Antimony-selenide thin-film solar battery using black phosphorene as conducting material and preparation method thereof
A technology of solar cells and conductive materials, applied in circuits, photovoltaic power generation, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of cadmium being highly toxic, restricting development, and scarcity of tellurium resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
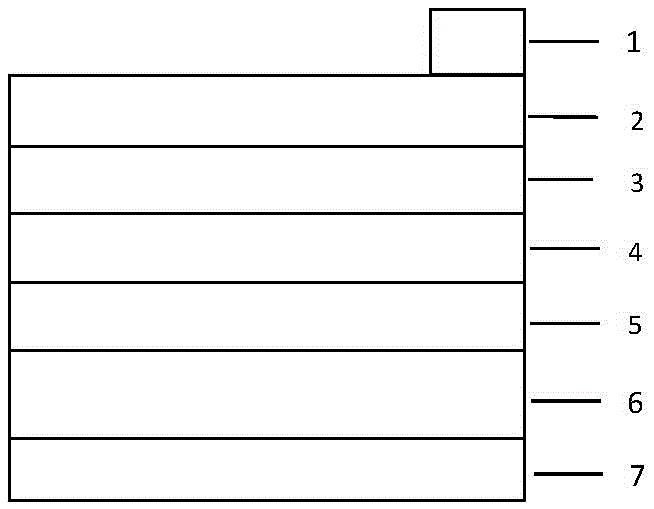
[0015] Embodiment 1: A kind of preparation method of antimony selenide thin-film solar cell using black phosphorene as conductive material, operate according to the following steps:
[0016] First, a p-type antimony selenide film was deposited on a p-type heavily doped black phosphorene substrate by a hydrazine solution method, and then an intrinsic hydrogenated nanocrystalline silicon film was prepared on a p-type antimony selenide film by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition , and then use chemical vapor deposition to deposit n-type molybdenum disulfide film on the intrinsic hydrogenated nanocrystalline silicon film, then use chemical vapor deposition to deposit n-type heavily doped black phosphorene film on the n-type molybdenum disulfide film, and finally On the surface of the n-type heavily doped black phosphorene film and the p-type heavily doped black phosphorene substrate, metal silver electrodes are deposited respectively by screen printing, that is, the required ...
Embodiment 2
[0017] Example 2: First, a p-type antimony selenide thin film is deposited on a p-type heavily doped black phosphorene substrate by magnetron sputtering, and then the p-type antimony selenide thin film is prepared by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Intrinsic hydrogenated nanocrystalline silicon film, and then deposit n-type molybdenum disulfide film on the intrinsic hydrogenated nanocrystalline silicon film by magnetron sputtering, and then deposit n-type heavily doped film on the n-type molybdenum disulfide film by mechanical exfoliation The black phosphorene thin film, and finally on the surface of the n-type heavily doped black phosphorene film and the p-type heavily doped black phosphorene substrate, metal aluminum electrodes are respectively deposited by vapor deposition, that is, the required black phosphorene as Antimony Selenide Thin Film Solar Cells of Conductive Materials.
Embodiment 3
[0018] Example 3: First, a p-type antimony selenide thin film is deposited on a p-type heavily doped black phosphorene substrate by an ultrasonic spray method, and then an intrinsic hydrogenation is prepared on a p-type antimony selenide thin film by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition Nanocrystalline silicon film, and then deposit n-type molybdenum disulfide film on the intrinsically hydrogenated nanocrystalline silicon film by magnetron sputtering, and then deposit n-type heavily doped black film on the n-type molybdenum disulfide film by chemical vapor deposition. Phosphene thin film, and finally on the surface of the n-type heavily doped black phosphorene film and the p-type heavily doped black phosphorene substrate, metal silver electrodes are respectively deposited by evaporation method, that is, the required black phosphorene as the conductive material is obtained. Materials for antimony selenide thin film solar cells.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com