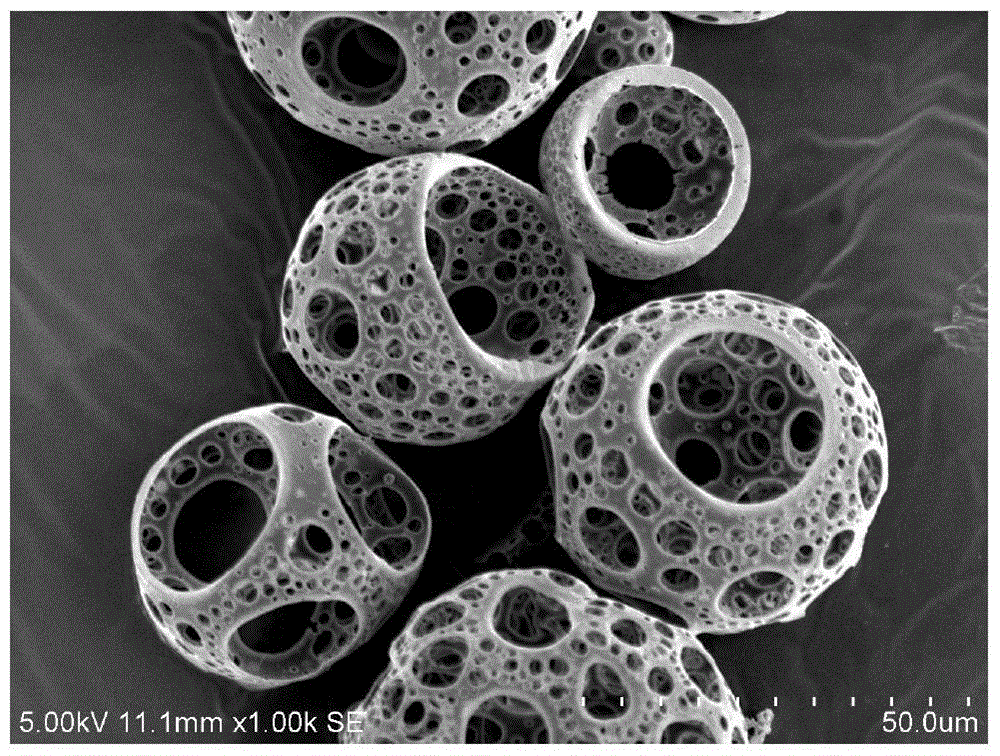
Method for preparing PLGA microspheres with porous surfaces
A technology with porous surface and microspheres, which is applied in the fields of medical science and prostheses, can solve the problems such as hard-to-form pores, achieve good sphericity, uniform shape and structure, and shorten the emulsification time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0027] Such as figure 1 Shown, the surface porous PLGA microsphere preparation method provided by the invention comprises:
[0028] S110: Add PLGA to the organic solvent, stir to dissolve, then drop into the porogenic solution, and ultrasonically emulsify to form an emulsion; wherein, the molar ratio of LA and GA of the PLGA ranges from 50:50 to 90:10 ;
[0029] S120: Add the emulsion to the stirred external water phase drop by drop, and add a preset volume of deionized water, change the speed and continue stirring until the organic solvent is completely volatilized, wherein the external water phase is a water-soluble surfactant added to remove ionized water;
[0030] S130: Centrifuge the solution after the organic solvent is completely volatilized, wash it with deionized water, remove the supernatant, and obtain PLGA microspheres;
[0031] S140: adding the NaOH solution into the PLGA microspheres, mixing evenly, and putting it on a shaker to continue the reaction;
[0032...
example 1
[0041] This embodiment takes the following steps:
[0042] 1) Add 100mg of PLGA (50:50) into 10mL of dichloromethane, and keep stirring until it is completely dissolved;
[0043] 2) Prepare 1wt% PVA solution (Mw=80000), draw 1mL PVA solution with a pipette gun, and add it dropwise to the oil phase in step 1) under the condition of ultrasonic intensity of 24W to form a water-in-oil emulsion , ultrasonic time 60s;
[0044] 3) Add the emulsion obtained in step 2) into 30mL of PVA aqueous solution under stirring, the stirring rate is 800rpm, after stirring for 30min, add 300mL of deionized water, change the stirring rate to 400rpm, and continue stirring for 4h until Dichloromethane is completely volatile.
[0045] 4) The PLGA microspheres were collected by centrifugation, and washed three times with deionized water at a rotation speed of 4500 rpm for 10 min.
[0046] 5) Add NaOH with a mass volume ratio of 1% and a concentration of 0.2M to the PLGA microspheres obtained in step...
example 2
[0049] This embodiment takes the following steps:
[0050] 1) Add 80mg of PLGA (65:35) into 12mL of chloroform, and keep stirring until it is completely dissolved;
[0051] 2) Prepare a 1wt% BSA solution, absorb 1mL of the BSA solution with a pipette gun, and add it dropwise to the oil phase in step 1) under the condition of an ultrasonic intensity of 32W to form a water-in-oil emulsion, and the ultrasonic time is 50s;
[0052] 3) Add the emulsion obtained in step 2) into 30mL PVA 1wt% aqueous solution under stirring, the stirring rate is 800rpm, after stirring for 30min, add 300mL deionized water therein, change the stirring rate to 400rpm, continue stirring for 4h, until the chloroform is completely evaporated.
[0053] 4) The PLGA microspheres were collected by centrifugation, and washed three times with deionized water at a rotation speed of 4500 rpm for 10 min.
[0054] 5) Add NaOH with a mass volume ratio of 1% and a concentration of 0.2M to the PLGA microspheres obtai...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com