Application of syringaldehyde in the preparation of protective drugs for intestinal damage caused by ionizing radiation
A technology of ionizing radiation and syringaldehyde is applied in the directions of drug combination, aldehyde active ingredients, digestive system, etc., which can solve the problems of low activity, high concentration, toxic and side effects, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Firstly, a mouse model of intestinal injury induced by radiation was established. C57BL / 6 mice aged 6-8 weeks, half male and half male (body weight 25±2g), were randomly divided into two groups: 8 mice in the irradiation group (10Gy) and syringaldehyde mice before irradiation. There were 8 mice in the administration group (10Gy+syringaldehyde); the whole body of the mice was uniformly irradiated with a single X-ray irradiation machine, and the absorbed dose of the mice was 10Gy. The syringaldehyde was dissolved in 0.5% sodium carboxymethylcellulose aqueous solution with a mass concentration of 0.5%, wherein the concentration of syringaldehyde was 5mg / ml, and the mice in the syringaldehyde administration group were administered by intragastric administration (dosage according to body weight: 100mg / kg) Irradiation was carried out 1 hour later, and the mice in the irradiation group were given an aqueous solution of 0.5% sodium carboxymethylcellulose in the same volume and m...
Embodiment 2
[0030] The rat intestinal epithelial cell IEC-6, which is more recognized in the research of intestinal injury in vitro, was selected as the model. Dissolve syringaldehyde in dimethyl sulfoxide, the concentration of the mother solution is 40mmol / L, and prepare and use syringaldehyde solutions with concentrations of 5, 10, 20, and 40μmol / L respectively by the method of serial dilution, and