Method for recycling tungsten carbide and metallic cobalt through waste tungsten-cobalt cemented carbide
A cemented carbide and tungsten carbide technology, which is applied in the field of recycling tungsten carbide and metal cobalt from waste tungsten-cobalt cemented carbide, can solve the problems of low-grade recycled alloy, high iron and oxygen content, cobalt metal loss, etc., and can achieve large-scale Small size, short process, and complete specifications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
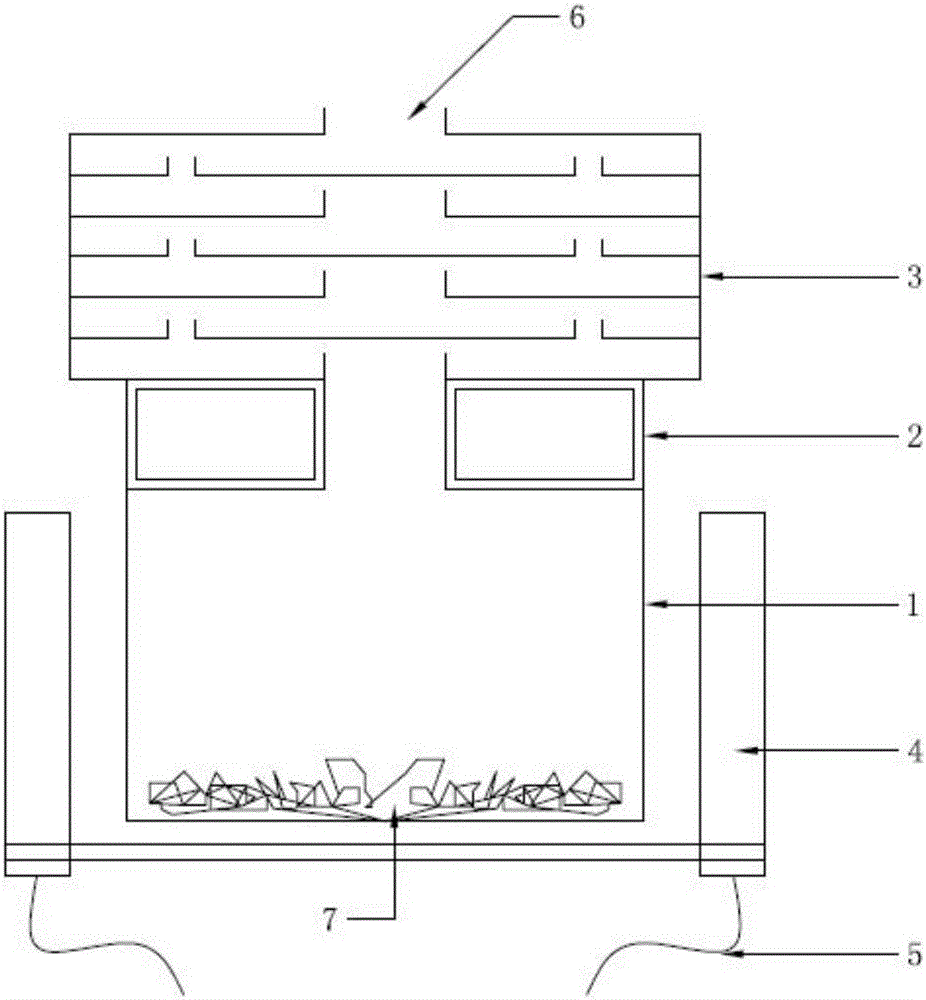
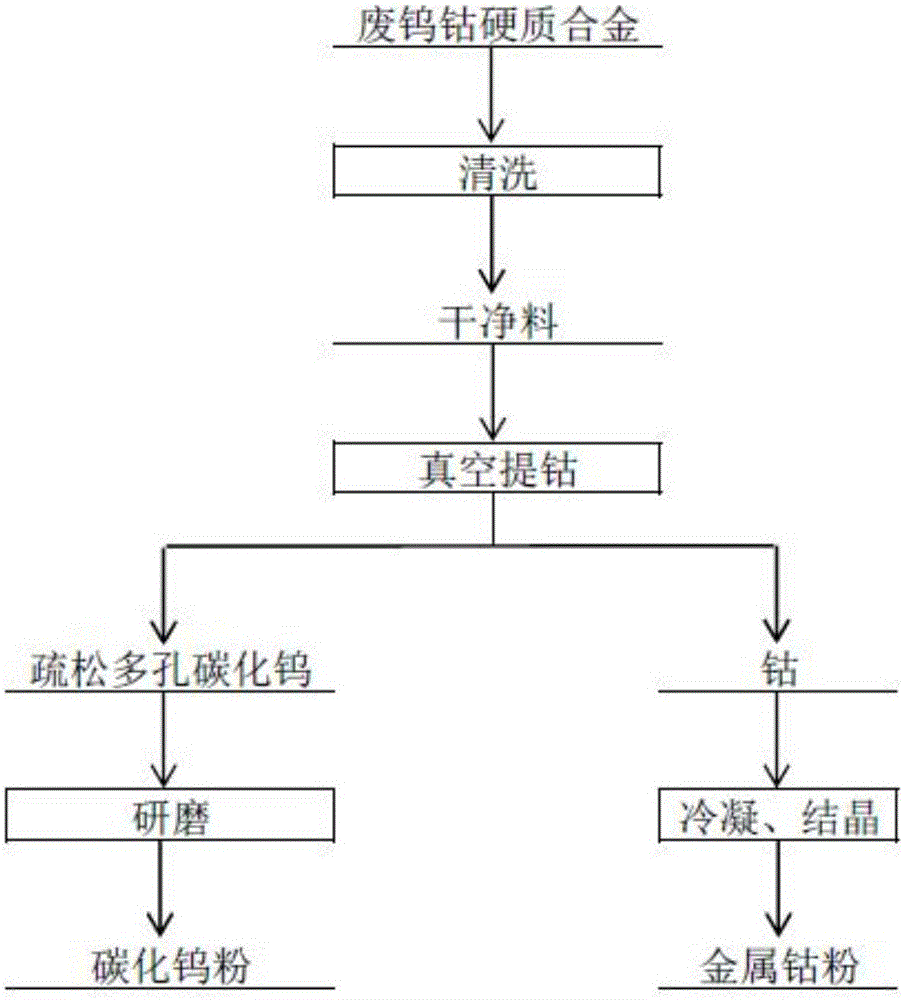
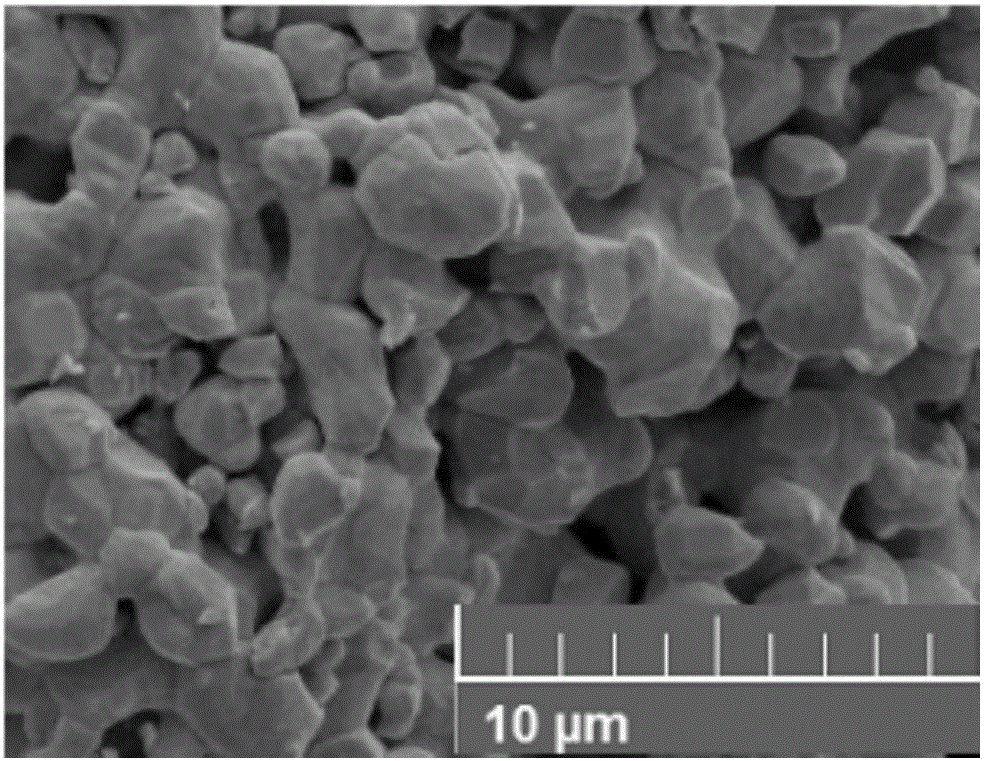
[0030] according to figure 2 The process is carried out: take 1000.0g of YG3 waste tungsten-cobalt cemented carbide, immerse it in the cemented carbide cleaning tank, the temperature is 40°C, the frequency of the ultrasonic generator is 25kHz, stir constantly, and wash away the sediment and oil entrained by the raw material Wait for impurities, then immerse in clean water at 60°C to wash, and dry to obtain 987.2 g of clean raw materials. Put the clean raw material in the graphite crucible of the internal heating vacuum furnace, install the transition section and the cobalt