 4 solution, the...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Step 1, is identical with embodiment 1;
[0034] Step 2, 0.832g Mg(OH) 2 Disperse in 75mL absolute ethanol (ultrasonic dispersion 5min), 2.085g FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O was dissolved in 75mL deionized water, and the two were transferred into a 500mL three-necked flask (concentration of 0.05mol / L (v absolute ethanol:v deionized water=1:1) FeSO 4 solution);
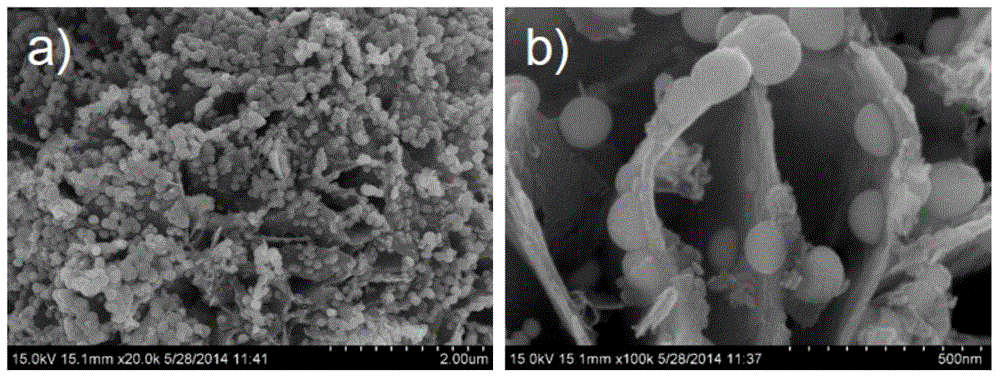
[0035] Step 3. Keep mechanical stirring at 300r / min, feed N 2 Isolate and protect, then add dropwise equal volume (150ml) 0.25mol / L NaBH to the there-necked flask 4 solution, the dropping rate is 3ml / min, and the stirring is continued for 30min after the addition is completed. The black solid obtained from the reaction is separated by centrifugation, washed with water and ethanol three times in turn, and vacuum-dried at 45°C for 12h to obtain Mg(OH) with a theoretical loading capacity of 33%. 2 Supported nano-zero-valent iron composites.
Embodiment 3
[0037] Step 1, is identical with embodiment 1;
[0038] Step 2, 0.208g Mg(OH) 2 Disperse in 75mL absolute ethanol (ultrasonic dispersion 5min), 2.085g FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O was dissolved in 75ml deionized water, and the two were moved into a 500ml three-necked flask (concentration was 0.05mol / L (v absolute ethanol:v deionized water=1:1) FeSO 4 solution);
[0039] Step 3. Keep mechanical stirring at 300r / min, feed N 2 Isolate and protect, then add dropwise an equal volume (150mL) of 0.25mol / L NaBH to the three-necked flask 4 solution, the dropping rate was 3mL / min, and the stirring was continued for 30 minutes after the dropping was completed. The black solid obtained from the reaction was separated by centrifugation, washed with water and ethanol three times in turn, and dried in vacuum at 45°C for 12 hours to obtain Mg(OH) with a theoretical loading capacity of 67%. 2 Supported nano-zero-valent iron composites.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com