Reducing method for lead dioxide in waste lead plaster
A technology of lead dioxide and waste lead paste, which is applied in the field of resource recycling, can solve problems such as high cost, easy decomposition, and secondary pollution, and achieve the effects of reducing energy consumption, reducing impurities, and increasing recovery rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0032] Preparation of calcium bisulfite suspension:
[0033] The calcium hydroxide suspension with a solid content of 15% was fed into commercially available sulfur dioxide or sulfur-containing flue gas, and reacted for 30 minutes under stirring at 100 rpm to prepare a 1.5 mol / L calcium bisulfite suspension for later use.
Embodiment 1
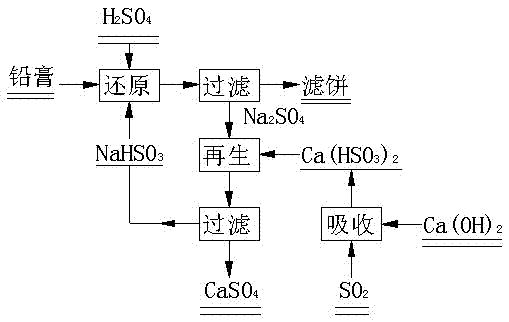
[0035] (1) Reduction reaction
[0036] Using NaHSO 3 As a reducing agent, weigh 10g of the prepared lead paste, add 100mL of water, mix well and add 3g of NaHSO 3 , add 10mL of 20% H 2 SO 4 When the stirring speed was 700 rpm, the reaction was carried out at room temperature for 90 min, and the product slurry was separated by filtration to obtain 102 mL of solution, 9 g of solid, and the reduction rate of lead dioxide was 92%.
[0037] (2) Regeneration reaction
[0038] Add 20ml of 1.5mol / L calcium bisulfite suspension to the 102mL solution obtained from the reduction reaction, react for 30min under stirring at 100rpm, filter the obtained solution for the preparation of lead plaster slurry, and collect and store the calcium sulfate filter cake.
Embodiment 2
[0040] (1) Reduction reaction
[0041] Take by weighing prepared lead plaster 10g, add the 102mL solution that obtains in the embodiment 1, add the H of 10mL20% 2 SO 4 The reaction was carried out at room temperature for 90 min at a stirring speed of 700 rpm, and the product slurry was filtered and separated to obtain 104 mL of solution, 9.2 g of solid, and the reduction rate of lead dioxide was 93%.
[0042] (2) Regeneration reaction
[0043]Add 20ml of 1.5mol / L calcium bisulfite suspension to the 104mL solution obtained from the reduction reaction, react for 30min under stirring at 100rpm, filter the obtained solution for the preparation of lead plaster slurry, and collect and store the calcium sulfate filter cake.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| quality score | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com