Alumina bioceramics material and preparation method therefor
A bio-ceramic material and alumina technology are applied in the field of alumina bio-ceramic materials and their preparation, which can solve the problems of limited service life and life of alumina ceramic materials, and achieve the effects of high compressive strength and hardness, and simple preparation process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
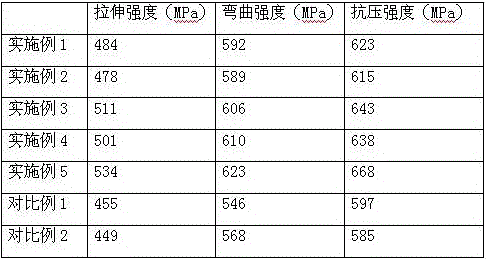
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Step 1: 28 parts of aluminum oxide, 3 parts of molybdenum boride, 5 parts of boron nitride, 2 parts of chromium boride, 3 parts of tungsten silicide, 4 parts of cobalt silicide, 4 parts of magnesium oxide, 2 parts of copper, 3 parts of zirconium, 2 parts of rubidium, and 3 parts of nickel are mechanically ball milled in a ball mill, the ball-to-material ratio in the ball mill is 30:1, and the ball milling time is 2 hours;
[0039] Step 2: After ball milling, mix the mixed cermet material evenly;
[0040] Step 3: Sinter the mixture evenly mixed in step (2) in a high-temperature sintering furnace at a temperature of 900°C for 3 hours, then increase the temperature to 1050°C, sinter for 4 hours, and cool to room temperature to prepare alumina bioceramic materials.
Embodiment 2
[0042] Step 1: 16 parts of aluminum oxide, 6 parts of molybdenum boride, 3 parts of boron nitride, 5 parts of chromium boride, 7 parts of tungsten silicide, 8 parts of cobalt silicide, 2 parts of magnesium oxide, 4 parts of copper, 1 part of zirconium, 5 parts of rubidium, and 1 part of nickel are mechanically ball milled in a ball mill, the ball-to-material ratio in the ball mill is 20:1, and the ball milling time is 4 hours;
[0043] Step 2: After ball milling, mix the mixed cermet material evenly;
[0044] Step 3: Sinter the mixture evenly mixed in step (2) at high temperature in a high-temperature sintering furnace, sinter at a temperature of 800°C for 3 hours, then increase the temperature to 950°C, sinter for 4 hours, and cool to room temperature to prepare alumina bioceramic materials.
Embodiment 3
[0046] Step 1: 20 parts of aluminum oxide, 5 parts of molybdenum boride, 3 parts of boron nitride, 3 parts of chromium boride, 6 parts of tungsten silicide, 5 parts of cobalt silicide, 4 parts of magnesium oxide, 3 parts of copper, 1 part of zirconium, 4 parts of rubidium, and 3 parts of nickel are mechanically ball milled in a ball mill. The ball-to-material ratio in the ball mill is 20:1, and the ball milling time is 4 hours;
[0047] Step 2: After ball milling, mix the mixed cermet material evenly;
[0048] Step 3: Sinter the mixture evenly mixed in step (2) in a high-temperature sintering furnace at a temperature of 900°C for 3 hours, then increase the temperature to 1050°C, sinter for 4 hours, and cool to room temperature to prepare alumina bioceramic materials.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com