Polylactic acid-bacterial cellulose composite material and preparation method thereof
A technology of bacterial cellulose and composite materials, applied in the field of biomaterials, can solve problems such as poor interface adhesion and thermodynamic incompatibility, and achieve the effects of reduced water absorption, high tensile strength and bending strength, and excellent mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
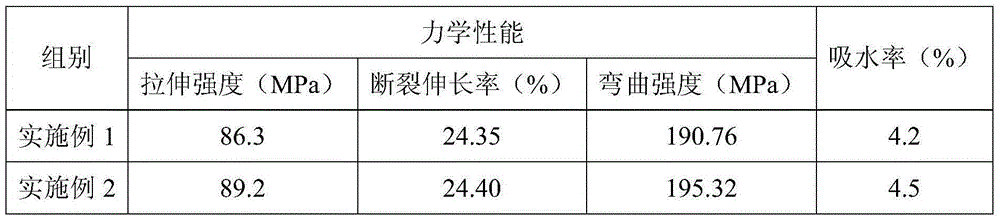
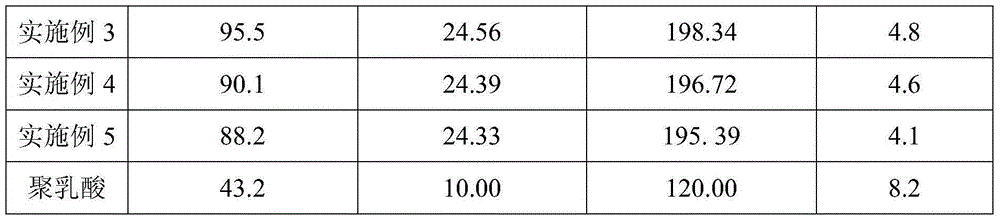
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] A polylactic acid-bacterial cellulose medical composite material, comprising the following components in parts by weight: 36 parts of polylactic acid, 34 parts of bacterial cellulose, 6 parts of graphene, 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphoryl 0.1 part of choline, 2 parts of proanthocyanidin, 2 parts of polyethylene glycol, 0.2 part of calcium chloride, 1 part of calcium stearate and 1 part of bentonite.
[0019] The preparation method comprises the steps of:
[0020] (1) Dry the polylactic acid in an oven at 50°C until the quality is constant, and set aside;
[0021] (2) The dried polylactic acid, bacterial cellulose and graphene are ultrafinely pulverized in step (1), mixed evenly, put into ethanol, and stirred rapidly to make a dispersion;
[0022] (3) Mix the polylactic acid dried in step (2) and other raw materials evenly, add them to the co-rotating twin-screw compounding extruder to extrude and granulate, and set the temperature of each section of the extruder to 100...
Embodiment 2
[0024] A polylactic acid-bacterial cellulose medical composite material, comprising the following components in parts by weight: 40 parts of polylactic acid, 40 parts of bacterial cellulose, 8 parts of graphene, 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphoryl 5 parts of choline, 3 parts of proanthocyanidin, 3 parts of polyethylene glycol, 0.4 part of calcium chloride, 2 parts of calcium stearate and 2 parts of mica.
[0025] The preparation method comprises the steps of:
[0026] (1) Dry the polylactic acid in an oven at 50°C until the quality is constant, and set aside;
[0027] (2) The dried polylactic acid, bacterial cellulose and graphene are ultrafinely pulverized in step (1), mixed evenly, put into ethanol, and stirred rapidly to make a dispersion;
[0028] (3) Mix the polylactic acid dried in step (1) and the remaining raw materials in step (2) evenly, and add them to the co-rotating twin-screw compounding extruder to extrude and granulate, and the temperature of each section of the...
Embodiment 3
[0030] A polylactic acid-bacterial cellulose medical composite material, comprising the following components in parts by weight: 41 parts of polylactic acid, 42 parts of bacterial cellulose, 9 parts of graphene, 2-methacryloxyethyl phosphoryl 6 parts of choline, 3 parts of proanthocyanidin, 3 parts of polyethylene glycol, 0.5 part of calcium chloride, 2 parts of calcium stearate and 2 parts of kaolin.
[0031] The preparation method comprises the steps of:
[0032] (1) Dry the polylactic acid in an oven at 55°C until the quality is constant, and set aside;
[0033] (2) The dried polylactic acid, bacterial cellulose and graphene are ultrafinely pulverized in step (1), mixed evenly, put into ethanol, and stirred rapidly to make a dispersion;
[0034] (3) Mix the polylactic acid dried in step (1) and the remaining raw materials in step (2) evenly, and add them to the co-rotating twin-screw compounding extruder to extrude and granulate, and the temperature of each section of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com