Antimicrobial cationic polycarbonates
An antimicrobial and cationic polymer technology, applied in biocides, antibacterials, antifungals, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
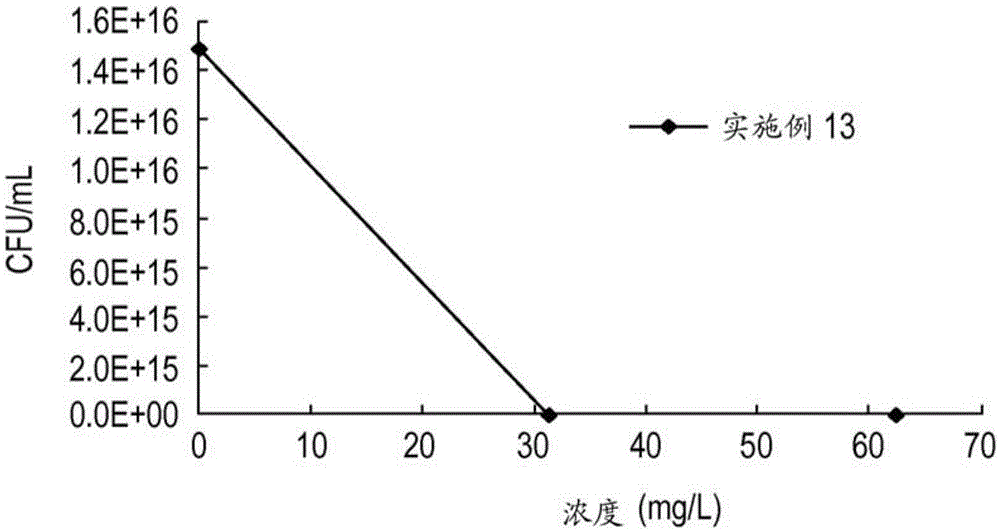
Embodiment 10
[0654] The preparation of Example 10 is representative. The cationic polymer was prepared according to the reaction sequence in Scheme 1.
[0655] plan 1.
[0656]
[0657] Part 1. In an inert glove box, a vial was charged with Chol-OPr-OH (0.179 g, 0.4 mmol), TU (0.04 g, 0.1 mmol), MTC-BnCl (0.6 g, 2 mmol), dichloromethane ( DCM) (3 g) and stir bar. The reaction mixture was stirred and polymerization was started by addition of DBU (20 μL, 0.15 mmol). After 15 minutes, excess acetyl chloride was added to quench the reaction and acetylate the end of IP-1 to form IP-2. Precipitation of the acetylated intermediate polymer IP-2 into isopropanol gave 0.73 g (94%) of white waxy polymer. use 1 HNMR (CDCl 3 ) and GPC (THF, 37°C) to characterize the polymer. Through the carbonate doublet (2H, -OCOOCH 2 -, 4.7ppm) disappear and include the newly formed linear carbonate methylene (-CH 2 OCOOCH 2 -) and the corresponding appearance of a broad multiplet (6H, 4.2 ppm) for both ...
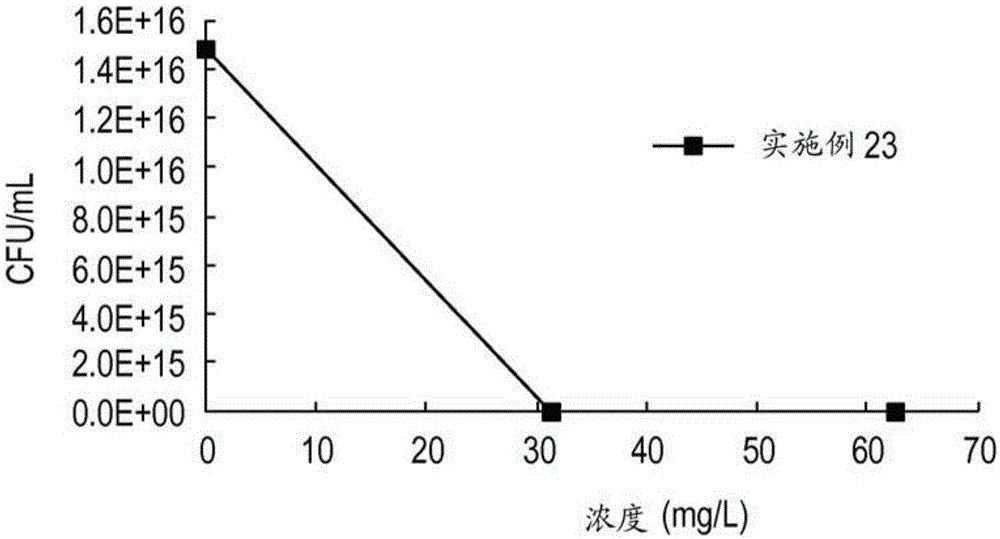
Embodiment 28-41
[0667] Examples 28-41. Using 4-methylbenzyl alcohol (4-MeBnOH) as an initiator, MTC-BnCl, MTC-PrCl or MTC-PrBr as a cyclic carbonate monomer, and various amine quaternizers Cationic polymers were prepared according to the general polymerization and quaternization procedures above.
