Technology of producing monosodium glutamate from potato starch
A monosodium glutamate and starch technology, applied in food preparation, food science, food ingredients and other directions, can solve the problems of difficulty in achieving high-purity salt-free monosodium glutamate, complex processes, and many impurities in the finished product, and achieve cost savings, high fermentation efficiency, and fermentation time. short effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
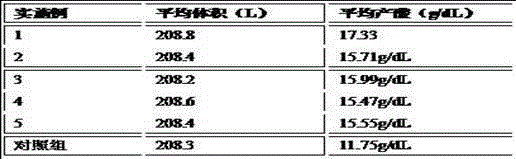
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] A kind of manufacturing process of potato starch making monosodium glutamate:
[0023] (1) Preparation of starch hydrolyzed sugar: Add water to potato starch with a fineness greater than 60 mesh to make a slurry, and adjust the concentration of the slurry to 15 degrees Baume; adjust the pH to 6.8, and add medium-temperature α-amylase according to 0.6% of the weight of potato starch , heat the slurry to 60°C and keep it for 50 minutes; then add 0.2% xylanase and 0.2% β-glucanase by starch weight to the slurry, keep it at 55°C, and the enzymolysis time is 80 minutes, and the powder Heat the slurry to 85°C for 15 minutes; then add 0.3% starch by weight, add glucoamylase, control the temperature at 60°C, maintain for 10 hours, then heat to 80°C for 15 minutes, and filter to obtain the starch enzymatic hydrolysis solution;
[0024] (2) Configure fermentation medium: starch enzymolysis solution 260ml / L, corn steep liquor 50g / L, sunflower oil: 0.5g / L, potassium dihydrogen sulf...
Embodiment 2
[0028] A kind of manufacturing process of potato starch making monosodium glutamate:
[0029] (1) Preparation of starch hydrolyzed sugar: Add water to potato starch with a fineness greater than 60 mesh to make a slurry, and adjust the concentration of the slurry to 15 degrees Baume; adjust the pH to 6.8, and add medium-temperature α-amylase according to 0.6% of the weight of potato starch , heat the slurry to 60°C and keep it for 60 minutes; then add 0.1% xylanase and 0.2% β-glucanase by starch weight to the slurry, keep it at 55°C, and the enzymolysis time is 100 minutes, and the powder Heat the slurry to 85°C for 15 minutes; then add 0.2% starch by weight, add glucoamylase, control the temperature at 65°C, maintain for 8 hours, then heat to 80°C for 15 minutes, and filter to obtain the starch enzymatic hydrolysis solution;
[0030] (2) Configure fermentation medium: starch enzymolysis solution 318ml / L, corn steep liquor 40g / L, sunflower oil: 0.5g / L, potassium dihydrogen sulf...
Embodiment 3
[0034] A kind of manufacturing process of potato starch making monosodium glutamate:
[0035] (1) Preparation of starch hydrolyzed sugar: Add water to potato starch with a fineness greater than 60 mesh to make a slurry, and adjust the concentration of the slurry to 15 degrees Baume; adjust the pH to 6.8, and add medium-temperature α-amylase according to 0.6% of the weight of potato starch , heat the slurry to 60°C and keep it for 55 minutes; then add 0.2% xylanase and 0.2% β-glucanase by starch weight to the slurry, keep it at 55°C, and the enzymolysis time is 90 minutes, and the powder Heat the slurry to 85°C for 15 minutes; then add 0.3% of the weight of starch, add glucoamylase, control the temperature at 61°C, maintain for 9 hours, then heat to 80°C for 15 minutes, and filter to obtain the starch enzymatic hydrolysis solution;
[0036] (2) Configure fermentation medium: starch enzymolysis solution 290ml / L, corn steep liquor 45g / L, sunflower oil: 0.5g / L, potassium dihydroge...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com