Method for recycling valuable elements in high-sulfur nickel-molybdenum ore smelting waste
A high-sulfur nickel-molybdenum and valuable element technology is applied in the field of recycling valuable elements in the smelting waste residue of high-sulfur nickel-molybdenum ore, which can solve the problems of easy leakage of toxic gas, low selenium recovery rate, environmental pollution, etc., and achieve low production cost , easy to operate, solve the effect of low recovery rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
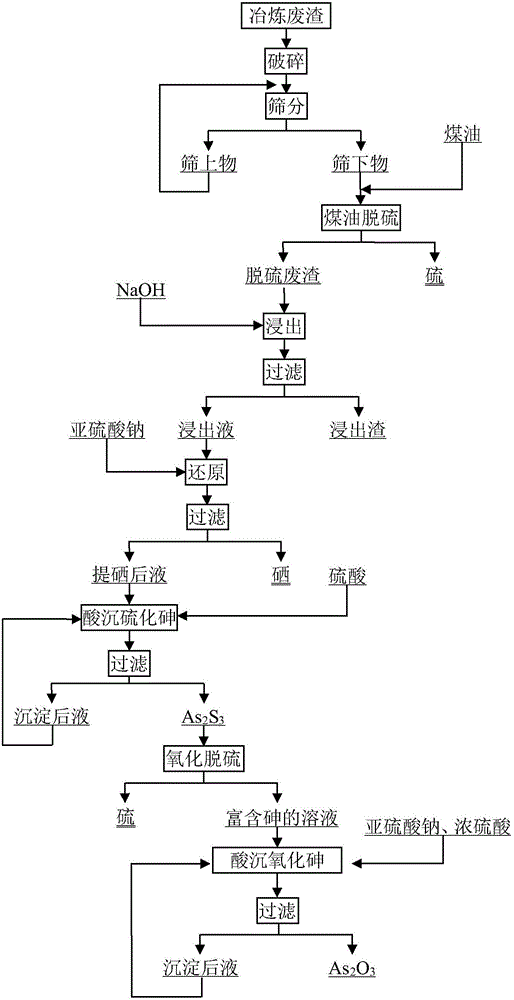
[0058] A method for recovering valuable elements in high-sulfur nickel-molybdenum ore smelting waste slag of the present invention, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
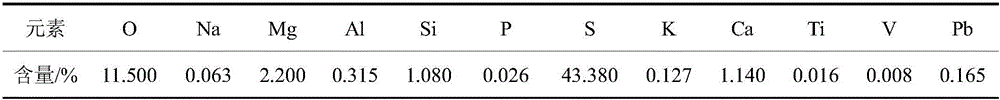
[0059] (1) Crushing, ball milling and screening high-sulfur nickel-molybdenum ore smelting waste residue to obtain smelting waste residue with a particle size of less than 0.1mm, and then using sulfonated kerosene as a solvent, under the conditions of desulfurization temperature of 140°C and desulfurization time of 30min Carry out hot filtration desulfurization, heat filtration, solid-liquid separation to obtain desulfurization waste residue and sulfonated kerosene loaded with elemental sulfur, cool the sulfonated kerosene loaded with elemental sulfur to room temperature, separate sulfonated kerosene, and obtain elemental sulfur, elemental sulfur The yield rate is 92.74%, and the product meets the requirements of the national standard;
[0060] (2) The desulfurization waste residue obtained...
Embodiment 2
[0066] A method for recovering valuable elements in high-sulfur nickel-molybdenum ore smelting waste slag of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0067] (1) Crushing, ball milling and screening high-sulfur nickel-molybdenum ore smelting waste residue to obtain smelting waste residue with a particle size of less than 0.1 mm, and then using sulfonated kerosene as a solvent, under the conditions of desulfurization temperature of 145 °C and desulfurization time of 40 minutes Carry out hot filtration desulfurization, heat filtration, solid-liquid separation to obtain desulfurization waste residue and sulfonated kerosene loaded with elemental sulfur, cool the sulfonated kerosene loaded with elemental sulfur to room temperature, separate sulfonated kerosene, and obtain elemental sulfur, elemental sulfur The yield rate is 92.81%, and the product meets the requirements of the national standard;
[0068] (2) The desulfurization waste residue obtained after the desulfur...
Embodiment 3
[0074] A method for recovering valuable elements in high-sulfur nickel-molybdenum ore smelting waste slag of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0075] (1) Crushing, ball milling and screening high-sulfur nickel-molybdenum ore smelting waste residues to obtain smelting waste residues with a particle size of less than 0.1 mm, and then using sulfonated kerosene as a solvent at a desulfurization temperature of 130°C and a desulfurization time of 30 minutes Carry out hot filtration desulfurization, heat filtration, solid-liquid separation to obtain desulfurization waste residue and sulfonated kerosene loaded with elemental sulfur, cool the sulfonated kerosene loaded with elemental sulfur to room temperature, separate sulfonated kerosene, and obtain elemental sulfur, elemental sulfur The yield rate is 91.96%, and the product meets the requirements of the national standard;
[0076] (2) The desulfurization waste residue obtained after the desulfurization in step (...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com