Method for detecting bismuth ions by utilizing rhodamine-type fluorescent probe
A technology of fluorescent probes and bismuth ions, applied in fluorescence/phosphorescence, measuring devices, and material analysis through optical means, can solve the problems of few aluminum ions, no indication of the detection range and detection limit of bismuth ions, etc., and achieve a good choice Sexuality, low cost, good use effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1: Synthesis of rhodamine fluorescent probe
[0039] (1) Synthesis of rhodamine B hydrazide
[0040] Take a 100 mL three-necked flask, weigh 1.200 g (2.5 mmol) of rhodamine B and dissolve it in 30 mL of absolute ethanol, stir vigorously at room temperature and slowly add 1 mL (19.8 mmol excess) of 98% hydrazine hydrate into the inside. Heat at 78°C under reflux for 2 hours until the solution turns from dark purple to clear yellow. After the reaction is completed, it is cooled to room temperature, and the solvent and excess hydrazine hydrate are evaporated using a rotary evaporator to obtain a pale yellow crude product of rhodamine B hydrazide. Take 50mL of the newly prepared 1M HCl and add it to the crude product. The product dissolves in a pink solution. Under stirring, slowly add 1M NaOH to the solution to adjust the pH to between 9-10. When NaOH was added dropwise to the mixed solution, a pale pink flocculent precipitate began to precipitate when the pH of the ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Take the prepared bismuth nitrate pentahydrate solution (6×10 -7 M) As the bismuth ion test solution, the method for detecting bismuth ions in the rhodamine-based fluorescent probe synthesized in Example 1 is as follows:
