Application of S-(carboxymethyl)-L-cysteine to preparation of medicines for preventing and treating respiratory system diseases
A respiratory system disease, cysteine technology, applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problem that the influence of NF-κB signaling pathway has not been seen, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
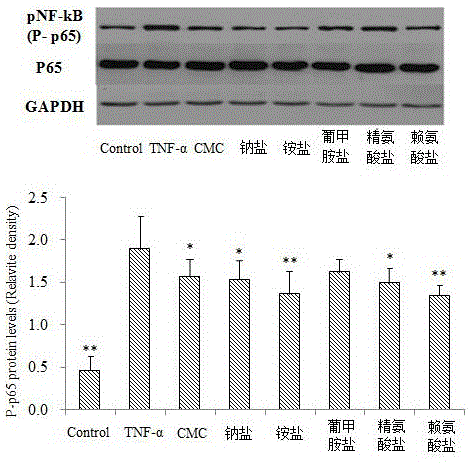
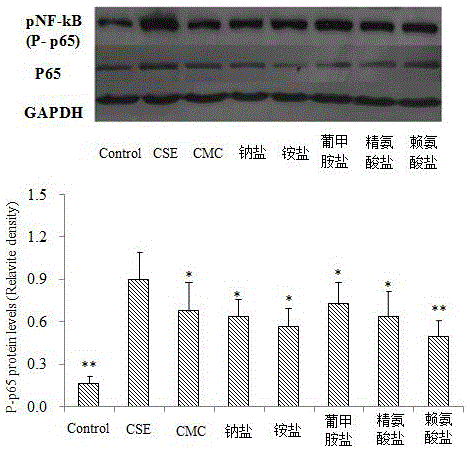
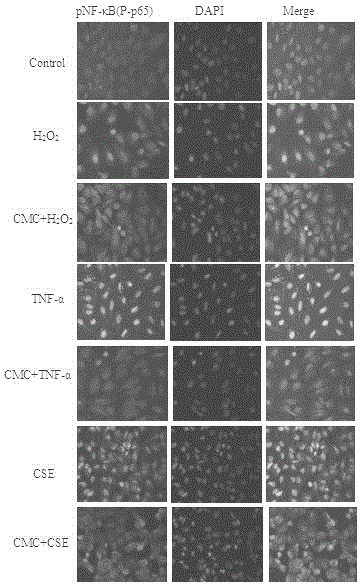
[0029] Example 1 CMC inhibits the expression of NF-κB and the release of IL-6 and IL-8
[0030] 1 Experimental method
[0031] 1.1 Western blot and ELISA method
[0032] A549 cells were cultured in RPMI-1640 containing 10% fetal bovine serum at 37°C and 5% CO 2 cultured in an incubator. Cells in the logarithmic growth phase were taken, and after trypsinization, the cell concentration was adjusted to 1×10 with RPMI-1640 6 cells / mL, inoculated in 6-well culture plate, after 12 hours of attachment, starved overnight, divided into H according to different treatments 2 o 2 Group (or TNF-α, CSE group), CMC group and its salt (add CMC or its salt, pre-incubation for 24h), control group added equal volume of PBS. The culture supernatant was taken, and the contents of IL-6 and IL-8 were determined by ELISA. At the same time, cells were collected, BCA protein quantification kit was used to measure protein concentration, 25 μg protein was quantitatively loaded, run on SDS polya...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Example 2 Inhibitory effect of CMC on the expression of NF-κB and the release of IL-6 and IL-8 in mice with acute lung injury
[0043] 1 Experimental method
[0044] Sixty male C57BL / 6 mice were randomly divided into 4 groups, namely normal group, model group, CMC group and ammonium salt group, with 15 mice in each group. The normal group and the model group were fed with 0.5% sodium carboxymethylcellulose, and the other groups were given corresponding drugs (suspension or dissolution of sodium carboxymethylcellulose). Continuous administration for 15 days.
[0045] 24 hours after the last administration, the mice in the normal group were intraperitoneally injected with the same amount of normal saline, and the other mice were injected with lipopolysaccharide (10 mg / kg body weight). Six hours after the above treatment, the mice were killed, and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF ), to determine the content of IL-6 and IL-8; after the lungs were taken to prepare ti...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Example 3 Inhibitory effect of CMC on expression of NF-κB and release of IL-6 and IL-8 in mice with bronchial asthma
[0049] 1 Experimental method
[0050] Sixty male BALB / c mice were randomly divided into 4 groups, namely normal group, model group, CMC group and ammonium salt group, with 15 mice in each group. The mice in the latter three groups were intraperitoneally injected with a mixed solution of 2% OVA and aluminum hydroxide (dissolved in 0.2mL PBS) on days 0, 7, and 14; Nebulization challenge, 1 time / day, 7 days in total. The normal group was sensitized and challenged with an equal amount of normal saline. From the 21st day, each group was intragastrically administered half an hour before the nebulization challenge (the normal group and the model group were administered with the same amount of normal saline). Within 24 hours of the last challenge, the mice were sacrificed, and the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) was collected to determine the content...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com