Carbonation-resistant basic magnesium sulfate cement and preparation method thereof
A magnesium sulfate, anti-carbonization technology, applied in the field of cementitious materials, to achieve high folding ratio, improve toughness, and increase strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
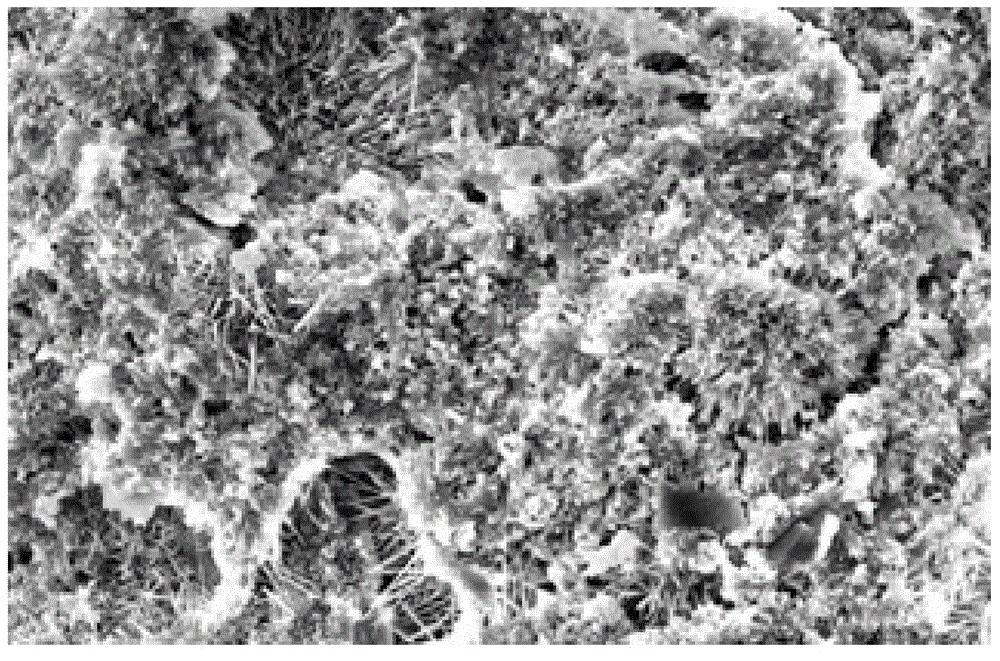
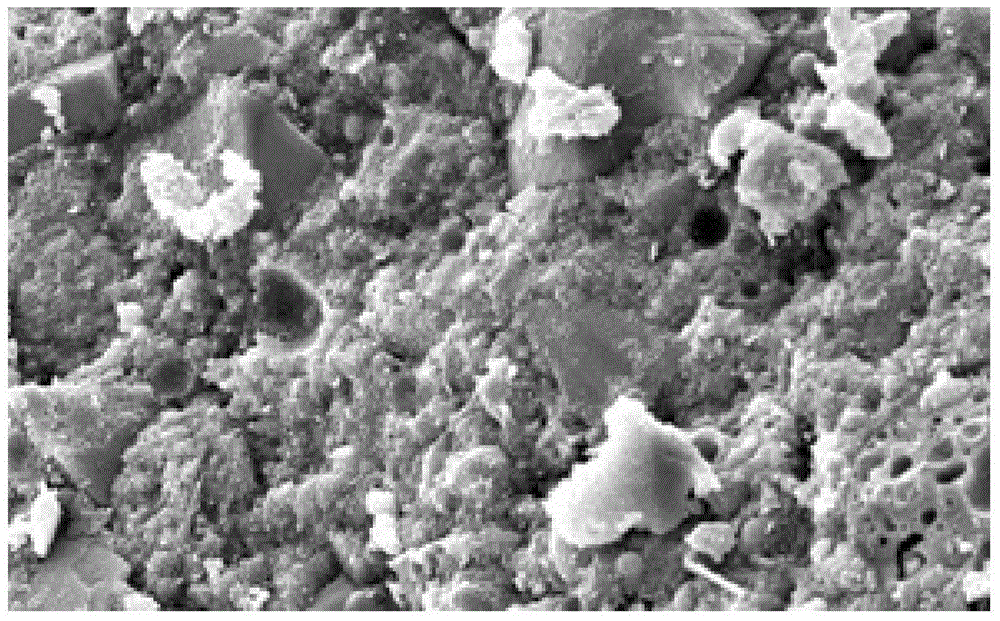
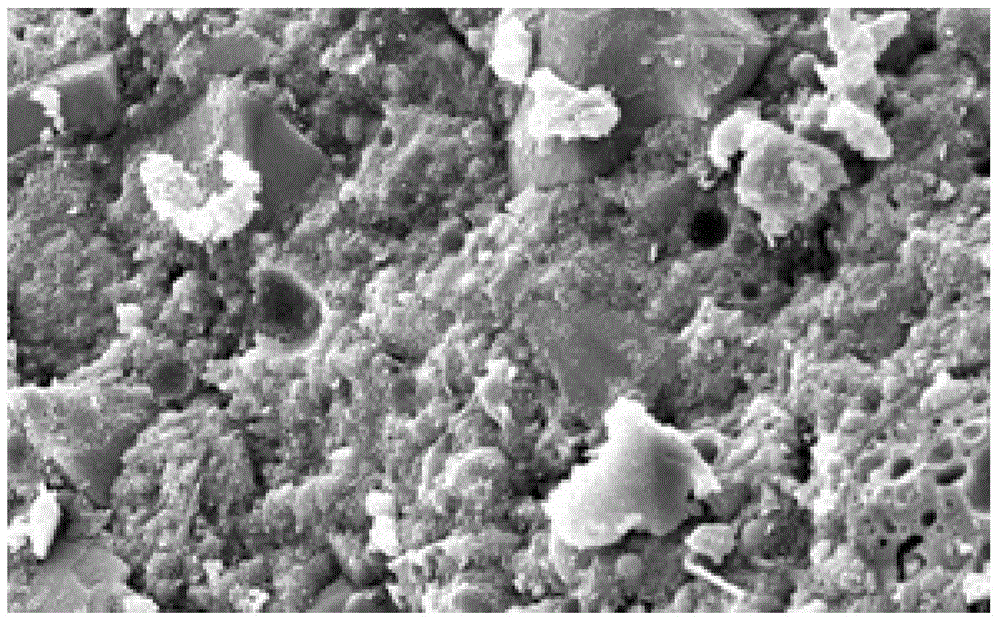
[0030] like figure 1 and figure 2 as shown, figure 1 It is the SEM topography of the microstructure of traditional magnesium oxysulfide cement after 30 days of hydration; figure 2 It is the SEM image of the anti-carbonation basic magnesium sulfate cement 30d of the present invention; the hydration product of the anti-carbonization basic magnesium sulfate cement prepared from industrial raw materials is 5.1.7 whiskers.
[0031] It can be seen that the hydration structure of traditional magnesium oxysulfide cement is mainly composed of a large number of flaky Mg(OH)2 crystals, and the structure is loose and the pores are more. The microstructure of anti-carbonation basic magnesium sulfate cement after hydration is composed of a large number of needle-like 5·1·7 whiskers with relatively uniform spatial distribution. The structure is dense, and there are both Mg(OH)2 gel phase and needle The rod-shaped 5.1.7 whisker crystals are interwoven into a continuous three-dimensional ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] The difference between embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is: a kind of anti-carbonization basic magnesium sulfate cement of the present invention, described anti-carbonization basic magnesium sulfate cement is made up of the component of following mass percentage:
[0053]
[0054]