[0668] Table 8 lists cationic homopolymers prepared using 4-MeBnOH initiator, their degree of polymerization (DP), quaternizing agent, CMC, and the total number of carbons of each cationic repeat unit.
[0669] Table 8.
[0670]
[0671] a "None" means that the terminal hydroxyl groups of the polycarbonate chain are not protected.
[0672] b N.D. means not determined.
[0673] c actual, as by 1 determined by HNMR analysis
[0674] C. Cationic random copolymer prepared with MTC-VitE having side chain α-tocopheryl moieties
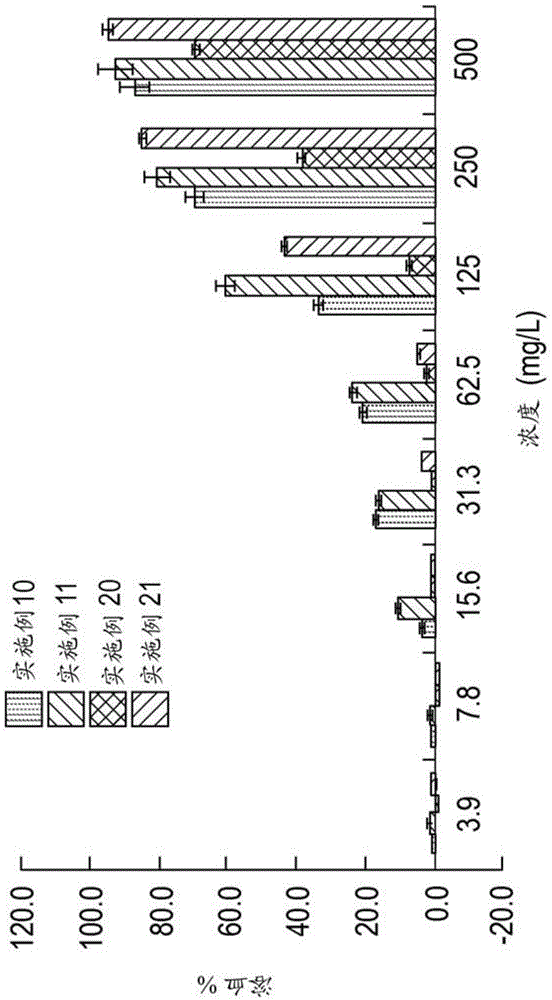
Embodiment 42-50
[0675] Examples 42-50. Using MTC-PrBr and MTC-BnCl precursors for the cationic carbonate repeat unit, MTC-VitE as the hydrophobic comonomer, benzyl alcohol (BnOH) initiator, and DBU / Preparation of random cationic copolymers with thiourea. Quaternization with trimethylamine or N-substituted imidazoles. The reaction sequence is shown in Scheme 2.
[0676] Scenario 2.
[0677]
[0678] Example 50 is representative. MTC-BnCl (608.8 mg, 2.04 mmol, 30 equiv), MTC-VitE (40.0 mg, 68 micromol, 1.0 equiv) and TU (25.2 mg, 68 mol, 1.0 eq) was dissolved in dichloromethane (3 mL). To this solution, BnOH (7.0 μl, 68 μmol, 1.0 equiv) was added followed by DBU (10.2 μl, 68 μmol, 1.0 equiv) to initiate polymerization. The reaction mixture was allowed to stir at room temperature for 20 minutes and quenched by adding excess (-20 mg) of benzoic acid. The mixture was then precipitated into ice-cold methanol (50 mL) and centrifuged at -5°C for 30 minutes. The resulting translucent oil wa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com