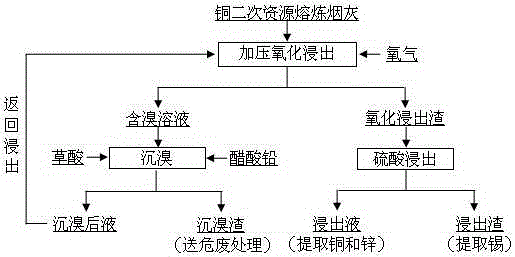
Treatment method of copper secondary source smelting soot
A technology for secondary resources and treatment methods, which is applied in the field of effective treatment of copper secondary resource smelting soot, which can solve problems such as high reactor pressure, polluted operating environment, and easy volatilization of ammonia water, and achieves inhibition of dissolution, low corrosion, and environmental friendliness Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Copper secondary resource smelting soot finely ground to a particle size of less than 0.149mm, its main components are (%): Cu4.09, Zn33.98, Br1.48, Sn6.06 and Pb22.68; industrial grade sodium hydroxide, of which Sodium hydroxide content ≥ 96%; industrial grade sulfuric acid, of which H 2 SO 4 Content ≥ 98%; industrial grade oxygen, of which O 2 Content ≥ 99%; industrial grade oxalic acid, of which H 2 C 2 o 4 Content ≥ 99.5%; industrial grade lead acetate, of which C 4 h 6 o 4 Pb·3H 2 O content ≥ 98%.
[0021] Weigh 8g of industrial-grade sodium hydroxide and make a solution with 1000ml of water, then add 200g of copper secondary resource smelting soot of the above components to make slurry, put the slurry solution into the high-pressure reactor, seal the reactor and start stirring to heat up, when the reactor When the temperature rises to 120°C, start to feed oxygen, control the partial pressure of oxygen to be 0.20MPa, cool down after 3 hours of reaction, an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com