Electrolyte taking propylene carbonate as main solvent and secondarily liquid injected lithium ion battery
A technology of propylene carbonate and lithium-ion batteries, applied in the field of lithium-ion batteries, can solve problems affecting battery performance, poor cycle performance, and low reversible capacity of batteries, and achieve good compatibility and wide application range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] 1. Electrolyte preparation: The electrolyte is prepared in a BRAUN glove box filled with nitrogen gas with a purity of 99.999%, the moisture in the glove box is controlled at ≤5ppm, and the temperature is at room temperature. Mix the solvent system with a mass ratio of EC:PC:=1:9 evenly, seal it, put it in the refrigerator until it cools down to 8°C, transfer it to the glove box, and then add LiPF in two batches 6 Mix well to form a non-aqueous electrolyte solution for lithium-ion batteries with a molar concentration of lithium salt of 2.6mol / L, add a conventional additive 1% VC to the above non-aqueous electrolyte solution, and mix uniformly to obtain a lithium-ion non-aqueous electrolyte solution.
[0027] 2. Preparation of positive electrode for lithium-ion battery: Dissolve polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) with a mass percentage of 3% in 1-methyl-9-pyrrolidone solution, and lithium cobaltate (LCO) with a mass percentage of 96% The conductive agent carbon black with a ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2 The first liquid injection volume is 60%, the second injection volume is 40% after formation, the conventional electrolyte solution for the second injection is EC:EA=1:1, the concentration is 1M, and the solvent is LiPF 6 .
Embodiment 3
[0034] Example 3 The first injection volume is 90%, the second injection volume is 10% after formation, the second injection electrolyte is EC:EA=3:7, the concentration is 1M, and the solvent is LiPF 6 .
[0035] The amount of liquid injected for the first time in Comparative Examples 1-4 was 100%, and no liquid was injected after formation.
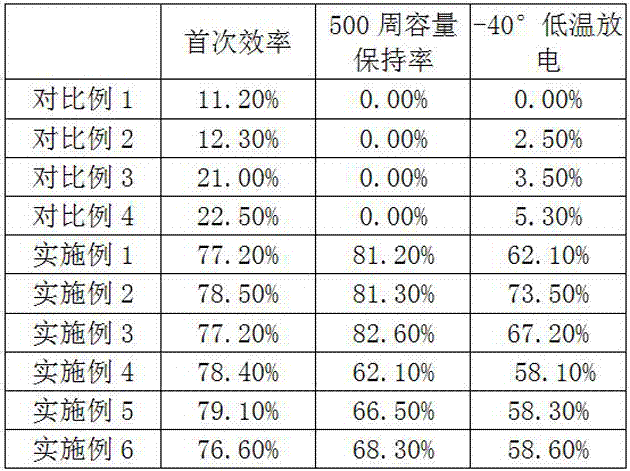
[0036] As shown in Table 1 to Table 3, the various indicators and performance tests of the embodiments and comparative examples carried out by the present invention are as shown in the table.
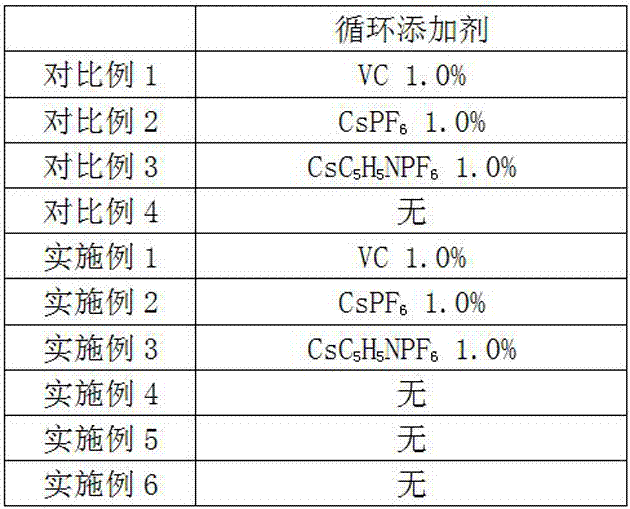
[0037] Table 1: Comparison table of positive and negative electrodes and solvent materials and contents of batteries used in Comparative Examples 1-4 and Examples 1-6.
[0038]
[0039] Note: LMO, lithium manganese oxide; LFP, lithium iron phosphate; LCO, lithium cobalt oxide.
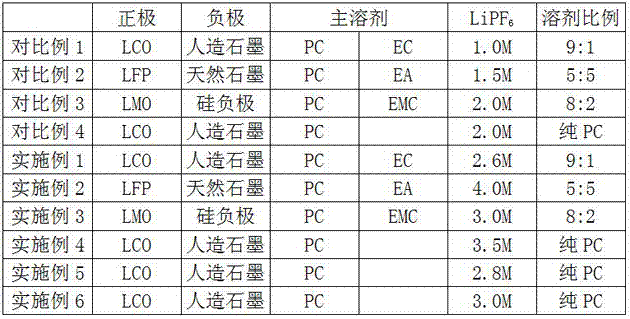
[0040] Table 2: LiPF used in Comparative Examples 1-4 and Examples 1-6 6 Concentration, additives and additive dosage comparison table.
[0041]
[0042] Table 3...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com