the dilution is for culturing cells DMEM medium. The control group was treated with an equal volume of DMSO in 40 μmol / L syringaldehyde solution. IEC-6 cells were seeded in a 96-well plate. When the cells were in the logarithmic growth phase, the above-mentioned different concentrations of syringaldehyde solution and dimethyl sulfoxide were added respectively. After 72 hours of treatment, CCK8 (purchased from Beyond Biotechnology Co., Ltd., operated The method followed the instructions) to detect cell growth. The results are attached figure 2 As shown, 40 μmol / L syringaldehyde still did n...
Embodiment 3
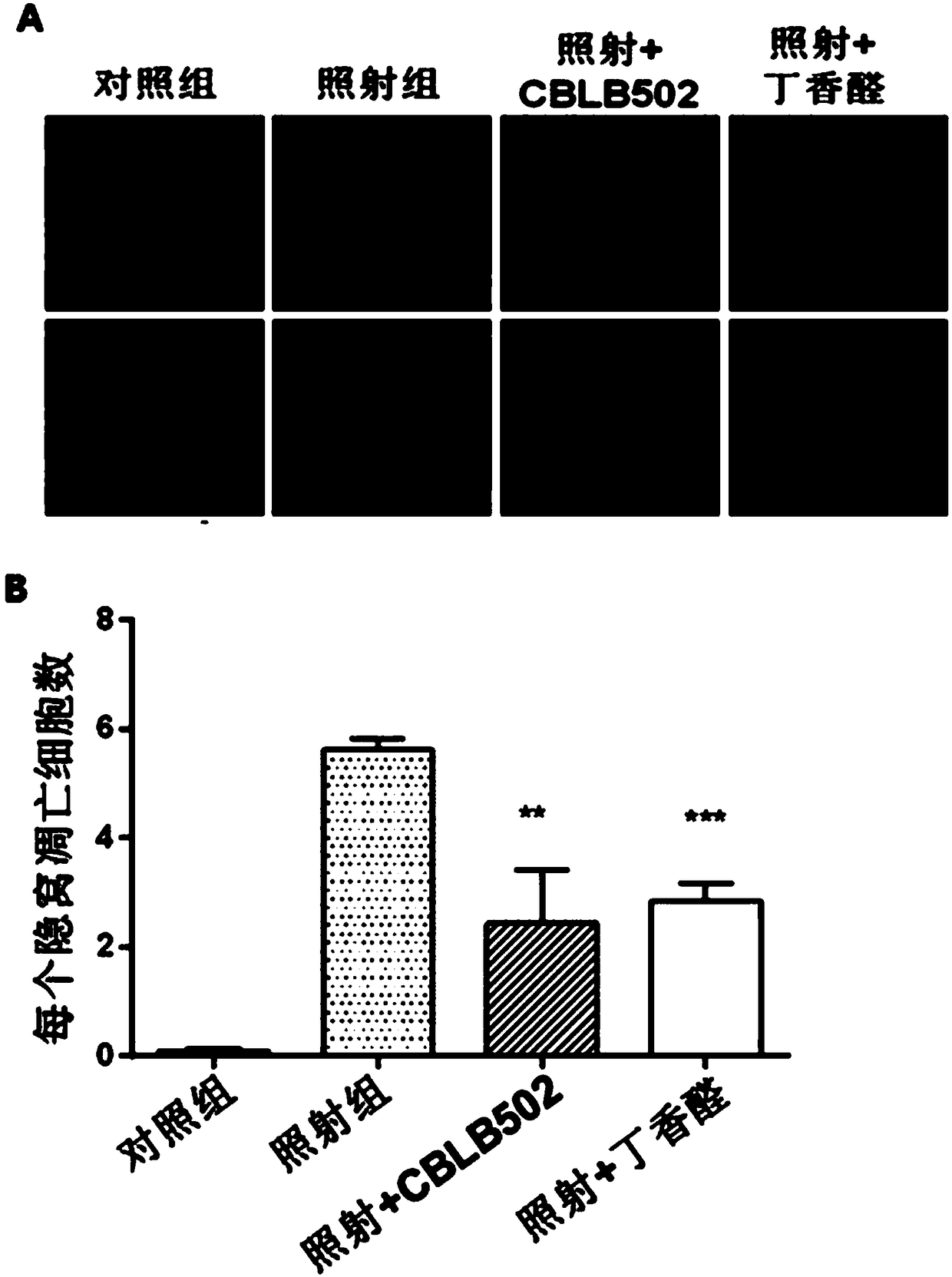
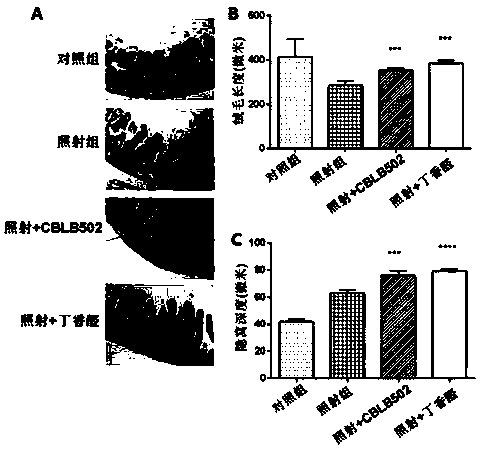
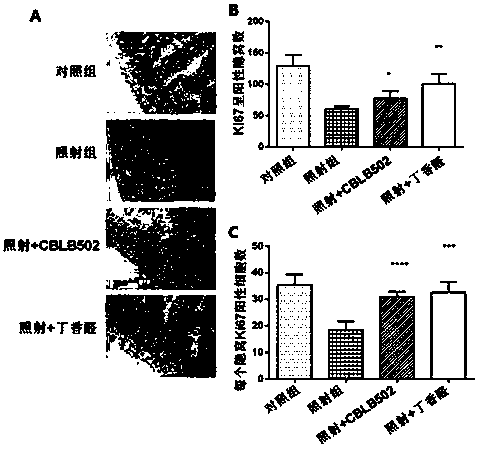
[0032] (1) Firstly, a mouse model of intestinal injury induced by cobalt-60γ-rays was established. Select 6-8 weeks old C57BL / 6 mice, half male and half male (body weight 25±2g), and randomly divide them into four groups: 6 mice in the blank group without irradiation treatment, 6 mice in the normal feeding group, 6 mice in the irradiation group, and syringaldehyde before irradiation. There were 6 rats in the drug group (irradiation + syringaldehyde), and 6 rats in the positive control flagellin administration group (irradiation + CBLB502) before irradiation. The mice were uniformly irradiated with a cobalt-60γ-ray source, and the absorbed dose of the mice was 9Gy. The syringaldehyde was dissolved in 1% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose aqueous solution in which the concentration of syringaldehyde was 10mg / ml, and the mice in the syringaldehyde administration group were administered by intragastric administration (dosage according to body weight: 100mg / kg) Irradiation was carried...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com