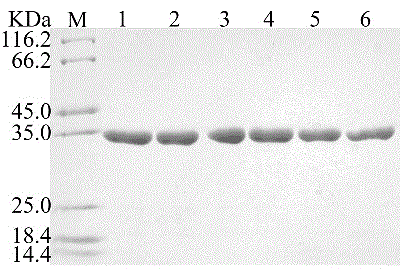
Symbiobacterium thermophilum meso-diaminopimelate dehydrogenase mutants
A technology of diaminopimelate dehydrogenase and mutants, which is applied in the field of protein engineering and can solve problems such as research reports without the preference modification of DAPDH family enzymes and coenzymes.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Example 1: Gene mutation
[0019] Used St Dapdh The Genbank number of the gene is AP006840.1. First, the gene is fully synthesized and connected to the pET32 vector to obtain a plasmid: pET32- St Dapdh , and soluble express the wild-type gene in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3), and the N-terminus of the expressed protein has 6*histag. According to the site to be mutated, refer to the instructions of the QuickChangeMutagenesisKit kit, synthesize the PCR mutation primers used in Table 1, extract the plasmid DNA from the wild-type strain, and use it as a template to amplify the PCR product. Dpn1 cutting, nucleic acid recovery after cutting and transformation into TOP10 competent, single colonies were picked and sent for sequencing, and for the samples with correct sequencing, the BL21 strain was transformed.
[0020] Table 1: Mutant PCR Primers
[0021]
[0022] by p ET32- St Dapdh The plasmid was used as a template, and primers 1 and 2 were used to introduce th...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Example 2: Expression and preliminary purification of mutant enzymes
[0024] The mutant strains obtained in Example 1 were cultured in 2LLB liquid medium, and cultured at 37°C to OD 600 After about 0.8, add isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) at a final concentration of 0.5 mM to induce expression, the induction temperature is 25°C, and the induction time is 20 hours. After induction of expression, the cells were collected by centrifugation at 5000 rpm for 5 minutes, resuspended and washed with buffer A (20 mM Tris-Cl pH 8.0, 50 mM sodium chloride), and centrifuged again. All subsequent purification experiments were performed at 4°C, and all buffers were pre-cooled to 4°C. Resuspend the washed cells with 100mL of buffer A, homogenate under high pressure, and centrifuge at 14,000rpm for 30 minutes to remove the broken precipitate. B (20mM Tris-Cl pH8.0, 50mM imidazole, 500mM sodium chloride) removes impurity proteins, and buffer C (20mM Tris-Cl pH8.0, 250mM imi...
Embodiment 3
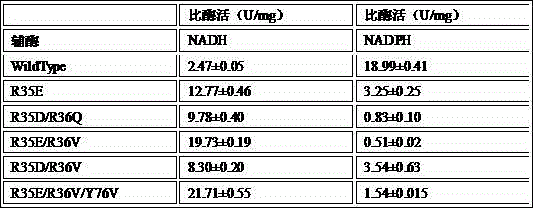
[0025] Example 3: Viability assay of mutants
[0026] The activity of the mutants was determined using a SPECTRAMAXM2e (MD, USA) microplate reader, and the activity measurement system used was as follows: the final concentrations of each component were: 20mM substrate pyruvate, 200mM substrate ammonium chloride, 1mM coenzyme NADH (or NADPH ), an appropriate amount of StDapdh mutant pure enzyme, the assay activity buffer was 100 mM sodium carbonate / sodium bicarbonate buffer solution pH 9.0, and the final volume was 200 μL. The substrate and protein samples were first added to a 96-well plate and equilibrated at 30°C for 10 minutes, then the coenzyme NADH was added to initiate the reaction, and the enzyme activity was determined by measuring the decrease in absorbance at 340nm (the molar extinction coefficient of NADH at 340nm is 6.22 mM -1 ?cm -1 ), the enzyme activity unit is defined as the amount of enzyme required to consume 1 μmol of coenzyme NADH per minute when cataly...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Extinction coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com