Catalyst for selective hydrogenation reaction of aromatic nitrocompound and preparation method of catalyst
A technology for aromatic nitro groups and catalysts, which is applied in the field of catalysts and preparations for selective hydrogenation of aromatic nitro compounds, and can solve problems such as difficulty in realizing catalyst reuse, increasing catalyst preparation costs, and limiting the practical application of catalysts. No degradation in performance, easy separation, and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
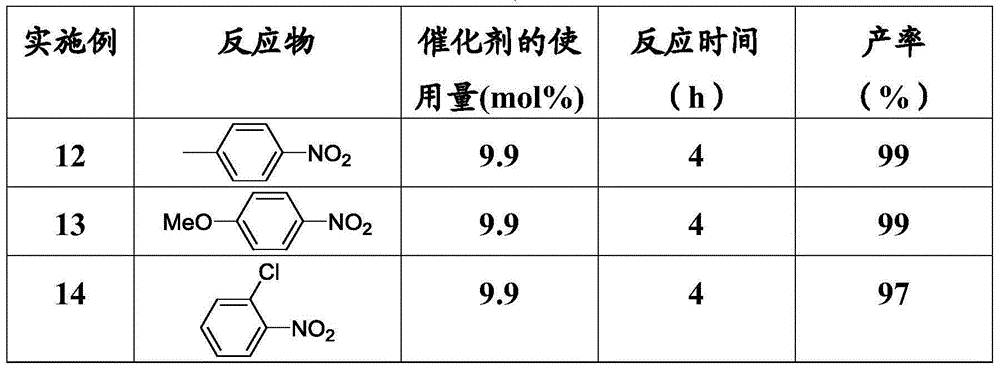
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1. Catalyst based on Co and nanographitic carbon
[0036] Take 20ml of distilled water, add 1.875g of tartaric acid under stirring, then add 1.819g of Co(NO3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O, then add 60ml glycerin aqueous solution (glycerin: water = 4:1, volume ratio) and 5.0g polyethylene glycol PEG6000, finally add 0.5g nano-graphite carbon, after stirring evenly, place in a hydrothermal kettle at 150°C for 13h, After the obtained solid was dried, it was transferred to a tube furnace and calcined at 800° C. for 2.0 h under argon to obtain a carbon layer-coated Co catalyst dispersed on nano-graphitic carbon, with a Co content of 29.2 wt%.
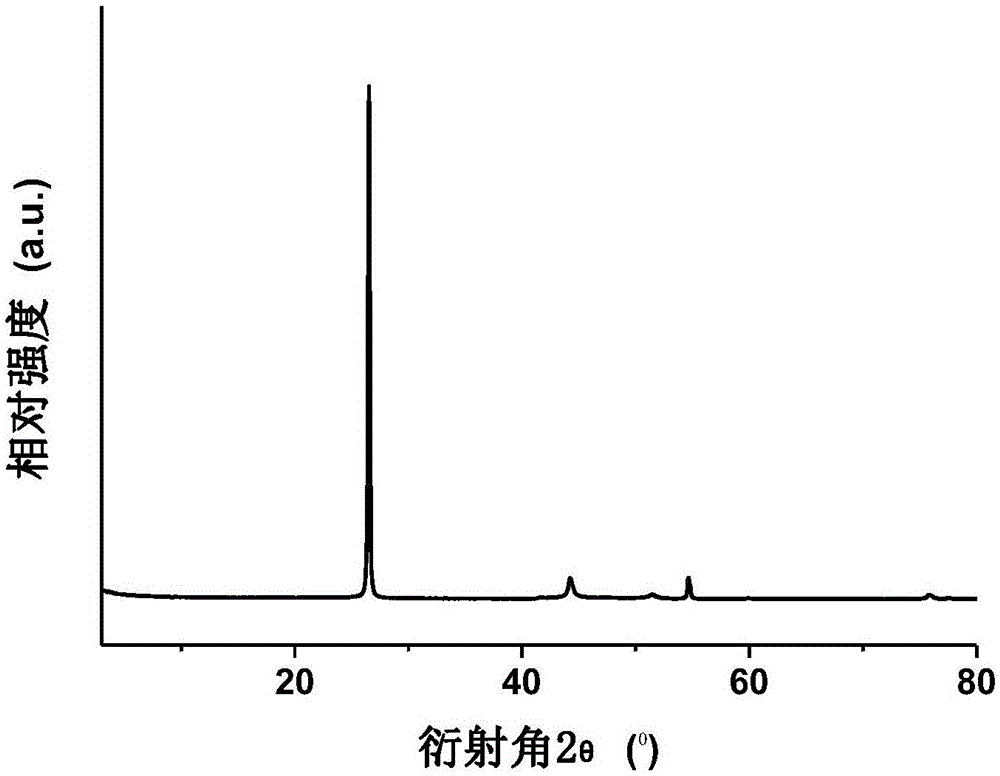
[0037] figure 1 The X-ray diffraction pattern of the carbon-coated cobalt-based catalyst shows that the active metal cobalt is in a reduced state.
