Method of using phanerochaete chrysosporium for bio-augmentation treatment of pulping wastewater
A technology for P. trichomes and pulping wastewater, which is applied in biological water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, processing wastewater treatment, etc. It can solve the problems of system balance and stability risks, complex components, and difficulty in achieving effluent quality. , to achieve good economic and social effects, good practicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] A method for utilizing Phanerochaete chrysosporium to biointensify treatment of pulping wastewater, the steps are as follows:
[0027]1) Acclimatization and film formation of activated sludge: Take several 2000 mL beakers to make a bioreactor, add industrial composite filler and activated sludge to it, the concentration of activated sludge is about 20g / L, and add 500mg / L Glucose is used as the carbon source, aeration is carried out, the aeration is stopped for one hour every day, the supernatant is sucked by siphon method, and then the same volume of nutrient water (500mg / L glucose aqueous solution) as the supernatant is added, after a period of aeration , the sludge successfully hangs film.
[0028] 2) Preparation of bacterial liquid: inoculate Phanerochaete chrysosporium into potato liquid culture medium in a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask from an inclined surface to make bacterial suspension, and culture it on a shaker at a constant temperature of 37°C for three to four day...
Embodiment 2
[0033] The method of using Phanerochaete chrysosporium to biointensify the treatment of pulping wastewater is the same as in Example 1, wherein, in the biointensification treatment step, the process parameters are temperature 18°C, pH 7.0, glucose content 300 mg / L, ammonium tartrate content of 0.02 mg / L, Phanerochaete chrysosporium suspension dosage of 100 mL / L and dissolved oxygen of 4 mg / L, measured COD and chromaticity after seven days of continuous reaction. Under these conditions, the COD removal rate was 71.36%, The chroma removal rate is 75%.
Embodiment 3
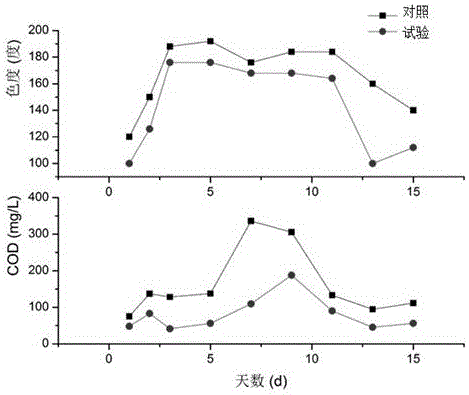
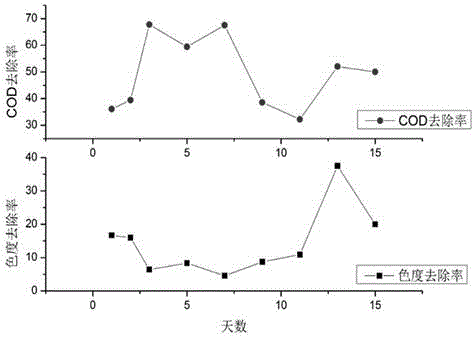
[0035] Utilize the method for Phanerochaete chrysosporium biointensification treatment of pulping wastewater, the same as in Example 1, wherein, in the biointensification treatment step, the glucose content is 300 mg / L, the pH is 6.0, and the ammonium tartrate content is 0.2 mg / L , the dosage of Phanerochaete chrysosporium was 100 mL / L, the temperature was 26°C, and the DO was 8 mg / L. After seven days of continuous reaction, the COD and chromaticity were measured. At this time, the COD removal rate and chromaticity removal rate respectively reached 89.74%, 66.67%, that is, the COD of the original wastewater is 368.12 mg / L, and the chroma is 60, and the COD of the treated effluent is 37.76mg / L, and the chroma is 20, which fully meets the national discharge standards. At this time, the COD removal ability is about 10% higher than that of the existing technology.
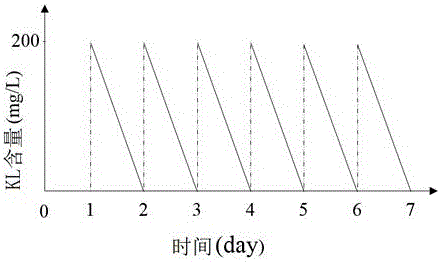
[0036] At the same time, the lignin content of the effluent was measured every day, which was determined by image ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com