Method for identifying phenotype of indoor wheat dwarf virus resistance of triticeae crops and application
A technology of wheat dwarf virus and crops, applied in the field of agricultural biology, can solve the problems of large-scale identification in the field, poor control effect of wheat dwarf virus disease, difficulty in identification of disease resistance and research on pathogenic mechanism , to achieve the effect of low cost and high efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Embodiment 1. Preparation of toxin source and mediator
[0035] The source of the wheat dwarf virus (WDV) virus is the isolate of wheat dwarf virus in Hancheng, Shaanxi. After the plants with obvious symptoms are identified as positive by PCR and serology, the living bodies are preserved on the host wheat. The virus-transmitting agent-Psammotettix striatus (Linnaeus) was collected from Hancheng, Shaanxi Province, and was bred and bred on healthy wheat all year round after detoxification and purification. The medium breeding and the wheat variety Yangmai No. 12 used as feed and virus transmission host were all raised in a light incubator at 22°C, with 16 hours of light and 8 hours of darkness, and the light intensity was 20000Lx.
Embodiment 2
[0036] Embodiment 2. Feeding poison and inoculation of mediator
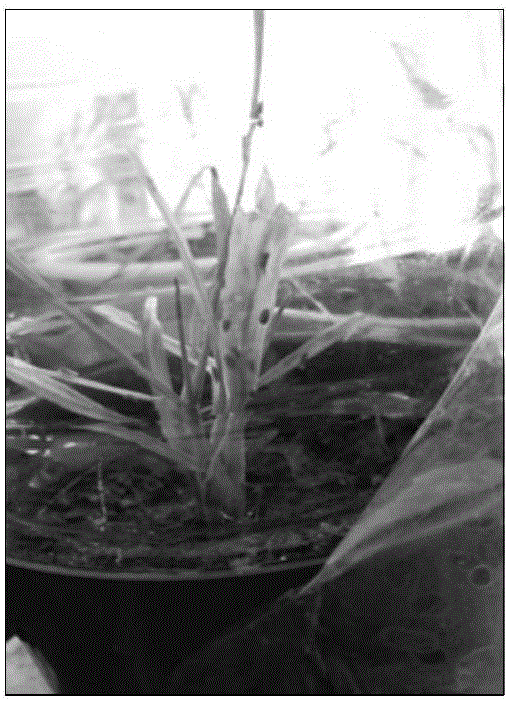
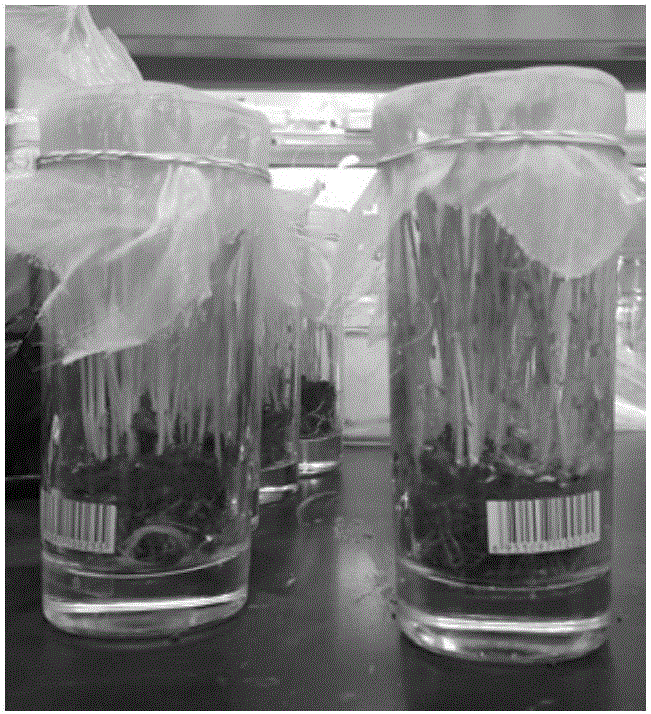
[0037] Draw 60-80 headline sand leafhoppers with an insect sucker, place it on the wheat dwarf virus source plant and feed it with a cover for 3 days ( figure 1 ), on the other hand, the work is to plant the wheat material to be identified 3 days in advance, that is, sow 25 seeds of the material to be identified in each glass cup filled with sterilized soil of 1 / 4 volume, and sow the 7th seed of the identified material to grow. The day is the 4th day of vector feed poisoning, after all the leafhoppers fed poison are sucked out with an insect sucker, they are placed in the glass cups of the seedlings to be identified, the mouth of the bottle is immediately covered with gauze cloth, and the rubber band is tightened ( figure 2 ). Then place it in a light incubator for 3 days and inoculate it for 3 days. On the 4th day, suck out all the leafhoppers, carefully scoop out the material to be identified in the glass cu...
Embodiment 3
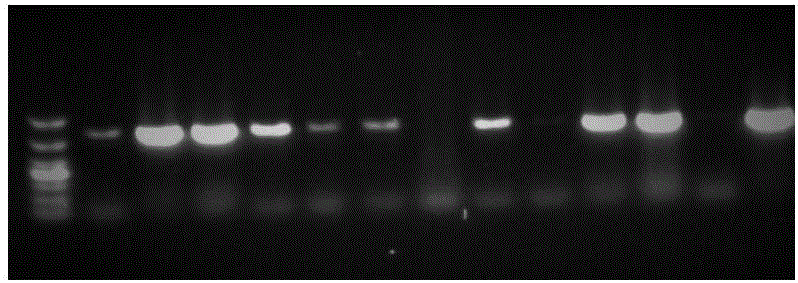
[0038] Example 3. The rate of poisoning in the population of leafhoppers detected by PCR after being fed with poison
[0039] The poisoned leafhoppers were taken out with a suction device, and the total DNA of the leafhoppers was extracted from each head. The Wizard Genomic DNA Extraction Kit from Promega Company was used, and the reference manual of the extraction method was slightly changed. The extracted DNA samples were stored at -20°C for future use. PCR amplification primers were CP / F:5'-ATGGTGACCAACAAGGACTCC-3'; CP / R:5'-TTACTGAATGCCGATGGCTTTG-3', which were synthesized by Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. Taking the total system 50 μL as an example, the PCR amplification system is as follows: rTaq 0.25 μL; 10×PCR Buffer 5 μL; dNTP Mixture (2.5 mmol / L each) 4 μL; upstream primer and downstream primer (10 μmol / L) 2 μL each; / μL) 2 μL, ddH 2 O 34.75 μL. PCR amplification program: 94°C for 3min; (94°C for 45sec, annealing temperature for 50sec, 72°C for 30sec) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com