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2. Catalysts based on Ni and nanographitic carbon
[0039] Take 20ml of distilled water, add 1.875g of tartaric acid under stirring, then add 1.818g of Ni(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O, then add 60ml glycerin aqueous solution (glycerin: water = 4:1, volume ratio) and 5.0g polyethylene glycol PEG6000, finally add 0.5g nano-graphite carbon, after stirring evenly, place in a hydrothermal kettle at 150°C for 13h, After the obtained solid was dried, it was transferred to a tube furnace and calcined at 800° C. for 2.0 h under argon to obtain a carbon layer-coated Ni catalyst dispersed on nano-graphitic carbon, and the Ni content was 28.0 wt%.
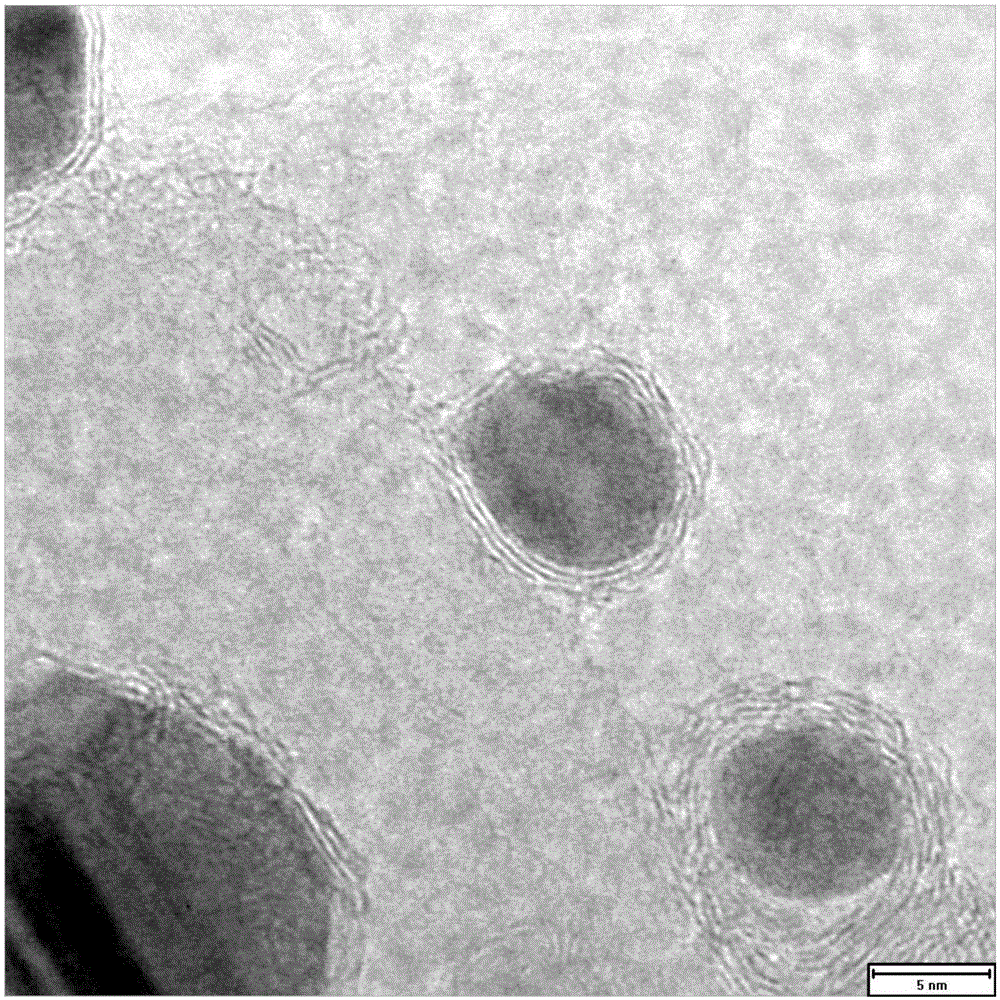
[0040] figure 2 The transmission electron microscope image of the cobalt-based catalyst coated with the carbon layer shows that the active metal cobalt nanoparticles are coated with a carbon layer of about 2-5nm.
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3. Catalysts based on Cu and nanographitic carbon
[0042] Take 20ml of distilled water, add 1.875g of tartaric acid under stirring, then add 1.51g of Cu(NO 3 ) 2 ·3H 2 O, then add 60ml glycerin aqueous solution (glycerin: water = 4:1, volume ratio) and 5.0g polyethylene glycol PEG6000, finally add 0.5g nano-graphite carbon, after stirring evenly, place in a hydrothermal kettle at 150°C for 13h, After the obtained solid was dried, it was transferred to a tube furnace and calcined at 800° C. for 2.0 h under argon to obtain a carbon layer-coated Cu catalyst dispersed on nano-graphitic carbon, with a Cu content of 30.1 wt%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com