crystallizer, evacuate, wait until the pressure in the furnace drops to 5Pa, start the heating system, and raise the temperature to 400°C at a heating rate of 5°C / min , keep warm for 25min, when the pressure in the furnace drops below 1Pa during the keep warm process, start the high vacuum system, and keep warm. The temperature was raised to 1700°C at a heating rate of 5°C / min, the temperature was raised t...
Embodiment 2
[0032] according to figure 2 The process flow is carried out: Take 1000.0g of YG5 waste tungsten-cobalt cemented carbide, immerse it in the cleaning tank, the temperature is 45°C, the frequency of the ultrasonic generator is 25kHz, stir continuously, and wash away the impurities such as sediment and oil entrained in the raw material , then immersed in 60°C clear water to wash, and then dried to obtain 985.4 g of clean raw materials. Put the clean raw material in the graphite crucible of the internal heating vacuum furnace, install the transition section and the cobalt crystallizer, vacuumize, wait until the pressure in the furnace drops to 6Pa, start the heating system, and raise the temperature to 420°C at a heating rate of 6°C / min , keep warm for 30min, when the pressure in the furnace drops below 1Pa during the keep warm process, start the high vacuum system, and keep warm. The temperature was raised to 1650°C at a heating rate of 6°C / min, the temperature was raised to 16...
Embodiment 3
[0034] according to figure 2 The process is carried out as follows: Take 1000.0g of YG15 waste tungsten-cobalt cemented carbide, immerse it in the cleaning tank, the temperature is 50°C, the frequency of the ultrasonic generator is 25kHz, stir continuously, and wash away the impurities such as sediment and oil entrained in the raw material , and then immersed in clean water at 70°C for cleaning, and then dried to obtain 983.0 g of clean raw materials. Put the clean raw material in the graphite crucible of the internal heating vacuum resistance furnace, install the transition section and the cobalt crystallizer, evacuate, wait until the pressure in the furnace drops to 3Pa, start the heating system, and raise the temperature to 440 at a heating rate of 10°C / min ℃, keep warm for 20 minutes, when the pressure in the furnace drops below 1Pa during the heat preservation process, start the high vacuum system, and the heat preservation ends. The temperature was raised to 1600°C at ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com