A kind of lignin cross-linked modified polymer separation membrane and use thereof
A cross-linking modification and lignin technology, which is applied in the field of lignin cross-linking modification polymer separation membrane, can solve the problems of difficult hydrophilicity and pollution resistance, single type of hydrophilic modifier, high synthesis cost, etc. , to achieve the effect of reducing preparation cost, low cost and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Mix polysulfone, lignosulfonate, water, and N,N-dimethylacetamide with a mass ratio of 15:0.4:1:85, stir and dissolve at 60°C for 4 hours to form a uniform solution, and then Stir at ℃ for 30 minutes, add glutaraldehyde with a mass percentage that is 4 times the lignin mass percentage in the solution, leave it to defoam for 12 hours to obtain a casting solution, and process it through a film forming machine to form a nascent film. In the last 10 minutes, immerse in an aqueous solution with a mass percentage of 15% N,N-dimethylacetamide at 50°C for 5 hours to promote crosslinking, and then transfer to a water bath at 60°C for 2 hours to stabilize crosslinking and obtain hydrophilic permanent polysulfone membrane.
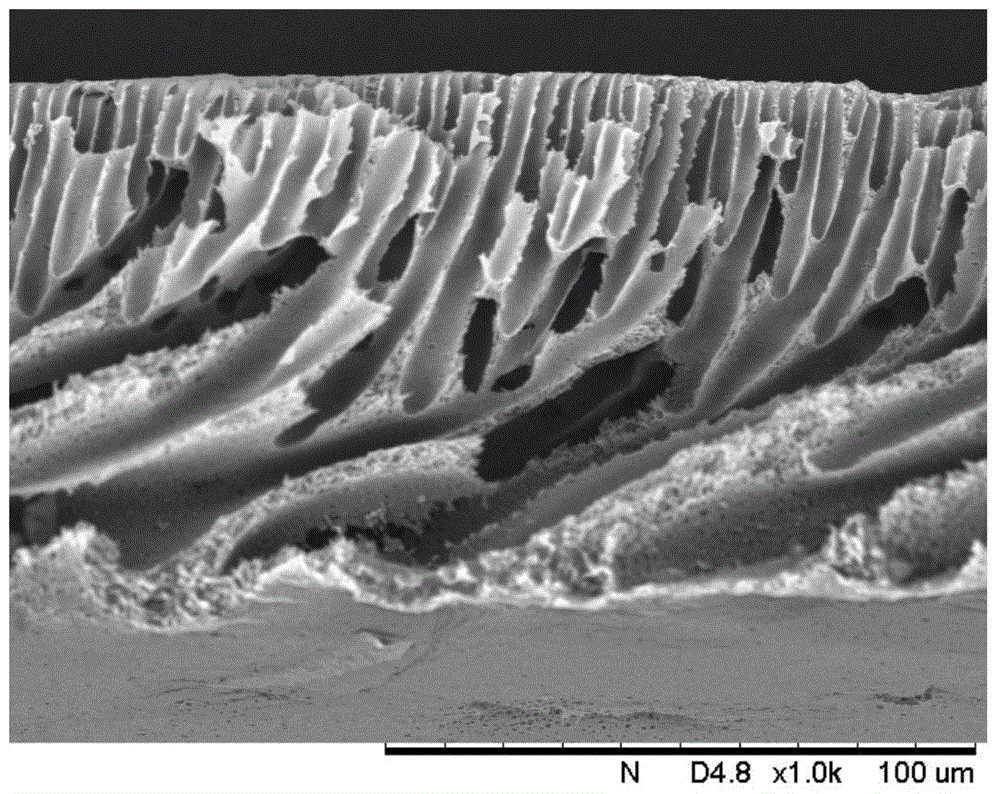
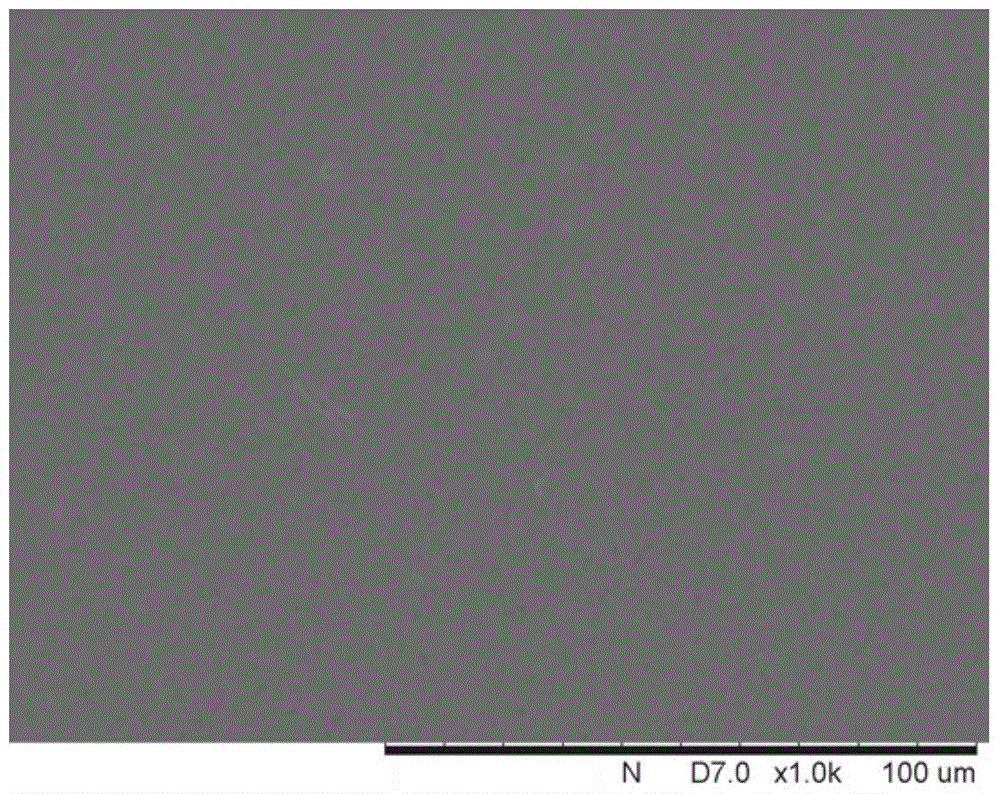
[0021] figure 1 with 2 They are the scanning electron micrographs of the upper surface and cross-sectional structure of Example 1, respectively.
Embodiment 2
