Negative selection marker for escherichia coli gene knock-in
An Escherichia coli, gene knock-in technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as increasing workload
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
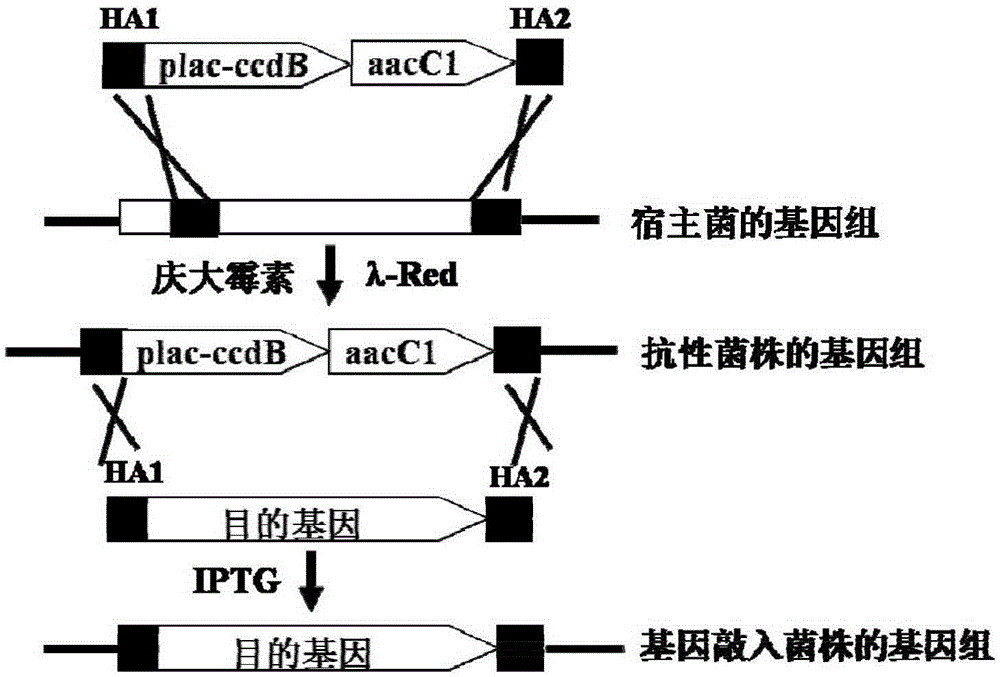
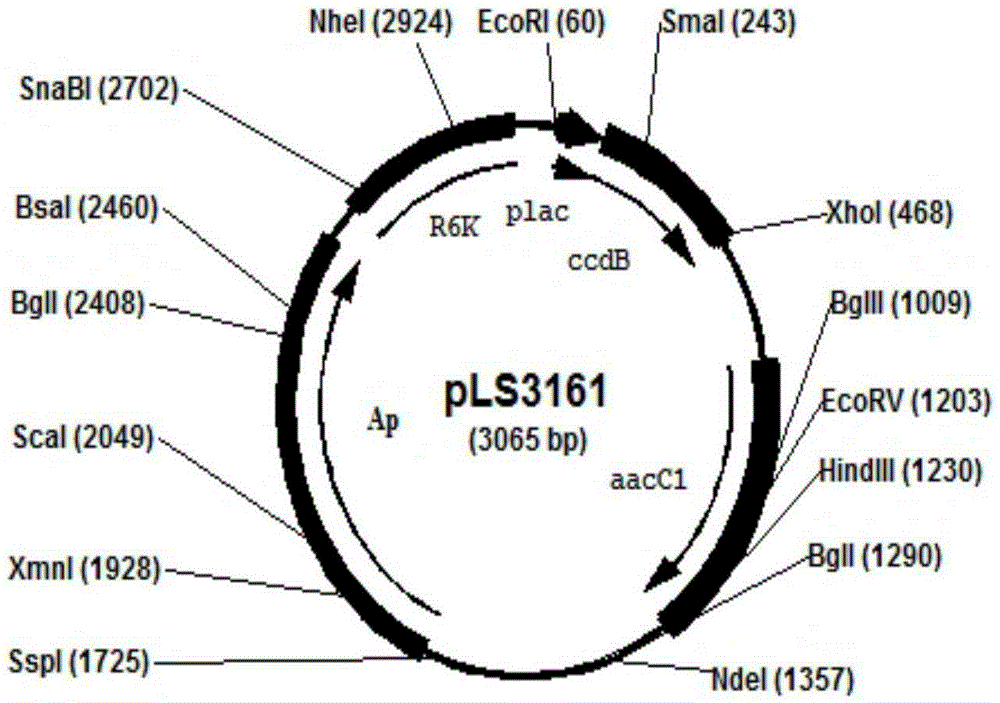
[0039] Example 1. Construction of the plac-ccdB-aacC1 gene cassette
[0040] The plac-ccdB fragment was first PCR amplified. Design primer R2101: 5'-GTATGTTGTGTGGAATTGTGAGCGGATAACAATTTCACACAGGAAACAGCTATGCAGTTTAAGGTTTACACC-3', (SEQ ID NO.1), R2102: 5'-GGA CTCGAG TTATATTCCCCCAGAACATCAGG-3', (SEQ ID NO. 2), R2103: 5'-G GAATTC TCACTCATTAGGCACCCCAGGCTTTACACTTTATGCTTCCGGCTCGTATGTTGTGTGGAATTGTGAGC-4', (SEQ ID NO. 3), restriction sites XhoI and HindIII are underlined. Using pMK2010 as a template, PR2101 and R2102 PCR amplified the 3' end of plac and ccdB gene of 363 bp, purified the 363 bp, and used it as a template, PCR amplified R2103 and R2102 to obtain a complete 414 bp of plac and ccdB gene. Secondly, aacC1 (gentamycin resistance gene) fragment was amplified by PCR. Design primer R2104: 5'-GGA CTCGAG TCGAATTGACATAAGCCTGTTC, (SEQ ID NO. 4), R2105: 5'-C AAGCTT TTAGGTGGCGGTACTTGGGTC, (SEQ ID NO.5), restriction sites XhoI and EcoRI are underlined. Using pBAD322G as a templa...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Example 2. Knock-in of the I-SceI gene to the uidA site of Escherichia coli MG1655
[0043] Escherichia coli MG1655 is a model Escherichia coli strain, and it is also a commonly used gene manipulation strain, so it has good applicability to carry out the negative screening function test of the present invention. The I-SceI gene is a homing nuclease, and its recognition site is 18 base pairs TAGGGATAA↓CAGGGTAAT- (representing the enzyme cutting site). Knocking it into the genome is beneficial to the gene shearing experiment of the resulting strain.
