Treatment method of waste water generated in condensation reaction during disperse blue 56 production process
A technology of production process and treatment method is applied in the field of treatment of condensation wastewater in the production process of disperse blue 56, and achieves the effects of simple process, mild conditions, and safe and efficient method.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
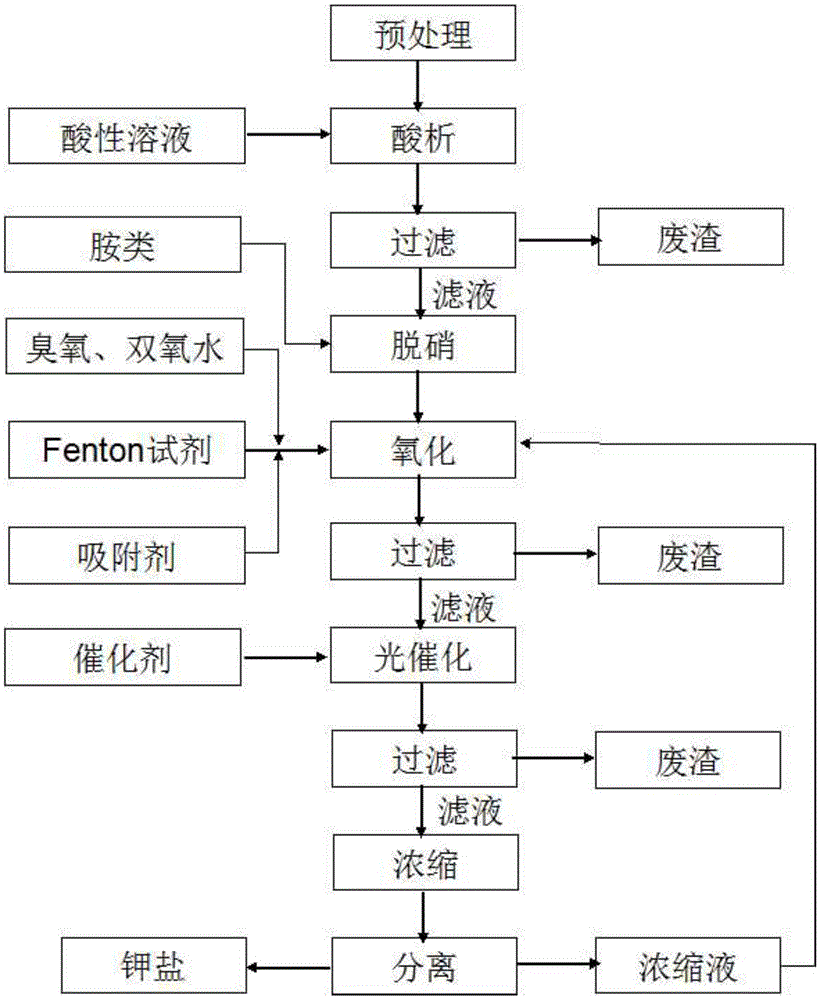
[0050] The condensation waste water produced in the production process of Disperse Blue 56 is preliminarily filtered, and the measured pH is 11, COD is about 89154mg / L, containing 1.5% of potassium hydroxide (based on the quality of waste water), and 11% of potassium nitrite (based on the quality of waste water). waste water quality as the benchmark).
[0051] (1) Pretreatment: Heat the wastewater to 50° C., keep stirring and react for 1.5 hours to obtain solution I. Colorless gas is produced during the reaction, and the waste water is still black and opaque after the reaction.
[0052] (2) Acid analysis: Add the waste acid produced by the primary nitrification in the production process of Disperse Blue 56 to the pretreated waste water (solution I), adjust the pH to 0.5, and filter after acid analysis with aeration at 70°C for 1 hour to obtain Filtrate I and waste residue. During the reaction, a reddish-brown gas is produced, which is absorbed by a mixed solution of sodium h...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Keeping the other conditions in Example 1 unchanged, removing the photocatalytic step, and directly concentrating, it was found that the solution gradually turned yellow during the concentration process, resulting in a slightly yellow isolated potassium sulfate salt with a purity of 92.8%, and COD of condensed water=33mg / L, nitrate nitrogen is 16mg / L.
Embodiment 3
[0064] The condensation waste water produced in the production process of Disperse Blue 56 is preliminarily filtered, and the measured pH is 11, COD is about 89154mg / L, containing 1.5% of potassium hydroxide (based on the quality of waste water), and 11% of potassium nitrite (based on the quality of waste water). waste water quality as the benchmark).
[0065] (1) Pretreatment: Heat the wastewater to 50° C., keep stirring and react for 1 hour to obtain solution I.
[0066] (2) Acid analysis: the pretreated waste water (solution I) was added with nitrification waste acid once to adjust the pH to 0.5, aerated at 70° C. for 1 hour and then filtered to obtain filtrate I and waste residue. During the reaction process, a reddish-brown gas is produced, which is sequentially absorbed with sodium hydroxide and sodium carbonate solutions; after the reaction is completed, filter, and the waste water COD=4801mg / L.
[0067] (3) Denitrification: add sulfamic acid to the filtrate I, and sti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com