Process method for extracting cobalt and nickel from manganese waste slag
A process method and technology of manganese waste slag, applied in the field of comprehensive utilization of resources, can solve the problems of high energy consumption, pollution, and high cost of full wet extraction and separation by pyrolysis, and achieve good separation effect, cost reduction, and high iron removal efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
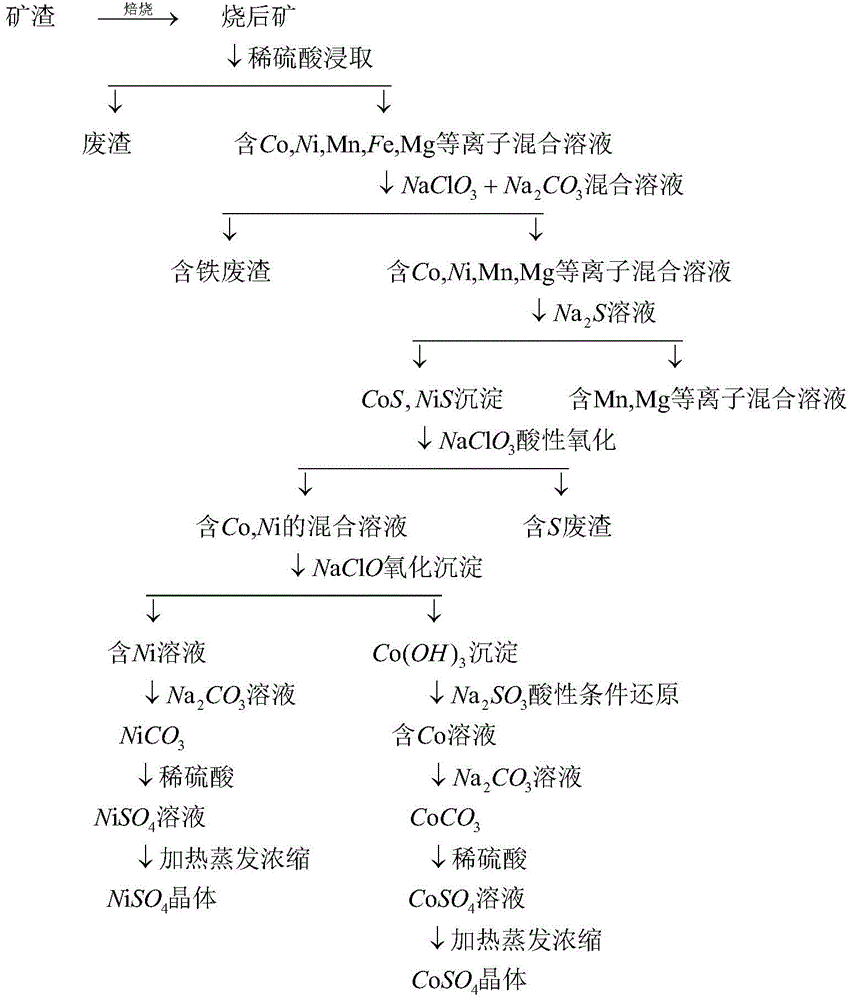
[0030] (1) Oxidation roasting-dilute sulfuric acid leaching: After grinding the slag, pass it through an 80-mesh sieve, and roast it at 300°C for 4 hours in an air atmosphere; take 1000g of the burned ore, add 0.2mol / L H 2 SO 4 The solution was 1500mL stirred and acid leached for 10 hours, most of the cobalt, nickel, and part of the iron entered the solution, and the leached solution was separated from the solid-liquid-liquid, and the leached residue was washed several times by suction filtration or centrifugation, and the filter residue was discarded. The leaching rate of Co was 94%, the leaching rate of Ni was 70%, the leaching rate of Mn was 90%, the leaching rate of Fe was 10%, and the leaching rate of Mg was 66%.
[0031] (2) Oxidative hydrolysis to remove iron: add 6.0gNaClO in the filtrate in (1) step 3 and 13.0gNa 2 CO 3 Mix the solution, adjust the pH of the solution to 4.0, react with electric stirring for 20 minutes, then heat and boil for 10 minutes to obtain Fe...
Embodiment 2
[0038] (1) Oxidation roasting-dilute sulfuric acid leaching: After grinding the slag, pass it through an 80-mesh sieve, and roast it at 450°C for 3 hours in an oxygen atmosphere; take 1000g of the burned ore, add 0.2mol / L H 2 SO 4 The solution is 2500mL stirred and acid leached for 10h, most of the cobalt, nickel, and part of the iron enter the solution, the leached solution is separated from the solid-liquid-liquid, and the leached residue is washed several times by suction filtration or centrifugation, and the filter residue is discarded. The leaching rate of Co was 95.6%, the leaching rate of Ni was 72.1%, the leaching rate of Mn was 92.0%, the leaching rate of Fe was 7.5%, and the leaching rate of Mg was 60.2%.
[0039] (2) Oxidative hydrolysis to remove iron: add 5.5gNaClO in the filtrate in (1) step 3 and 11.0gNa 2 CO 3 Mix the solution, adjust the pH of the solution to 5.0, react with electric stirring for 20 minutes, then heat and boil for 10 minutes to obtain Fe 2...
Embodiment 3
[0046] (1) Oxidation roasting-dilute sulfuric acid leaching: After grinding the slag, pass it through an 80-mesh sieve, and roast it at 600°C for 2 hours in an oxygen atmosphere; take 1000g of the burnt ore, add 0.5mol / L H 2 SO 4 The solution was 1500mL stirred and acid leached for 10 hours, most of the cobalt, nickel, and part of the iron entered the solution, and the leached solution was separated from the solid-liquid-liquid, and the leached residue was washed several times by suction filtration or centrifugation, and the filter residue was discarded. The leaching rate of Co was 94.9%, the leaching rate of Ni was 71.9%, the leaching rate of Mn was 92.0%, the leaching rate of Fe was 9.3%, and the leaching rate of Mg was 63.8%.
[0047] (2) Oxidative hydrolysis to remove iron: add 5.5gNaClO in the filtrate in (1) step 3 and 11.0gNa 2 CO 3 Mix the solution, adjust the pH of the solution to 5.0, react with electric stirring for 20 minutes, then heat and boil for 10 minutes t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com