[0053] Step 1: Dissolve the rhodamine-based fluorescent probe synthesized in Example 1 in the solvent acetonitrile, and use the solvent acetonitrile to dilute the volume in a 100 mL volumetric flask to obtain a concentration of 1.0×10 -3 M probe stock solution, pipette the probe stock solution into a 100mL volumetric flask, use the solvent acetonitrile to make a constant volume in a 100mL volumetric flask to obtain a concentration of 1.0×10 -4 M probe solution;
[0054] Step 2: Dissolve bismuth nitrate (containing pentahydrate crystal water) in the solvent deionized water, and use the solvent deionized water to make the volume in a 100mL volumetric flask to obtain a concentration of 1.0×10 -2 M bismuth ion stock solution; pipet the bismuth ion stock solution...
Embodiment 3
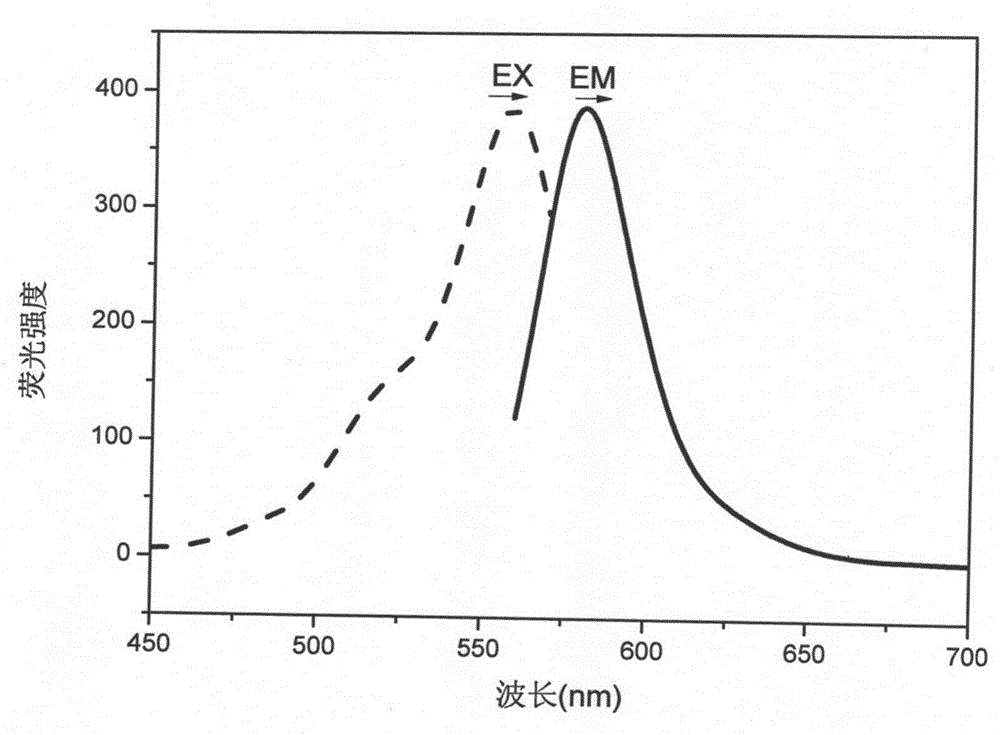
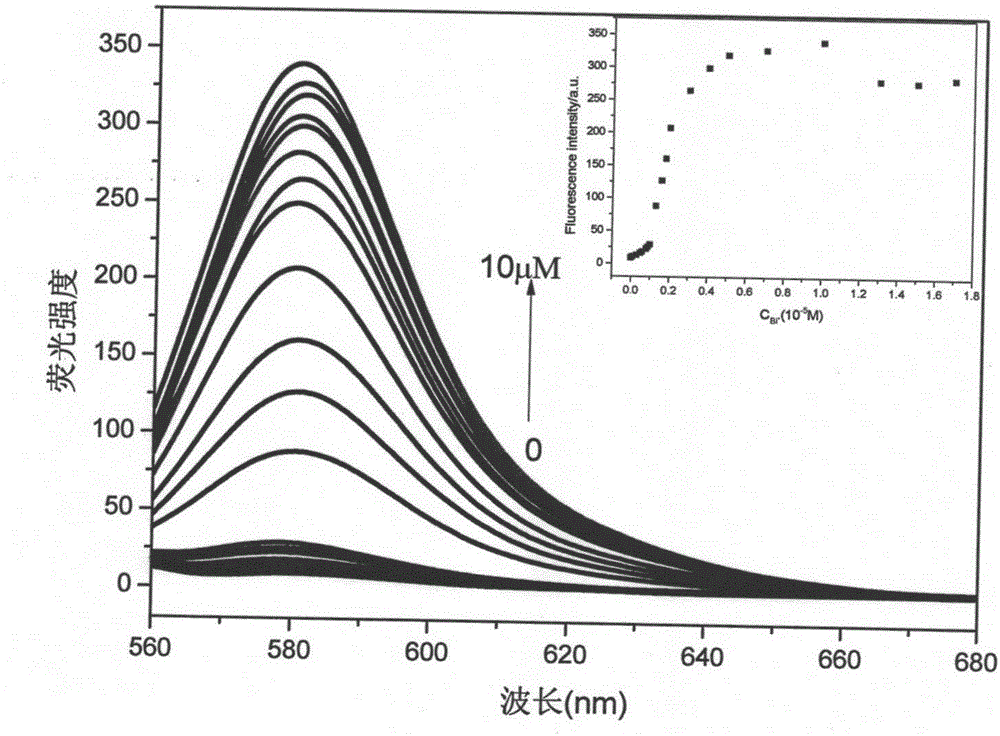
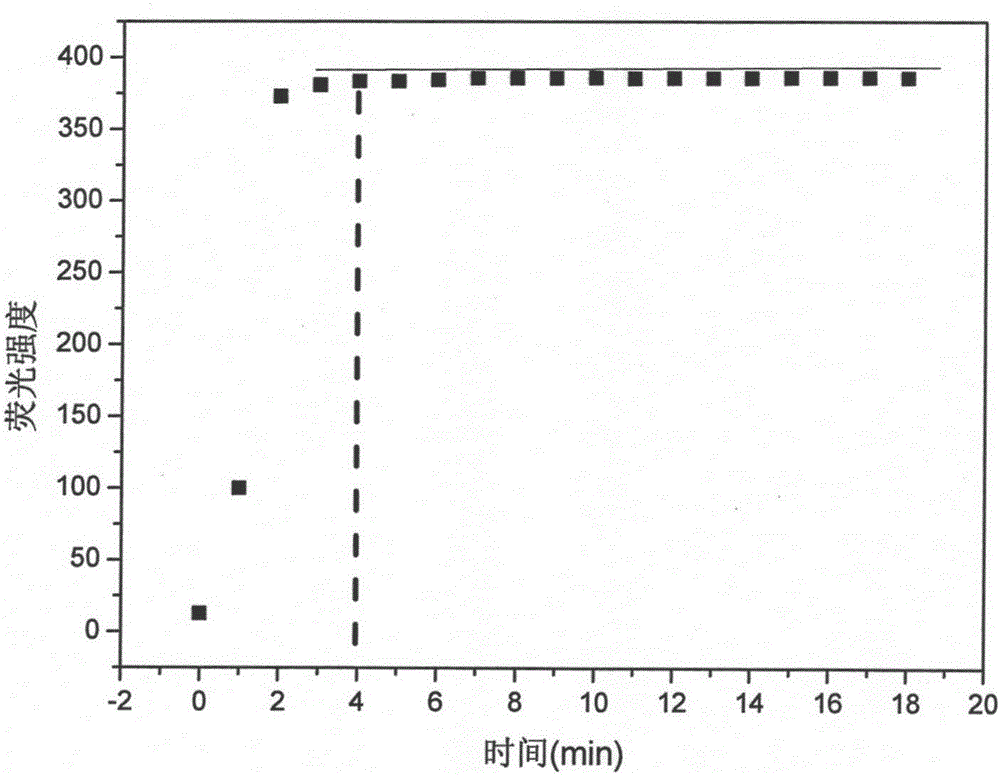
[0058] Bismuth nitrate (containing pentahydrate crystal water) was added to acetonitrile to obtain a bismuth ion solution with a concentration of 100 nM. The fluorescent probe synthesized in Example 1 was dissolved in acetonitrile to obtain 10 -5 M concentration of fluorescent probe solution, add 15ml fluorescent probe (10 -5 M) Add 10ml of bismuth ion solution to the solution and test the fluorescence intensity after standing for 5 minutes. The excited state absorption spectrum and fluorescence emission spectrum of the complex of probe and bismuth ion in acetonitrile solution.
[0059] figure 1 Shown using 557nm light for excitation (probe-Bi 3+ ) Complex, the emission peak is located at 580nm, the ligand fluorescent probe (10 -5 M) Measure the fluorescence intensity at an excitation wavelength of 557nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com