[0055] The magnesium oxide refers to any one or a combination of the magnesium oxide powder material produced by calcined magnesite and the by-product magnesium oxide powder material produced in the process of extracting lithium carbonate from salt lake brine.
[0056] Described magnesium oxide is made up of the component of following mass percentage:
[0057]
[0058] The method for preparing the described anti-carbonation basic magnesium sulfate cement of the present invention comprises the following steps: in step (1), each component of the above-mentioned ratio is taken by proportioning, magnesium oxide 45%, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 23 %, industrial waste powder 15%, white sl...
Embodiment 3
[0061] The difference between embodiment 3 and embodiment 1 is: a kind of anti-carbonization basic magnesium sulfate cement of the present invention, the described anti-carbonization basic magnesium sulfate cement is made up of the component of following mass percentage:
[0062]
[0063] The method for preparing the described anti-carbonation basic magnesium sulfate cement of the present invention comprises the following steps: in step (1), each component of the above-mentioned ratio is weighed by proportioning, magnesium oxide 55%, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 25% %, industrial waste powder 20%, white slag 9%, mineral admixture 8%, desulfurization gypsum 4%, slag 8%, straw 4%, silica fume 3%, coagulant 3%;
[0064] In step (3), the magnesium oxide is calcined and ground at a temperature of 980° C. to obtain a powder with a fineness of 300 mesh. The stirring speed is 2000r / min.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pulverization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flexural strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com