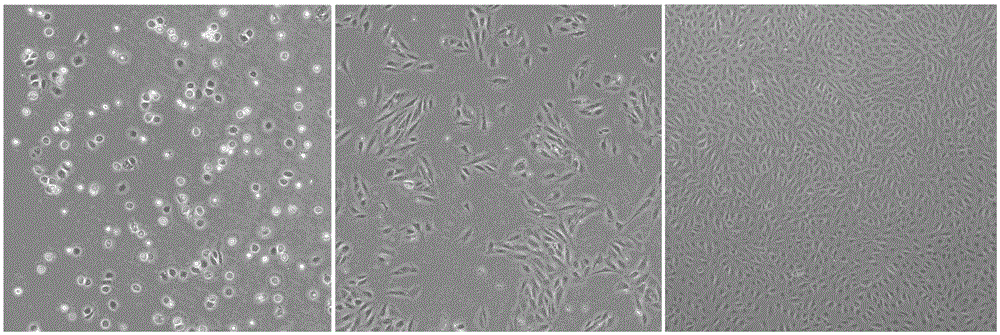
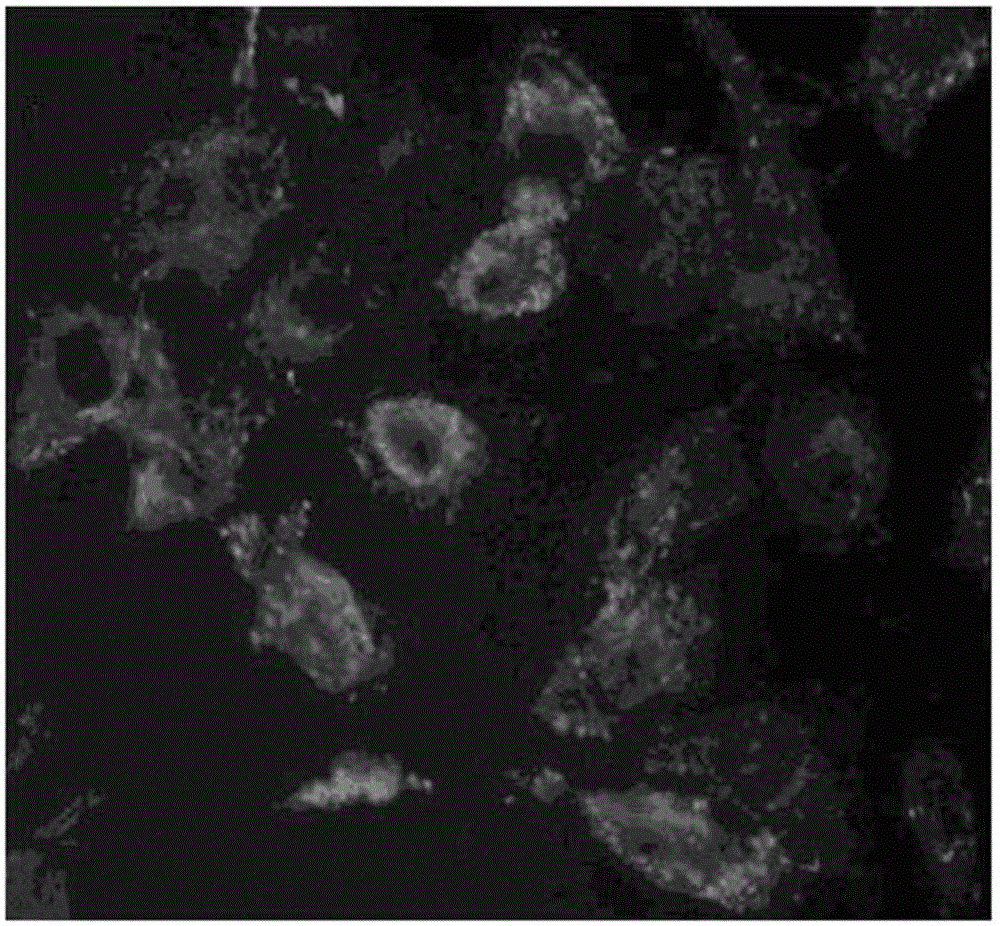
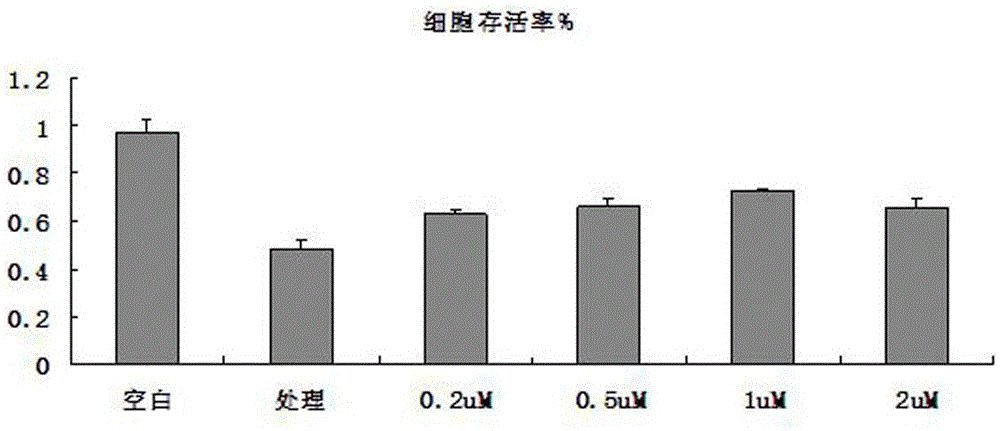
Method for separating and cultivating endothelial cells of common carotid arteries of SD (Sprague Dawley) rats
A common carotid artery and endothelial cell technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of destroying cell integrity, affecting cell viability, and low cell number, and achieving the effects of strong cell adhesion, improved drug efficacy, and a wide range of material sources.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] A method for separating and culturing SD rat common carotid artery endothelial cells, comprising the following steps:
[0037] 1) Select SD rats with a weight of 100-150g, cut out the common carotid artery of SD rats under sterile conditions and remove blood stains, and set aside;
[0038] 2) Cut the common carotid artery into a long section of 3-5cm and put it in PBS solution, peel off the adventitia of the common carotid artery, cut the common carotid artery longitudinally, and spread the intima of the common carotid artery downward In a container containing a digestive enzyme solution, the intima of the common carotid artery is fully contacted with the digestive enzyme solution in the container to achieve digestion of the intima of the common carotid artery. The digestive enzyme solution is composed of type I Collagenase and trypsin with a mass concentration of 0.125% are mixed at a volume ratio of 1:1 and stirred evenly;
[0039] 3) Vibrate the container during the...
Embodiment 2
[0049] A method for separating and culturing SD rat common carotid artery endothelial cells, comprising the following steps:
[0050] 1) Select SD rats with a weight of 100-150g, cut out the common carotid artery of SD rats under sterile conditions and remove blood stains, and set aside;
[0051] 2) Cut the common carotid artery into a long section of 3-5cm and put it in PBS solution, peel off the adventitia of the common carotid artery, cut the common carotid artery longitudinally, and spread the intima of the common carotid artery downward In a container containing a digestive enzyme solution, the intima of the common carotid artery is fully contacted with the digestive enzyme solution in the container to achieve digestion of the intima of the common carotid artery. The digestive enzyme solution is composed of type I Collagenase and trypsin with a mass concentration of 0.125% are mixed at a volume ratio of 1:1 and stirred evenly;
[0052] 3) Vibrate the container during the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com