[0044] Design primers R2111: 5'-CCTTCCCGGCTTCGGAGAATTCCCCCCAAAATATTCACTGTAGCCATATGCTCACTCATTAGGCACCCCAG, (SEQ ID NO. 8), R2112: 5'-GTCCAGCGTTTTTGCAGCAGAAAAGCCGCCGACTTCGGTTTGCGGTCGCGTTAGGTGGCGGTACTTGGGTC, (SEQ ID NO. 9). Using pLS3161 as a template, R2111 and R2112 were amplified to obtain a 1265bp linear DNA fragment, which was recovered by ethanol precipitation and washed with ddH 2 O dissolved. Escherichia coli MG1655 co...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Example 3. Knock-in of the pir gene into the lacZ site of Escherichia coli MG1655
[0047] Because the genotype of Escherichia coli DB3.1λpir is not clear, and the transformation efficiency is low, the second embodiment of this method is about to knock the pir gene into the genome of Escherichia coli MG1655, and the gained bacterial strain helps to contain the R6K replicon plasmid. clone.
[0048] Design primers R2117: 5'-GCGTGGGCGTATTCGCAAAGGATCAGCGGGCGCGTCTCTCCAGGTAGCGACTCACTCATTAGGCACCCCAG, (SEQ ID NO. 14), R2118: 5'-GCTGCTGCTGAACGGCAAGCCGTTGCTGATTCGAGGCGTTAACCGTCACGTTAGGTGGCGGTACTTGGGTC, (SEQ ID NO. 15). Using pLS3161 as a template, R2117 and R2118 were amplified to obtain a 1265bp linear DNA fragment, which was recovered by ethanol precipitation and washed with ddH 2 O dissolved. Electroporation competent cells of the MG1655 strain expressing the recombinase were prepared as above, 1 μg of DNA fragments were electroporated, and 1020 clones were obtained under the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com