[0023] Mix polysulfone, alkali lignin, dioxane, and N,N-dimethylformamide with a mass ratio of 10:2:4:90, stir and dissolve at 40°C for 2 hours to form a uniform solution, and then Stirring at 20°C for 10 minutes, adding glutaraldehyde with a mass percentage content 6 times the lignin mass percentage content in the solution, standing for 12 hours for defoaming to obtain a casting solution, and forming a primary film through a film forming machine. Within 10 minutes after molding, immerse in an aqueous solution of 10% N,N-dimethylformamide at 60°C for 8 hours to promote crosslinking, then transfer to a water bath at 80°C for 12 hours to stabilize crosslinking, and obtain a hydrophilic Aqueous polysulfone membrane.
Embodiment 3
[0025] Mix polysulfone, lignosulfonate, water, and N,N-dimethylacetamide with a mass ratio of 30:0.2:1:70, stir and dissolve at 80°C for 12 hours to form a uniform solution, and then Stirring at ℃ for 1 hour, adding glutaraldehyde with a mass percentage of twice the lignin mass percentage in the solution, standing for 12 hours for defoaming to obtain a casting solution, processing and forming a primary film by a film forming machine, forming After 10 minutes, enter 15°C in an aqueous solution with a mass percentage of 60% N,N-dimethylacetamide and immerse for 10 minutes to promote crosslinking, and then transfer to a 40°C water bath for 8 hours to stabilize crosslinking and obtain hydrophilic permanent polysulfone membrane.
[0026] The measurement results are: the static water contact angle of the polysulfone membrane is 69°; the average pore size is 0.11 μm; the pure water flux of the membrane is 130L m at 25°C and 0.1MPa pressure -2 h -1 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| contact angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| contact angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com